Immunizations in Older Adults_Dec2011
... • PBMC produce less IFNγ • Decreased CD8+ cell response • Frail had even poorer response ...
... • PBMC produce less IFNγ • Decreased CD8+ cell response • Frail had even poorer response ...
221_exam_4_2002
... _____ Which of the following vaccines is/are accurately described as a subunit vaccine? A. Vaccine composed of killed bacteria. B. Vaccine composed of a pilus protein C. Vaccine composed of a live attenuated virus. D. Antibodies injected into a non-immune person exposed to a disease _____ Toxoid vac ...
... _____ Which of the following vaccines is/are accurately described as a subunit vaccine? A. Vaccine composed of killed bacteria. B. Vaccine composed of a pilus protein C. Vaccine composed of a live attenuated virus. D. Antibodies injected into a non-immune person exposed to a disease _____ Toxoid vac ...
SEPRL Avian Influenza Research Team David L. Suarez Vaccine
... • Baculovirus expressed protein for efficient and clean protein ...
... • Baculovirus expressed protein for efficient and clean protein ...
Purposes and uses of epidemiology The ultimate purpose of
... reservoirs. Diseases that are transmitted from person to person without intermediate host include the sexually transmitted diseases, measles, mumps, streptococcal infection, and many respiratory pathogens. Animal reservoirs: Humans are also subject to diseases that have animal reservoirs. Many of th ...
... reservoirs. Diseases that are transmitted from person to person without intermediate host include the sexually transmitted diseases, measles, mumps, streptococcal infection, and many respiratory pathogens. Animal reservoirs: Humans are also subject to diseases that have animal reservoirs. Many of th ...
Cattle Vaccination and Immunity - NMSU ACES
... Developing immunity in cattle requires an effective herd health program. Vaccinations are not a silver bullet cure all for disease in a cowherd, but are a primary component of a complete herd health program. Vaccines contain antigens of disease-causing agents, and are used to stimulate cattle’s immu ...
... Developing immunity in cattle requires an effective herd health program. Vaccinations are not a silver bullet cure all for disease in a cowherd, but are a primary component of a complete herd health program. Vaccines contain antigens of disease-causing agents, and are used to stimulate cattle’s immu ...
Vaccines: A Molecular View
... • Why is it important? • Vaccines protect individuals (and communities) from a large number of infectious pathogens by enabling them to rapidly mount a protective immune response upon encounter. ...
... • Why is it important? • Vaccines protect individuals (and communities) from a large number of infectious pathogens by enabling them to rapidly mount a protective immune response upon encounter. ...
Powerful Vaccine Discovery
... reach large populations and prevent endemic disease. Using novel technologies such as flagellin-based fusion proteins, scientists at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center and Wake Forest University are developing highly potent, cost-effective vaccines that provide protective immunity against a range of ...
... reach large populations and prevent endemic disease. Using novel technologies such as flagellin-based fusion proteins, scientists at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center and Wake Forest University are developing highly potent, cost-effective vaccines that provide protective immunity against a range of ...
Programme
... Ebola and several influenza A subtypes). Such infections are potentially devastating, since there is usually no immunity in the population. These infections have also an important economic impact by derailing the global economy and travel. Vaccination and other immunotherapeutic interventions provid ...
... Ebola and several influenza A subtypes). Such infections are potentially devastating, since there is usually no immunity in the population. These infections have also an important economic impact by derailing the global economy and travel. Vaccination and other immunotherapeutic interventions provid ...
`immunisation` and `vaccine-preventable diseases`.
... Natural immunity and vaccine-induced immunity are both natural responses of the body’s immune system. The body’s immune response in both circumstances is the same. In some cases, vaccine-induced immunity may diminish with time; natural immunity, acquired by catching the disease is usually life-long. ...
... Natural immunity and vaccine-induced immunity are both natural responses of the body’s immune system. The body’s immune response in both circumstances is the same. In some cases, vaccine-induced immunity may diminish with time; natural immunity, acquired by catching the disease is usually life-long. ...
Immunization - Liaquat University of Medical & Health Sciences
... McIntyre P. JAMA (SEA Suppl) 1993; 9: 5-10. 4 Shapiro ED, Ward, JI. The epidemiology and prevention of disease caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b. Epidemiologic Reviews 1991; 13:112-143. 1WHO ...
... McIntyre P. JAMA (SEA Suppl) 1993; 9: 5-10. 4 Shapiro ED, Ward, JI. The epidemiology and prevention of disease caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b. Epidemiologic Reviews 1991; 13:112-143. 1WHO ...
Методические разработки
... A number of Phase I and II trials have shown that cancer vaccines are generally well-tolerated, particularly with the viral and peptide vaccines. Phase I trials have reported very few significant toxicities with these vaccines. The most common toxicity in all of these trials has been local irritatio ...
... A number of Phase I and II trials have shown that cancer vaccines are generally well-tolerated, particularly with the viral and peptide vaccines. Phase I trials have reported very few significant toxicities with these vaccines. The most common toxicity in all of these trials has been local irritatio ...
MICR 201 Microbiology for Health Related Sciences
... inactivated agent that does not cause major disease Induce cross-reactive antibodies or T cells Herd immunity is sufficient to prevent epidemic diseases Must weigh the benefit of protection versus the danger of vaccine associated disease ...
... inactivated agent that does not cause major disease Induce cross-reactive antibodies or T cells Herd immunity is sufficient to prevent epidemic diseases Must weigh the benefit of protection versus the danger of vaccine associated disease ...
MICR 201 Microbiology for Health Related Sciences
... inactivated agent that does not cause major disease Induce cross-reactive antibodies or T cells Herd immunity is sufficient to prevent epidemic diseases Must weigh the benefit of protection versus the danger of vaccine associated disease ...
... inactivated agent that does not cause major disease Induce cross-reactive antibodies or T cells Herd immunity is sufficient to prevent epidemic diseases Must weigh the benefit of protection versus the danger of vaccine associated disease ...
Principles of Vaccination - Dow University of Health Sciences
... – Identification of the seroprotective threshold requires measurement of antibody levels in vaccinees who develop the disease (vaccine failures) – 5-year data shows that HPV vaccine efficacy is almost 100%, as measured by reduction in disease in clinical trials – As a result, it is not possible to d ...
... – Identification of the seroprotective threshold requires measurement of antibody levels in vaccinees who develop the disease (vaccine failures) – 5-year data shows that HPV vaccine efficacy is almost 100%, as measured by reduction in disease in clinical trials – As a result, it is not possible to d ...
Vaxart`s Tablet Vaccine for H1N1 Influenza Generates Protective
... SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Vaxart, Inc., a privately held, clinical-stage company developing recombinant vaccines that are administered by tablet rather than by injection, today announced clinical results demonstrating that its H1N1 tablet vaccine generates protective immunity com ...
... SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Vaxart, Inc., a privately held, clinical-stage company developing recombinant vaccines that are administered by tablet rather than by injection, today announced clinical results demonstrating that its H1N1 tablet vaccine generates protective immunity com ...
Viral Vaccines - Molecular Immunology
... • Resistance developed in response to stimulus by an antigen (infecting agent or vaccine) and is characterized by the production of antibodies by the host. ...
... • Resistance developed in response to stimulus by an antigen (infecting agent or vaccine) and is characterized by the production of antibodies by the host. ...
葉才明
... • A wide range of antigen preparations are in use as vaccines. • Adjuvants enhance antibody production. • Most vaccines are still given by injection. • Vaccine efficacy needs to be reviewed from time to time. • Vaccine safety is an overriding consideration. • Vaccines in general use have variable su ...
... • A wide range of antigen preparations are in use as vaccines. • Adjuvants enhance antibody production. • Most vaccines are still given by injection. • Vaccine efficacy needs to be reviewed from time to time. • Vaccine safety is an overriding consideration. • Vaccines in general use have variable su ...
the programme
... DL Woodland (Silverthorne) Maintenance of Peripheral T Cell Responses during Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection WJ Britton (Sydney) Protein vaccines against tuberculosis: new antigens and new delivery strategies A Cooper (New York) TB vaccination: do we know what we are trying to achieve at a cell ...
... DL Woodland (Silverthorne) Maintenance of Peripheral T Cell Responses during Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection WJ Britton (Sydney) Protein vaccines against tuberculosis: new antigens and new delivery strategies A Cooper (New York) TB vaccination: do we know what we are trying to achieve at a cell ...
Vaccines - UCLA Health
... fatigue, toxicities, resistance • Behavior-based prevention: human nature, cultural issues • Vaccines: capacity for global impact (e.g. smallpox, polio), limited requirements for infrastructure and adherence ...
... fatigue, toxicities, resistance • Behavior-based prevention: human nature, cultural issues • Vaccines: capacity for global impact (e.g. smallpox, polio), limited requirements for infrastructure and adherence ...
GeoVax Labs, Inc. (Form: 8-K, Received: 12/09/2015
... mucin 1) are over-expressed (that is, produced in very large quantities) and aberrantly expressed (that is, produced in abnormal forms) in many advanced types of cancer. These antigens in the actual tumors are often recognized as abnormal by patients’ immune systems but are not sufficiently immunoge ...
... mucin 1) are over-expressed (that is, produced in very large quantities) and aberrantly expressed (that is, produced in abnormal forms) in many advanced types of cancer. These antigens in the actual tumors are often recognized as abnormal by patients’ immune systems but are not sufficiently immunoge ...
Start Summer Protected: Template Newsletter Article
... increases during the teen and young adult years. One type of vaccine, called the quadrivalent vaccine, protects against four types of meningococcal bacteria (serogroups A, C, W, and Y). This vaccine is recommended for all US adolescents at age 11-12 years, with a booster dose at age 16 years. Vaccin ...
... increases during the teen and young adult years. One type of vaccine, called the quadrivalent vaccine, protects against four types of meningococcal bacteria (serogroups A, C, W, and Y). This vaccine is recommended for all US adolescents at age 11-12 years, with a booster dose at age 16 years. Vaccin ...
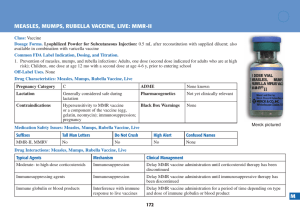
m measles, mumps, rubella vaccine, live: mmr-ii
... Efficacy Monitoring Parameters. Prevention of measles, mumps, and rubella infections; although antibody concentrations might be measured, routine measurement for vaccine response is not recommended. Toxicity Monitoring Parameters. Syncope within 15 min of vaccine administration. Key Patient Counseli ...
... Efficacy Monitoring Parameters. Prevention of measles, mumps, and rubella infections; although antibody concentrations might be measured, routine measurement for vaccine response is not recommended. Toxicity Monitoring Parameters. Syncope within 15 min of vaccine administration. Key Patient Counseli ...
Document
... Antibody to HBsAg indicates clinical recovery and is associated with immunity to Hepatitis B. Antibody to HBcAg is also produced and is first to appear after infection. – Present in blood of acute and chronic subjects as well as those recovered. – This antibody does not neutralize virus. ...
... Antibody to HBsAg indicates clinical recovery and is associated with immunity to Hepatitis B. Antibody to HBcAg is also produced and is first to appear after infection. – Present in blood of acute and chronic subjects as well as those recovered. – This antibody does not neutralize virus. ...
Vaccine

A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing micro-organism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and keep a record of it, so that the immune system can more easily recognize and destroy any of these micro-organisms that it later encounters.The administration of vaccines is called vaccination. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified; for example, the influenza vaccine, the HPV vaccine, and the chicken pox vaccine. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases; widespread immunity due to vaccination is largely responsible for the worldwide eradication of smallpox and the restriction of diseases such as polio, measles, and tetanus from much of the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that licensed vaccines are currently available to prevent or contribute to the prevention and control of twenty-five infections.Vaccines can be prophylactic (example: to prevent or ameliorate the effects of a future infection by any natural or ""wild"" pathogen), or therapeutic (e.g., vaccines against cancer are also being investigated; see cancer vaccine).The terms vaccine and vaccination are derived from Variolae vaccinae (smallpox of the cow), the term devised by Edward Jenner to denote cowpox. He used it in 1798 in the long title of his Inquiry into the...Variolae vaccinae...known...[as]...the Cow Pox, in which he described the protective effect of cowpox against smallpox. In 1881, to honour Jenner, Louis Pasteur proposed that the terms should be extended to cover the new protective inoculations then being developed.