university of oslo
... Initially, the ribosome and mRNA are aligned such that the initiator tRNA is positioned in the peptidyl site by codon-anticodon interactions. In the elongation phase of translation tRNAs, charged with amino acids, enter the complex through the A site, mediated by elongation factor 1A (EF-1A). Format ...
... Initially, the ribosome and mRNA are aligned such that the initiator tRNA is positioned in the peptidyl site by codon-anticodon interactions. In the elongation phase of translation tRNAs, charged with amino acids, enter the complex through the A site, mediated by elongation factor 1A (EF-1A). Format ...
DNA Strand 1 - Duncanville ISD
... 1. How many amino acids were made from this strand of DNA? _______ 2. How many proteins were made from this strand of DNA? ________ Codon Charts: knowing how to All of the amino the amino acids ...
... 1. How many amino acids were made from this strand of DNA? _______ 2. How many proteins were made from this strand of DNA? ________ Codon Charts: knowing how to All of the amino the amino acids ...
DNA Synthesis (Replication)
... The role of tRNA is to specify which sequence from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid One end of the tRNA complements the genetic code in a threenucleotide sequence called the anticodon On the other end of the tRNA is a covalent attachment to the amino acid that corresponds to th ...
... The role of tRNA is to specify which sequence from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid One end of the tRNA complements the genetic code in a threenucleotide sequence called the anticodon On the other end of the tRNA is a covalent attachment to the amino acid that corresponds to th ...
Biology with Junk: Protein Synthesis and Words
... Procedure for the Teacher: 1. Make up all the DNA Template Cards and the Anti-Codon/word cards 2. Hang up the Ant-codon word cards, so the anti-codons are showing. 3. Show the students the cards and tell them what they are. 4. Tell the students that your desk is the nucleus and the DNA templates ca ...
... Procedure for the Teacher: 1. Make up all the DNA Template Cards and the Anti-Codon/word cards 2. Hang up the Ant-codon word cards, so the anti-codons are showing. 3. Show the students the cards and tell them what they are. 4. Tell the students that your desk is the nucleus and the DNA templates ca ...
CAD_issue_#3 - University of Illinois Archives
... implications of the notion transcend translation per se; going into the dynamic of the mechanism's evolution; beyond that into the evolution of (all or most) biological macromolecules; then to the evolution of biological entities (and processes?) at all its organizational levels; and (see CAD issue ...
... implications of the notion transcend translation per se; going into the dynamic of the mechanism's evolution; beyond that into the evolution of (all or most) biological macromolecules; then to the evolution of biological entities (and processes?) at all its organizational levels; and (see CAD issue ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... production of proteins within the cell. Genetic messages can be decoded by copying part of the nucleotide sequence from DNA into RNA. RNA contains coded information for making proteins. ...
... production of proteins within the cell. Genetic messages can be decoded by copying part of the nucleotide sequence from DNA into RNA. RNA contains coded information for making proteins. ...
DNA.Protein.Synthesis Notes
... attachment site • Does the order of amino acids matter? Yes, they must be in order for the protein to fold correctly. ...
... attachment site • Does the order of amino acids matter? Yes, they must be in order for the protein to fold correctly. ...
Hydrophobic: tending to repel and not absorb water
... mixture of compounds that is formed by a combination of smaller molecules. ...
... mixture of compounds that is formed by a combination of smaller molecules. ...
Pharmacogenomics: Translating Functional Genomics into Rational
... Types of RNA three types – ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – transfer RNA (tRNA) – messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
... Types of RNA three types – ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – transfer RNA (tRNA) – messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
Is this an inducible or repressible operon?
... changed so that it encodes a premature stop codon D. Frame shift mutation- causes reading frame to be shifted, often caused by point insertions or point deletions In what case are missense mutations neutral? In what cases are nonsense and frameshift mutations neutral? What consequences will happen f ...
... changed so that it encodes a premature stop codon D. Frame shift mutation- causes reading frame to be shifted, often caused by point insertions or point deletions In what case are missense mutations neutral? In what cases are nonsense and frameshift mutations neutral? What consequences will happen f ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins Protein Synthesis Central Dogma DNA -> mRNA -> protein -> trait RNA vs DNA Single stranded Uracil Ribose mRNA, rRNA, tRNA RNA can move in and out of the nucleus Transcription (DNA -> RNA) Initiation Promoter TAT ...
... What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins Protein Synthesis Central Dogma DNA -> mRNA -> protein -> trait RNA vs DNA Single stranded Uracil Ribose mRNA, rRNA, tRNA RNA can move in and out of the nucleus Transcription (DNA -> RNA) Initiation Promoter TAT ...
Protein Synthesis – Level 1
... 2. If the underlined portions represent introns, what will the mature mRNA be/read? 3. Prior to leaving the nucleus, what will be added to the mature mRNA? What will the mRNA look like after this occurs? What is the purpose of this processing? ...
... 2. If the underlined portions represent introns, what will the mature mRNA be/read? 3. Prior to leaving the nucleus, what will be added to the mature mRNA? What will the mRNA look like after this occurs? What is the purpose of this processing? ...
CH 17 PPT
... • Base-pair substitution—the replacement of 1 base pair with another; occurs when a nucleotide and its partner from the complementary DNA strand are replaced with another pair of nucleotides according to base-pairing rules. • Missense mutation—base-pair substitution that alters an amino acid codon t ...
... • Base-pair substitution—the replacement of 1 base pair with another; occurs when a nucleotide and its partner from the complementary DNA strand are replaced with another pair of nucleotides according to base-pairing rules. • Missense mutation—base-pair substitution that alters an amino acid codon t ...
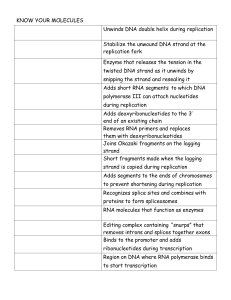
Know your molecules organizer
... Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA primers and replaces them with deoxyribonucleotides Joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging ...
... Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA primers and replaces them with deoxyribonucleotides Joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging ...
CHAPTER 15
... the possible mRNA codons. FIGURE 15.15 Concept check: Explain how mRNA plays a role in all three stages. Answer: A site in mRNA promotes the binding of the mRNA to the ribosome. The codons are needed during elongation to specify the polypeptide sequence. The stop codon is needed to terminate transcr ...
... the possible mRNA codons. FIGURE 15.15 Concept check: Explain how mRNA plays a role in all three stages. Answer: A site in mRNA promotes the binding of the mRNA to the ribosome. The codons are needed during elongation to specify the polypeptide sequence. The stop codon is needed to terminate transcr ...
Ribosome structural studies
... Australian William Henry Bragg and his son William Lawrence Bragghas won the 1915 Noble Prize in Physics for the invention of the X-Ray Crystallography (XRC) method. Due to difficulties in crystallization, ribosomes were not analyzed using XRC until the illuminating work by Yonath and Wittman in 198 ...
... Australian William Henry Bragg and his son William Lawrence Bragghas won the 1915 Noble Prize in Physics for the invention of the X-Ray Crystallography (XRC) method. Due to difficulties in crystallization, ribosomes were not analyzed using XRC until the illuminating work by Yonath and Wittman in 198 ...
Molecular Genetics - Lake Travis Independent School District
... A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides that specify for a single amino acid Amino acids are strung together to form proteins (polypeptides) ...
... A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides that specify for a single amino acid Amino acids are strung together to form proteins (polypeptides) ...
From DNA to Proteins
... The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. –three stop codons –one start codon, codes for methionine ...
... The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. –three stop codons –one start codon, codes for methionine ...
Resources: http://sciencevideos
... Explain the process of transcription in prokaryotes, including the following: promoter region, RNA polymerase, 5’-3’ direction, free nucleoside triphosphates, complementary base pairing, terminator region. ...
... Explain the process of transcription in prokaryotes, including the following: promoter region, RNA polymerase, 5’-3’ direction, free nucleoside triphosphates, complementary base pairing, terminator region. ...
File
... -- joins with ribosomal proteins (from nucleolus) to form ribosomes. -- produced in the nucleolus. -- one ribosome has two subunits: a. Large subunit (3 rRNAs and proteins) b. Small subunit (1 rRNA and proteins) -- the two subunits remain close together but do not actually attach until just prior to ...
... -- joins with ribosomal proteins (from nucleolus) to form ribosomes. -- produced in the nucleolus. -- one ribosome has two subunits: a. Large subunit (3 rRNAs and proteins) b. Small subunit (1 rRNA and proteins) -- the two subunits remain close together but do not actually attach until just prior to ...
Translation Activity - SeaWorld/Busch Gardens ANIMALS
... TRANSLATION VOCABULARY Amino Acid: An organic molecule possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Amino acids serve as the monomers of proteins. Antibody: An antigen-binding immunoglobulin, produced by B cells, that functions as the effector in an immune response. Anticodon: A specialized base trip ...
... TRANSLATION VOCABULARY Amino Acid: An organic molecule possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Amino acids serve as the monomers of proteins. Antibody: An antigen-binding immunoglobulin, produced by B cells, that functions as the effector in an immune response. Anticodon: A specialized base trip ...
8.5 Translation
... – The now empty tRNA molecule exits the ribosome. – A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the next exposed codon. – Once the stop codon is reached, the ribosome releases the protein and disassembles. ...
... – The now empty tRNA molecule exits the ribosome. – A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the next exposed codon. – Once the stop codon is reached, the ribosome releases the protein and disassembles. ...
Gene expression: Translation
... smaller average effect on polarity of amino acids (hydropathy/hydrophily) than all but 0.02% of randomly generated genetic codes with the same level of degeneracy (Haig and Hurst 1991, J. Mol. Evol. 33:412-417). ...
... smaller average effect on polarity of amino acids (hydropathy/hydrophily) than all but 0.02% of randomly generated genetic codes with the same level of degeneracy (Haig and Hurst 1991, J. Mol. Evol. 33:412-417). ...
Transfer RNA

A transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and archaically referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length, that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. It does this by carrying an amino acid to the protein synthetic machinery of a cell (ribosome) as directed by a three-nucleotide sequence (codon) in a messenger RNA (mRNA). As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins according to the genetic code.The specific nucleotide sequence of an mRNA specifies which amino acids are incorporated into the protein product of the gene from which the mRNA is transcribed, and the role of tRNA is to specify which sequence from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. One end of the tRNA matches the genetic code in a three-nucleotide sequence called the anticodon. The anticodon forms three base pairs with a codon in mRNA during protein biosynthesis. The mRNA encodes a protein as a series of contiguous codons, each of which is recognized by a particular tRNA. On the other end of the tRNA is a covalent attachment to the amino acid that corresponds to the anticodon sequence. Each type of tRNA molecule can be attached to only one type of amino acid, so each organism has many types of tRNA (in fact, because the genetic code contains multiple codons that specify the same amino acid, there are several tRNA molecules bearing different anticodons which also carry the same amino acid).The covalent attachment to the tRNA 3’ end is catalyzed by enzymes called aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. During protein synthesis, tRNAs with attached amino acids are delivered to the ribosome by proteins called elongation factors (EF-Tu in bacteria, eEF-1 in eukaryotes), which aid in decoding the mRNA codon sequence. If the tRNA's anticodon matches the mRNA, another tRNA already bound to the ribosome transfers the growing polypeptide chain from its 3’ end to the amino acid attached to the 3’ end of the newly delivered tRNA, a reaction catalyzed by the ribosome.A large number of the individual nucleotides in a tRNA molecule may be chemically modified, often by methylation or deamidation. These unusual bases sometimes affect the tRNA's interaction with ribosomes and sometimes occur in the anticodon to alter base-pairing properties.