tRNA and Translation
... 1. What is the structure and function of transfer RNA? (MCA-II science standard) 2. How does translation work? (MCA-II science standard) 3. What is evolution? (MCA-II science standard) INTRODUCTION DNA, the molecule which provides the blueprint for life, is located in the nucleus of cells. mRNA, whi ...
... 1. What is the structure and function of transfer RNA? (MCA-II science standard) 2. How does translation work? (MCA-II science standard) 3. What is evolution? (MCA-II science standard) INTRODUCTION DNA, the molecule which provides the blueprint for life, is located in the nucleus of cells. mRNA, whi ...
Protein Synthesis - TangHua2012-2013
... • The second step in protein synthesis is called translation. • Translation is the process of ________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ (protein). It occurs in 3 steps. • Translation occurs at __________________ ...
... • The second step in protein synthesis is called translation. • Translation is the process of ________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ (protein). It occurs in 3 steps. • Translation occurs at __________________ ...
Bio/CS 251 Bioinformatics Homework 4 20 points
... The peptidyl site would be occupied by a peptidyl-tRNA that carries the MET-GLU-ILE tripeptide, and the aminoacyl site would contain the next aa-tRNA to be added to the growing peptide. In this case the aminoacyl site would contain the UGG codon to pair with the anticodon of Trp-tRNA. ...
... The peptidyl site would be occupied by a peptidyl-tRNA that carries the MET-GLU-ILE tripeptide, and the aminoacyl site would contain the next aa-tRNA to be added to the growing peptide. In this case the aminoacyl site would contain the UGG codon to pair with the anticodon of Trp-tRNA. ...
Protein Synthesis Notes Review
... If a mRNA sequence had the following nucleotides: AAGGUCAGACGGUGA, how many codons are there? What is the start codon? What is Translation? Where does Translation occur? Where in the cell does transcription occur? Where in the cell does translation occur? When does translation begin? What brings ami ...
... If a mRNA sequence had the following nucleotides: AAGGUCAGACGGUGA, how many codons are there? What is the start codon? What is Translation? Where does Translation occur? Where in the cell does transcription occur? Where in the cell does translation occur? When does translation begin? What brings ami ...
Gene to Protein
... can also only attach in the 5’->3’ direction produces the chain at the rate of 60 nucleotides/sec the RNA detaches from the RNA polymerase while the DNA goes back into helix g. multiple RNA polymerases can ride along the DNA transcribing multiple copies of the gene in question ...
... can also only attach in the 5’->3’ direction produces the chain at the rate of 60 nucleotides/sec the RNA detaches from the RNA polymerase while the DNA goes back into helix g. multiple RNA polymerases can ride along the DNA transcribing multiple copies of the gene in question ...
Codon Dictionary Worksheet
... Codon Dictionary Worksheet To the right is a codon dictionary. This is a listing of messenger RNA (mRNA) triplets that correspond to the anticodons found on transfer RNA (tRNA) and the amino acids that tRNA carries. Remember that the sense strand of DNA carries the original genetic code for each ami ...
... Codon Dictionary Worksheet To the right is a codon dictionary. This is a listing of messenger RNA (mRNA) triplets that correspond to the anticodons found on transfer RNA (tRNA) and the amino acids that tRNA carries. Remember that the sense strand of DNA carries the original genetic code for each ami ...
CHNOPS- Simulating Protein Synthesis
... form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by mRNA is “read” on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in turn ...
... form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by mRNA is “read” on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in turn ...
Replication of the DNA
... – Central dogma: basic plan of genetic information flow in living cells that relates genes(DNA), RNA, and proteins ...
... – Central dogma: basic plan of genetic information flow in living cells that relates genes(DNA), RNA, and proteins ...
No Slide Title
... Eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes are larger and more complex than prokaryotic ribosomes. Mitochondrial and chloroplast ribosomes differ from both examples shown. ...
... Eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes are larger and more complex than prokaryotic ribosomes. Mitochondrial and chloroplast ribosomes differ from both examples shown. ...
Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
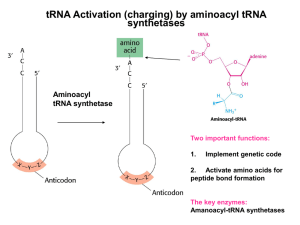
... charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correct tRNAs via by interacting with specific regions of tR ...
... charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correct tRNAs via by interacting with specific regions of tR ...
Review Topics for Final Part 1
... Two different classes of synthetases attach the amino acids in slightly different ways Does it cost energy to “charge” a tRNA with an amino acid? What proofreading mechanism ensures that the right amino acid is added? Different sequences in varying tRNAs allow recognition by the right syntheta ...
... Two different classes of synthetases attach the amino acids in slightly different ways Does it cost energy to “charge” a tRNA with an amino acid? What proofreading mechanism ensures that the right amino acid is added? Different sequences in varying tRNAs allow recognition by the right syntheta ...
CHAPTER 15
... it will recognize a 5–CCC–3 codon, which should specify proline. It is essential that the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase known as prolyl-tRNA-synthetase recognizes this tRNA and attaches proline to the 3 end. The other aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases should not recognize this tRNA. C15. Answer: In the cont ...
... it will recognize a 5–CCC–3 codon, which should specify proline. It is essential that the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase known as prolyl-tRNA-synthetase recognizes this tRNA and attaches proline to the 3 end. The other aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases should not recognize this tRNA. C15. Answer: In the cont ...
Protein Synthesis
... factor Tu (EF-Tu) and an aminoacyl-tRNA. The amino-terminal domain of EF-Tu is a Ploop NTPase domain similar to those in other G proteins ...
... factor Tu (EF-Tu) and an aminoacyl-tRNA. The amino-terminal domain of EF-Tu is a Ploop NTPase domain similar to those in other G proteins ...
Translation - Advanced
... The 5’ cap and 3’ poly(A) tail are involved in the recruitment of the ribosome. In eukaryotes the ribosome scans along the mRNA for the first start methionine codon. Translation may begin at all AUG codons, however only an in-frame AUG will produce a functional polypeptide. The tRNAs with attached a ...
... The 5’ cap and 3’ poly(A) tail are involved in the recruitment of the ribosome. In eukaryotes the ribosome scans along the mRNA for the first start methionine codon. Translation may begin at all AUG codons, however only an in-frame AUG will produce a functional polypeptide. The tRNAs with attached a ...
Lecture 17 Expanded Genetic Code
... 2) Engineer a tRNA that is orthogonal to all other tRNAs 3) Evolve an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to uniquely recognize this tRNA 4) Evolve a synthetase to uniquely charge this tRNA with the 21st amino acid 5) Biosynthesize or transport amino acid (most amino acids are transported into bacteria as the ...
... 2) Engineer a tRNA that is orthogonal to all other tRNAs 3) Evolve an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to uniquely recognize this tRNA 4) Evolve a synthetase to uniquely charge this tRNA with the 21st amino acid 5) Biosynthesize or transport amino acid (most amino acids are transported into bacteria as the ...
I. DNA A. WHAT IS IT?
... • DNA has the “message” that is replicated for all new cells. • The message is sent out into the cells by transcription. • Proteins are assembled by translating the message. ...
... • DNA has the “message” that is replicated for all new cells. • The message is sent out into the cells by transcription. • Proteins are assembled by translating the message. ...
The Path From Genes to Proteins
... Three Stages of Translation mRNA-transcript information directs synthesis of a polypeptide chain during translation Translation proceeds in three stages • Initiation • Elongation • Termination ...
... Three Stages of Translation mRNA-transcript information directs synthesis of a polypeptide chain during translation Translation proceeds in three stages • Initiation • Elongation • Termination ...
Section 7: How Are Proteins Made? (Translation)
... • The ribosome will read the codons until AUG is reached and then the initiator tRNA binds to the P-site of the ribosome. • Stop codons have tRNA that recognize a signal to stop translation. Release factors bind to the ribosome which cause the peptidyl transferase to catalyze the addition of water t ...
... • The ribosome will read the codons until AUG is reached and then the initiator tRNA binds to the P-site of the ribosome. • Stop codons have tRNA that recognize a signal to stop translation. Release factors bind to the ribosome which cause the peptidyl transferase to catalyze the addition of water t ...
Transcription and Translation
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
2-centrioles & fibers disappear
... DNA, and replaced with 40. Thymine is in ______ Uracil on the _____ RNA strand. (p. 297-299 & 302) ...
... DNA, and replaced with 40. Thymine is in ______ Uracil on the _____ RNA strand. (p. 297-299 & 302) ...
RNA does not - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases complexed with cognate tRNAs ...
... Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases complexed with cognate tRNAs ...
bio12_sm_07_1
... random mutations caused by the X-ray radiation. The radiation altered the genetic code in different genes involved in the synthesis of different essential molecules. ...
... random mutations caused by the X-ray radiation. The radiation altered the genetic code in different genes involved in the synthesis of different essential molecules. ...
(CH14) Translation (Slides)
... that are far more powerful than anything we ever attempted with ribosomal proteins in the past. So today we work on rRNA; we would be crazy not to. Peter B. Moore, The Ribosome. Structure, Function, and Evolution (1990), p. xxi ...
... that are far more powerful than anything we ever attempted with ribosomal proteins in the past. So today we work on rRNA; we would be crazy not to. Peter B. Moore, The Ribosome. Structure, Function, and Evolution (1990), p. xxi ...
Transfer RNA

A transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and archaically referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length, that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. It does this by carrying an amino acid to the protein synthetic machinery of a cell (ribosome) as directed by a three-nucleotide sequence (codon) in a messenger RNA (mRNA). As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins according to the genetic code.The specific nucleotide sequence of an mRNA specifies which amino acids are incorporated into the protein product of the gene from which the mRNA is transcribed, and the role of tRNA is to specify which sequence from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. One end of the tRNA matches the genetic code in a three-nucleotide sequence called the anticodon. The anticodon forms three base pairs with a codon in mRNA during protein biosynthesis. The mRNA encodes a protein as a series of contiguous codons, each of which is recognized by a particular tRNA. On the other end of the tRNA is a covalent attachment to the amino acid that corresponds to the anticodon sequence. Each type of tRNA molecule can be attached to only one type of amino acid, so each organism has many types of tRNA (in fact, because the genetic code contains multiple codons that specify the same amino acid, there are several tRNA molecules bearing different anticodons which also carry the same amino acid).The covalent attachment to the tRNA 3’ end is catalyzed by enzymes called aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. During protein synthesis, tRNAs with attached amino acids are delivered to the ribosome by proteins called elongation factors (EF-Tu in bacteria, eEF-1 in eukaryotes), which aid in decoding the mRNA codon sequence. If the tRNA's anticodon matches the mRNA, another tRNA already bound to the ribosome transfers the growing polypeptide chain from its 3’ end to the amino acid attached to the 3’ end of the newly delivered tRNA, a reaction catalyzed by the ribosome.A large number of the individual nucleotides in a tRNA molecule may be chemically modified, often by methylation or deamidation. These unusual bases sometimes affect the tRNA's interaction with ribosomes and sometimes occur in the anticodon to alter base-pairing properties.