Example of Research Proposal
... by Scott Strobel Hypothesis What is the chirality of the tetrahedral intermediate that occurs during ribosome catalyzed peptide bond formation? How does the ribosome provide transition state stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate ? Background Information Ribosomes are the macromolecular machi ...
... by Scott Strobel Hypothesis What is the chirality of the tetrahedral intermediate that occurs during ribosome catalyzed peptide bond formation? How does the ribosome provide transition state stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate ? Background Information Ribosomes are the macromolecular machi ...
Discovering the material for heredity: DNA
... up properly. It also catalyzes the synthesis of the new peptide (covalent) bonds between the amino acids. The ribosome is made of proteins and rRNA. ...
... up properly. It also catalyzes the synthesis of the new peptide (covalent) bonds between the amino acids. The ribosome is made of proteins and rRNA. ...
Answer Key to Short Answer Questions for
... From the charts above, there are a total of 5 mutations that could have occurred in Harry’s two genes WITHOUT resulting in a change in the amino acid (amino acid conserved). c. Which position (first, second, or third) did the changes occur within the DNA triplet codes you listed above? In all 5 of t ...
... From the charts above, there are a total of 5 mutations that could have occurred in Harry’s two genes WITHOUT resulting in a change in the amino acid (amino acid conserved). c. Which position (first, second, or third) did the changes occur within the DNA triplet codes you listed above? In all 5 of t ...
- Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
... 27. Proteins to be sent out of the cell or to the cell membrane are made in attached ribosomes (bound to the ER); proteins to be used in the cytoplasm are made in free ribosomes (floating in the cytoplasm) 28. A ribosome binds mRNA between the large and small subunits ; it has three binding sites fo ...
... 27. Proteins to be sent out of the cell or to the cell membrane are made in attached ribosomes (bound to the ER); proteins to be used in the cytoplasm are made in free ribosomes (floating in the cytoplasm) 28. A ribosome binds mRNA between the large and small subunits ; it has three binding sites fo ...
Write True if the statement is true
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
Molecular Genetics
... The release factor hydrolyzes the bond between the last tRNA at the P site and the polypeptide, releasing them. The ribosomal subunits dissociate. ...
... The release factor hydrolyzes the bond between the last tRNA at the P site and the polypeptide, releasing them. The ribosomal subunits dissociate. ...
Protein Synthesis
... DNA triplets encode for each one of the 20 amino acids that make proteins • During transcription, a DNA triplet will produce an mRNA codon. • During translation, a codon will constitute an amino acid ...
... DNA triplets encode for each one of the 20 amino acids that make proteins • During transcription, a DNA triplet will produce an mRNA codon. • During translation, a codon will constitute an amino acid ...
RNA, Transcription, Translation
... Then do a sketch of an RNA molecule (at least 10 nucleotides long using the all the appropriate bases at least twice). ...
... Then do a sketch of an RNA molecule (at least 10 nucleotides long using the all the appropriate bases at least twice). ...
CHAPTER 6 Gene Expression: Translation
... 3. Ribosome-binding assay is another approach: a. An in vitro translation system is made that includes: i. ribosomes. ii. tRNAs charged with their respective amino acids. iii. an RNA trinucleotide (e.g., UUU). b. Protein synthesis does not occur, because the mRNA template contains only one codon. W ...
... 3. Ribosome-binding assay is another approach: a. An in vitro translation system is made that includes: i. ribosomes. ii. tRNAs charged with their respective amino acids. iii. an RNA trinucleotide (e.g., UUU). b. Protein synthesis does not occur, because the mRNA template contains only one codon. W ...
AA G
... gene. processing”. While average enzyme, human the mRNA key molecule molecule for has the about manufacture ...
... gene. processing”. While average enzyme, human the mRNA key molecule molecule for has the about manufacture ...
S4 Text
... Concentration of tRNA charged with aa i Concentration of free tRNA conjugate to aa i Total concentration of tRNA conjugate to aa i Total concentration of ribosome with an A-site for aa i Ribosomes with uncharged tRNA in an A-site for aa i Concentration of ppGpp Total concentration of aa (not incorpo ...
... Concentration of tRNA charged with aa i Concentration of free tRNA conjugate to aa i Total concentration of tRNA conjugate to aa i Total concentration of ribosome with an A-site for aa i Ribosomes with uncharged tRNA in an A-site for aa i Concentration of ppGpp Total concentration of aa (not incorpo ...
pdf
... 1. Actively translating proteins were labeled with radioactive amino acids for a brief time (short relative to the time required to complete synthesis). 2. Completed polypeptides were collected, digested with trypsin, and the amount of radioactivity in tryptic fragments was determined. 3. Tryptic fr ...
... 1. Actively translating proteins were labeled with radioactive amino acids for a brief time (short relative to the time required to complete synthesis). 2. Completed polypeptides were collected, digested with trypsin, and the amount of radioactivity in tryptic fragments was determined. 3. Tryptic fr ...
Insert Overview of Translation here 2 pages.
... addition of each amino acid to the polypeptide chain. These are proteins that associate with the small subunit of the ribosome specifically at the stage of translation initiation. A mRNA that contains the coding region of only a single gene. The opposite of monocistronic is polycistronic. Eukaryotes ...
... addition of each amino acid to the polypeptide chain. These are proteins that associate with the small subunit of the ribosome specifically at the stage of translation initiation. A mRNA that contains the coding region of only a single gene. The opposite of monocistronic is polycistronic. Eukaryotes ...
Lecture 4-5 Outline
... Differential gene expression: e.g. of 30,000 genes in a typical mammalian cell, only about 5,000 are being transcribed at any time. Which 5000 depends on the cell type. Some are housekeeping genes, all cells transcribe them; some are specific to cell function, such as red blood cells where 95% of pr ...
... Differential gene expression: e.g. of 30,000 genes in a typical mammalian cell, only about 5,000 are being transcribed at any time. Which 5000 depends on the cell type. Some are housekeeping genes, all cells transcribe them; some are specific to cell function, such as red blood cells where 95% of pr ...
Chapter 14 2015 - Franklin College
... B. Splicing out introns is a risky business (what if it’s done incorrectly) C. With these disadvantages, there must be an advantage or natural selection would not favor this arrangement ...
... B. Splicing out introns is a risky business (what if it’s done incorrectly) C. With these disadvantages, there must be an advantage or natural selection would not favor this arrangement ...
Complete the blank spaces in the following chart:
... 2. Assume that the base in position 6 of the original DNA strand mutates to an "A." How will the sequence be affected? ...
... 2. Assume that the base in position 6 of the original DNA strand mutates to an "A." How will the sequence be affected? ...
1 CHAPTER 3- DNA FUNCTION – THE EXPRESSION OF GENETIC
... Ribosomal RNAs – rRNAs – component of the ribosome Small nuclear RNAs – snRNAs – involved in RNA processing in eukaryotes Small cytoplasmic RNAs – scRNAs – protein trafficking in eukaryotes 2. How is RNA made from DNA? TRANSCRIPTION = Production of mRNA from DNA template (pg. 60-64) -in each gene, o ...
... Ribosomal RNAs – rRNAs – component of the ribosome Small nuclear RNAs – snRNAs – involved in RNA processing in eukaryotes Small cytoplasmic RNAs – scRNAs – protein trafficking in eukaryotes 2. How is RNA made from DNA? TRANSCRIPTION = Production of mRNA from DNA template (pg. 60-64) -in each gene, o ...
Overcoming the codon bias of E. coli for enhanced protein expression
... in many cases that the resident tRNA population available for target protein synthesis would more closely resemble that of the “Class II” genes in Table 1. Theoretically, modification of culture conditions (e.g. lowering the temperature, changing media composition, etc.) might shift the codon usage ...
... in many cases that the resident tRNA population available for target protein synthesis would more closely resemble that of the “Class II” genes in Table 1. Theoretically, modification of culture conditions (e.g. lowering the temperature, changing media composition, etc.) might shift the codon usage ...
Figure 5.x3 James Watson and Francis Crick
... The mRNA codon in the A site of the ribosome forms a H-bond with the anticodon of an incoming molecule of tRNA carrying its appropriate amino acid. This requires energy. (GTP) (A site) The ribosome catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the new amino acid and the growing polypeptide. Cata ...
... The mRNA codon in the A site of the ribosome forms a H-bond with the anticodon of an incoming molecule of tRNA carrying its appropriate amino acid. This requires energy. (GTP) (A site) The ribosome catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the new amino acid and the growing polypeptide. Cata ...
translation - Haloarchaea
... A site : site where an aminoacyl-tRNA enters to base pair with a codon. P site : site occupied by a peptidyl-tRNA Deacylated tRNA: has no amino acid or polypeptide chain attached Translocation: the movement of the ribosome, one codon at a time, along mRNA after the addition of an amino acid to the ...
... A site : site where an aminoacyl-tRNA enters to base pair with a codon. P site : site occupied by a peptidyl-tRNA Deacylated tRNA: has no amino acid or polypeptide chain attached Translocation: the movement of the ribosome, one codon at a time, along mRNA after the addition of an amino acid to the ...
Gene Expression
... RNA polymerase transcribes both the exons and introns, producing a long RNA molecule. Enzymes in the nucleus then add further nucleotides at the beginning (cap) and end (tail) of the RNA transcript. Other enzymes cut out the RNA introns and splice together the exons to form the true mRNA, which move ...
... RNA polymerase transcribes both the exons and introns, producing a long RNA molecule. Enzymes in the nucleus then add further nucleotides at the beginning (cap) and end (tail) of the RNA transcript. Other enzymes cut out the RNA introns and splice together the exons to form the true mRNA, which move ...
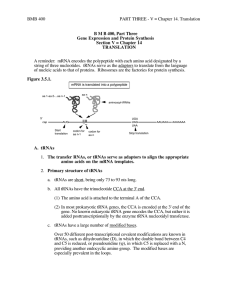
3.5.5 Explain the relationship between one gene
... A gene is a sequence of DNA which encodes a polypeptide sequence A gene sequence is converted into a polypeptide sequence via the processes of transcription (making an mRNA transcript) and translation (polypeptide synthesis) Translation uses tRNA molecules and ribosomes to join amino acids into a po ...
... A gene is a sequence of DNA which encodes a polypeptide sequence A gene sequence is converted into a polypeptide sequence via the processes of transcription (making an mRNA transcript) and translation (polypeptide synthesis) Translation uses tRNA molecules and ribosomes to join amino acids into a po ...
unit3_lesson10_translation1_markscheme
... POD Mark Scheme Explain the translation of a protein from DNA [8]. ...
... POD Mark Scheme Explain the translation of a protein from DNA [8]. ...
Transfer RNA

A transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and archaically referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length, that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. It does this by carrying an amino acid to the protein synthetic machinery of a cell (ribosome) as directed by a three-nucleotide sequence (codon) in a messenger RNA (mRNA). As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins according to the genetic code.The specific nucleotide sequence of an mRNA specifies which amino acids are incorporated into the protein product of the gene from which the mRNA is transcribed, and the role of tRNA is to specify which sequence from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. One end of the tRNA matches the genetic code in a three-nucleotide sequence called the anticodon. The anticodon forms three base pairs with a codon in mRNA during protein biosynthesis. The mRNA encodes a protein as a series of contiguous codons, each of which is recognized by a particular tRNA. On the other end of the tRNA is a covalent attachment to the amino acid that corresponds to the anticodon sequence. Each type of tRNA molecule can be attached to only one type of amino acid, so each organism has many types of tRNA (in fact, because the genetic code contains multiple codons that specify the same amino acid, there are several tRNA molecules bearing different anticodons which also carry the same amino acid).The covalent attachment to the tRNA 3’ end is catalyzed by enzymes called aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. During protein synthesis, tRNAs with attached amino acids are delivered to the ribosome by proteins called elongation factors (EF-Tu in bacteria, eEF-1 in eukaryotes), which aid in decoding the mRNA codon sequence. If the tRNA's anticodon matches the mRNA, another tRNA already bound to the ribosome transfers the growing polypeptide chain from its 3’ end to the amino acid attached to the 3’ end of the newly delivered tRNA, a reaction catalyzed by the ribosome.A large number of the individual nucleotides in a tRNA molecule may be chemically modified, often by methylation or deamidation. These unusual bases sometimes affect the tRNA's interaction with ribosomes and sometimes occur in the anticodon to alter base-pairing properties.