infection and immunity seminar schedule 2017
... Title: “New strategies for improved tuberculosis vaccines” ...
... Title: “New strategies for improved tuberculosis vaccines” ...
Chapter Seven Fighting Against Diseases
... knows how to defend itself against an attack of the same kind of germ What else helps fight Communicable diseases? Antibiotics are medicines that can kill many kinds of bacteria Penicillin is the most common- discovered in 1928 Bread mold What is AIDS? Acquired Immunity Deficiency Syndrome It is pre ...
... knows how to defend itself against an attack of the same kind of germ What else helps fight Communicable diseases? Antibiotics are medicines that can kill many kinds of bacteria Penicillin is the most common- discovered in 1928 Bread mold What is AIDS? Acquired Immunity Deficiency Syndrome It is pre ...
Diseases of the Immune System
... • Multiple sclerosis: myelin sheaths in the white matter of brain & spinal cord are destroyed • Causing muscle and neural deterioration, psychological issues, ...
... • Multiple sclerosis: myelin sheaths in the white matter of brain & spinal cord are destroyed • Causing muscle and neural deterioration, psychological issues, ...
35.2 Defenses against Infection
... • Histamine • Cell-mediated immunity • Interferon • Fever • Immune response • Antigen • antibody ...
... • Histamine • Cell-mediated immunity • Interferon • Fever • Immune response • Antigen • antibody ...
Protective oral vaccination against infectious Salmon Anaemia virus
... Among the challenged fish, first fish died at 13 DPC, mortality rate then increased. This results obtained are in agreement with the previously reported incubation period for ISAV infection of 10e20 days [23e26]. The cumulative mortality of the unvaccinated control fish was 93.3%, indicating the high vi ...
... Among the challenged fish, first fish died at 13 DPC, mortality rate then increased. This results obtained are in agreement with the previously reported incubation period for ISAV infection of 10e20 days [23e26]. The cumulative mortality of the unvaccinated control fish was 93.3%, indicating the high vi ...
Biology: Microbiology: Viruses II
... to fight against infection. It does this by attacking the white blood cells, which are in charge of protecting the body against infectious disease. Symptoms of AIDS are diarrhea, fatigue, fever, dry cough, shortness of breath, night sweats, difficulty in concentrating, etc. These symptoms are most l ...
... to fight against infection. It does this by attacking the white blood cells, which are in charge of protecting the body against infectious disease. Symptoms of AIDS are diarrhea, fatigue, fever, dry cough, shortness of breath, night sweats, difficulty in concentrating, etc. These symptoms are most l ...
Immune System
... If they ever encounter that same pathogen again, they rapidly produce large amounts of antibodies that destroy the pathogen before they have a chance to cause the disease a second time ...
... If they ever encounter that same pathogen again, they rapidly produce large amounts of antibodies that destroy the pathogen before they have a chance to cause the disease a second time ...
foot and mouth disease
... The carrier state in cattle usually does not persist for more than 6 months, although in a small proportion it may last up to 3 years Domestic buffalo, sheep and goats do not usually carry FMD viruses for more than a few months; African buffalo are the major maintenance host of SAT serotypes, and ma ...
... The carrier state in cattle usually does not persist for more than 6 months, although in a small proportion it may last up to 3 years Domestic buffalo, sheep and goats do not usually carry FMD viruses for more than a few months; African buffalo are the major maintenance host of SAT serotypes, and ma ...
Infectious Laryngotracheitis
... When a caseous plug occludes the larynx or trachea, the affected chickens will have extreme difficulty breathing ("pump handle" breathing) and will frequently die from suffocation. Mortality is approximately 1 % per day in a typical ILT outbreak. Milder forms of ILT outbreaks occur where less virule ...
... When a caseous plug occludes the larynx or trachea, the affected chickens will have extreme difficulty breathing ("pump handle" breathing) and will frequently die from suffocation. Mortality is approximately 1 % per day in a typical ILT outbreak. Milder forms of ILT outbreaks occur where less virule ...
Immunology study guide
... – Because mucus traps pathogen and stores as boogers – When you eat it, it is like you are eating the pathogen – It acts as a vaccine because your body will retain memory ...
... – Because mucus traps pathogen and stores as boogers – When you eat it, it is like you are eating the pathogen – It acts as a vaccine because your body will retain memory ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... many microorganisms.HSP-60 has been associated with atherosclerosis and Chlamydia pneumonia infection. 3. Financial Periodontal treatment puts a financial burden on the individuals suffering from it. Availability of vaccine for preventing or modulating periodontal disease would be of great benefit i ...
... many microorganisms.HSP-60 has been associated with atherosclerosis and Chlamydia pneumonia infection. 3. Financial Periodontal treatment puts a financial burden on the individuals suffering from it. Availability of vaccine for preventing or modulating periodontal disease would be of great benefit i ...
MUMPS
... What is Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)? HFMD is a viral illness that causes mild fever and rash, usually in young children. The rash is non-tender and vesicular or macular; it is found on the tongue and buccal mucosa. One day later ~75% develop rash commonly on the sides of the fingers, hands an ...
... What is Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)? HFMD is a viral illness that causes mild fever and rash, usually in young children. The rash is non-tender and vesicular or macular; it is found on the tongue and buccal mucosa. One day later ~75% develop rash commonly on the sides of the fingers, hands an ...
HERPESVIRIDAE
... Immunity and epidemiology: Infected animals remain carriers. Transmission is via aerosol, milk, or colostrum. The crowded 6 month winter housing as practised in Iceland allowed spread not only of V-MV but also of Johne's disease and SPA. Infection was introduced into the UK by French exotic breeds ...
... Immunity and epidemiology: Infected animals remain carriers. Transmission is via aerosol, milk, or colostrum. The crowded 6 month winter housing as practised in Iceland allowed spread not only of V-MV but also of Johne's disease and SPA. Infection was introduced into the UK by French exotic breeds ...
Immune System
... are coated with mucus; Mucus traps airborne pathogens & swept into the digestive system to be destroyed 3. Inflammation - Occurs when pathogens do enter the body (usually through skin); Blood vessels near wound expand; WBC leak from the vessels to invade the infected tissues; Phagocytes (wbc) engulf ...
... are coated with mucus; Mucus traps airborne pathogens & swept into the digestive system to be destroyed 3. Inflammation - Occurs when pathogens do enter the body (usually through skin); Blood vessels near wound expand; WBC leak from the vessels to invade the infected tissues; Phagocytes (wbc) engulf ...
PPT - Aquaculture Asia
... responses and immune memory, involving B cells and T cells, antibody and phagocytic cells. • This adaptive immune response enables them to specifically “remember” exposure to pathogens and respond with increased efficiency on subsequent exposure, forming the basis of vaccination • Understanding of t ...
... responses and immune memory, involving B cells and T cells, antibody and phagocytic cells. • This adaptive immune response enables them to specifically “remember” exposure to pathogens and respond with increased efficiency on subsequent exposure, forming the basis of vaccination • Understanding of t ...
Pathogen Paper - Murray State University
... The purpose of this project is to research a microbial pathogen and the disease it produces in humans. The assignment is divided into five parts. The first four papers you submit will be incorporated into the final, comprehensive term paper. A scoring rubric for this project is attached. Each writte ...
... The purpose of this project is to research a microbial pathogen and the disease it produces in humans. The assignment is divided into five parts. The first four papers you submit will be incorporated into the final, comprehensive term paper. A scoring rubric for this project is attached. Each writte ...
Immunity - porterhealthscience
... person has been infected with a microorganism and recovers from the disease, has had a subclinical or very mild infection, and/or is a carrier of the microorganism. Artificial aquired immunity – results from having been immunized, or vaccinated, with a killed or ...
... person has been infected with a microorganism and recovers from the disease, has had a subclinical or very mild infection, and/or is a carrier of the microorganism. Artificial aquired immunity – results from having been immunized, or vaccinated, with a killed or ...
Pertussis - East Central Health District
... Laboratory confirmation is difficult, so diagnosis often based on characteristic clinical manifestations Children may return to school after 5 days of appropriate antibiotic therapy ...
... Laboratory confirmation is difficult, so diagnosis often based on characteristic clinical manifestations Children may return to school after 5 days of appropriate antibiotic therapy ...
Document
... O Lamprey and Hagfish have a distinct lymphocyte derived molecule. O These molecules are believed to bind pathogenic antigens in a similar way to antibodies. ...
... O Lamprey and Hagfish have a distinct lymphocyte derived molecule. O These molecules are believed to bind pathogenic antigens in a similar way to antibodies. ...
医学史简论 A Brief History of Medicine
... Disease changed human itself - Impact on human genes In sub-Saharan Africa the incidence of sickle cell anamia as high as 1/400, Heterozygote--carriers of a single sickle cell allele are 810% The sickle cells have protection from malaria (plasmodium can not parasite), it may be the results of evolu ...
... Disease changed human itself - Impact on human genes In sub-Saharan Africa the incidence of sickle cell anamia as high as 1/400, Heterozygote--carriers of a single sickle cell allele are 810% The sickle cells have protection from malaria (plasmodium can not parasite), it may be the results of evolu ...
DOCX format - 32 KB - Office of the Gene Technology Regulator
... disposal of a live genetically modified (GM) dengue vaccine, Dengvaxia, as part of its commercial supply in Australia. What is dengue? Dengue is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue viruses. People infected for the first time can develop sudden and painful fever. The infection usually resolves ...
... disposal of a live genetically modified (GM) dengue vaccine, Dengvaxia, as part of its commercial supply in Australia. What is dengue? Dengue is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue viruses. People infected for the first time can develop sudden and painful fever. The infection usually resolves ...
Lesson 16 – Subtypes (Color Ink Saving)
... Immunodeficiencies (pronounced: ih-myoon-o-dih-fih-shun-seez) occur when a part of the immune system is not present or is not working properly. Sometimes a person is born with an immunodeficiency — these are called primary immunodeficiencies. (Although primary immunodeficiencies are conditions that ...
... Immunodeficiencies (pronounced: ih-myoon-o-dih-fih-shun-seez) occur when a part of the immune system is not present or is not working properly. Sometimes a person is born with an immunodeficiency — these are called primary immunodeficiencies. (Although primary immunodeficiencies are conditions that ...
Immune system notes
... – Epidemic – rapid outbreak of a disease that affects many people – Pandemic – when a disease is common in the population (like the common cold or flu) – Germ theory – specific microorganisms cause diseases – CDC – Center for Disease Control – based in Atlanta, Georgia; is responsible for monitoring ...
... – Epidemic – rapid outbreak of a disease that affects many people – Pandemic – when a disease is common in the population (like the common cold or flu) – Germ theory – specific microorganisms cause diseases – CDC – Center for Disease Control – based in Atlanta, Georgia; is responsible for monitoring ...
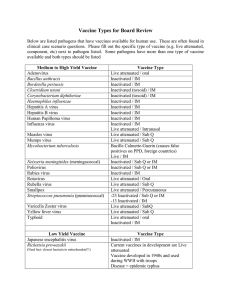
Vaccine Table for Board Review
... Vaccine Types for Board Review Below are listed pathogens that have vaccines available for human use. These are often found in clinical case scenario questions. Please fill out the specific type of vaccine (e.g. live attenuated, component, etc) next to pathogen listed. Some pathogens have more than ...
... Vaccine Types for Board Review Below are listed pathogens that have vaccines available for human use. These are often found in clinical case scenario questions. Please fill out the specific type of vaccine (e.g. live attenuated, component, etc) next to pathogen listed. Some pathogens have more than ...
Vaccination

Vaccination is the administration of antigenic material (a vaccine) to stimulate an individual's immune system to develop adaptive immunity to a pathogen. Vaccines can prevent or ameliorate morbidity from infection. When a sufficiently large percentage of a population has been vaccinated, this results in herd immunity. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified; for example, the influenza vaccine, the HPV vaccine, and the chicken pox vaccine. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases; widespread immunity due to vaccination is largely responsible for the worldwide eradication of smallpox and the restriction of diseases such as polio, measles, and tetanus from much of the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that licensed vaccines are currently available to prevent or contribute to the prevention and control of twenty-five infections.The active agent of a vaccine may be intact but inactivated (non-infective) or attenuated (with reduced infectivity) forms of the causative pathogens, or purified components of the pathogen that have been found to be highly immunogenic (e.g., outer coat proteins of a virus). Toxoids are produced for immunization against toxin-based diseases, such as the modification of tetanospasmin toxin of tetanus to remove its toxic effect but retain its immunogenic effect.Smallpox was most likely the first disease people tried to prevent by inoculating themselves and was the first disease for which a vaccine was produced. The smallpox vaccine was discovered in 1796 by the British physician Edward Jenner, although at least six people had used the same principles years earlier. Louis Pasteur furthered the concept through his work in microbiology. The immunization was called vaccination because it was derived from a virus affecting cows (Latin: vacca—cow). Smallpox was a contagious and deadly disease, causing the deaths of 20–60% of infected adults and over 80% of infected children. When smallpox was finally eradicated in 1979, it had already killed an estimated 300–500 million people in the 20th century.In common speech, 'vaccination' and 'immunization' have a similar meaning. This distinguishes it from inoculation, which uses unweakened live pathogens, although in common usage either can refer to an immunization. Vaccination efforts have been met with some controversy on scientific, ethical, political, medical safety, and religious grounds. In rare cases, vaccinations can injure people and, in the United States, they may receive compensation for those injuries under the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program. Early success and compulsion brought widespread acceptance, and mass vaccination campaigns have greatly reduced the incidence of many diseases in numerous geographic regions.