Bloodborne Pathogens
... blood, or other potentially infectious material such as certain bodily fluids (semen, breast milk, etc.) or tissues. ...
... blood, or other potentially infectious material such as certain bodily fluids (semen, breast milk, etc.) or tissues. ...
Attitudes toward mandatory occupational vaccinations and
... HCWs: all persons employed in a healthcare facility with or without direct patient care, regardless of employment status Immunity against VPDs: a history of completed and up-to-date vaccination or a history of natural infection resulting in permanent immunity (pertussis, tetanus and diphtheria were ...
... HCWs: all persons employed in a healthcare facility with or without direct patient care, regardless of employment status Immunity against VPDs: a history of completed and up-to-date vaccination or a history of natural infection resulting in permanent immunity (pertussis, tetanus and diphtheria were ...
Protozoan Diseases of Lower Digestive System
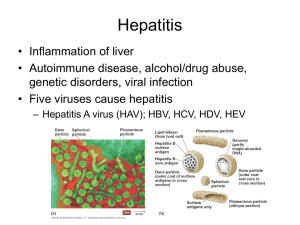
... Hepatitis • Inflammation of liver • Autoimmune disease, alcohol/drug abuse, genetic disorders, viral infection • Five viruses cause hepatitis – Hepatitis A virus (HAV); HBV, HCV, HDV, HEV ...
... Hepatitis • Inflammation of liver • Autoimmune disease, alcohol/drug abuse, genetic disorders, viral infection • Five viruses cause hepatitis – Hepatitis A virus (HAV); HBV, HCV, HDV, HEV ...
HIV - MULTIWEBCAST
... Definition “Inflammation of the liver, usually producing swelling and tenderness and sometimes permanent damage to the liver.” - American Liver Foundation Types of hepatitis ...
... Definition “Inflammation of the liver, usually producing swelling and tenderness and sometimes permanent damage to the liver.” - American Liver Foundation Types of hepatitis ...
Infection Control - - Covington County Schools
... person-to-person through the air when an infected person repeatedly comes in contact with an uninfected person. TB usually affects the lungs, ...
... person-to-person through the air when an infected person repeatedly comes in contact with an uninfected person. TB usually affects the lungs, ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... • Hepatitis B (HBV) – There has been a decline in HBV in recent years. • Transmission of hepatitis B virus results from exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. • The acute illness causes liver inflammation, vomiting, jaundice and—rarely—death. Chronic hepatitis B may eventually cause liver cirr ...
... • Hepatitis B (HBV) – There has been a decline in HBV in recent years. • Transmission of hepatitis B virus results from exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. • The acute illness causes liver inflammation, vomiting, jaundice and—rarely—death. Chronic hepatitis B may eventually cause liver cirr ...
Hepatitis G Virus Fact Sheet - Minnesota Department of Health
... HGV has been reported in adults and children throughout the world and is found in about 1.5% of blood donors in the United States. Infection has been reported in 10% to 20% of adults with chronic HBV or HCV infection, indicating that co-infection is a common occurrence. ...
... HGV has been reported in adults and children throughout the world and is found in about 1.5% of blood donors in the United States. Infection has been reported in 10% to 20% of adults with chronic HBV or HCV infection, indicating that co-infection is a common occurrence. ...
What is hepatitis A - Public Health Wales
... Incidence has been low since it last peaked in 1990 when 7,545 hepatitis A cases were reported for England and Wales. There were 669 reports in 2004 with 22 reported for Wales. Hepatitis A is more common in some other countries where sanitation and sewage disposal can be poor (particularly Africa, n ...
... Incidence has been low since it last peaked in 1990 when 7,545 hepatitis A cases were reported for England and Wales. There were 669 reports in 2004 with 22 reported for Wales. Hepatitis A is more common in some other countries where sanitation and sewage disposal can be poor (particularly Africa, n ...
Hepatitis A, B, C Screening
... An infected person can spread the disease 4 – 6 weeks before symptoms and an unpredictable period of time after infection The virus can live 1 week on contaminated objects Diagnosis is by laboratory analysis Testing is done to determine conversion and/or disease stage Acute Infection Chronic Active ...
... An infected person can spread the disease 4 – 6 weeks before symptoms and an unpredictable period of time after infection The virus can live 1 week on contaminated objects Diagnosis is by laboratory analysis Testing is done to determine conversion and/or disease stage Acute Infection Chronic Active ...
Employees who fail to follow established policies
... VRE- Vancomycin resistant enterococcus Healthy people usually not at risk Individuals with immunosuppression, underlying disease, presence of indwelling urinary catheter, Gtubes, etc are more susceptible. ...
... VRE- Vancomycin resistant enterococcus Healthy people usually not at risk Individuals with immunosuppression, underlying disease, presence of indwelling urinary catheter, Gtubes, etc are more susceptible. ...
Health Center 21 – Bloodborne Pathogens Using the Bloodborne
... 8. How does the Americans with Disabilities Act help patients with HIV or AIDS? 9. What is hepatitis? 10. What type of pathogen causes hepatitis? 11. How is each of the following types of hepatitis transmitted? a. Hepatitis A: b. Hepatitis B: c. Hepatitis C: d. Hepatitis D: e. Hepatitis E: 12. Which ...
... 8. How does the Americans with Disabilities Act help patients with HIV or AIDS? 9. What is hepatitis? 10. What type of pathogen causes hepatitis? 11. How is each of the following types of hepatitis transmitted? a. Hepatitis A: b. Hepatitis B: c. Hepatitis C: d. Hepatitis D: e. Hepatitis E: 12. Which ...
Bloodborne Pathogen in the Workplace
... persons who become infected with HCV and nearly all (85%-100%) persons with acute HCV infection become persistently infected; these persons are at risk for developing cirrhosis and liver cancer ...
... persons who become infected with HCV and nearly all (85%-100%) persons with acute HCV infection become persistently infected; these persons are at risk for developing cirrhosis and liver cancer ...
Hepatitis C pdf, 169kb
... Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease that results from infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV). It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. HCV is usually spread when blood from a person infected with HCV enters the body of someone who is not ...
... Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease that results from infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV). It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. HCV is usually spread when blood from a person infected with HCV enters the body of someone who is not ...
New Hepatitis C medicines – Factsheet for patients and consumers
... New Hepatitis C medicines – Factsheet for patients and consumers The Turnbull Government has set aside over $1 billion over five years to subsidise a range of breakthrough medicines on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) that could all but eradicate Hepatitis C in Australia within a generation. ...
... New Hepatitis C medicines – Factsheet for patients and consumers The Turnbull Government has set aside over $1 billion over five years to subsidise a range of breakthrough medicines on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) that could all but eradicate Hepatitis C in Australia within a generation. ...
Adjustments in Hepatitis C Infection
... J. Fraser, Master of Public Health Degree, University of Glasgow 1998 ...
... J. Fraser, Master of Public Health Degree, University of Glasgow 1998 ...
Hepatitis B Vaccine Form/Declination
... Hepatitis Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) which causes death in 1-2% of patients. Most people with Hepatitis B recover completely, but approximately 6-10% of acutely infected adults become chronic carriers of the virus. Most of these people have no symptoms but can ...
... Hepatitis Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) which causes death in 1-2% of patients. Most people with Hepatitis B recover completely, but approximately 6-10% of acutely infected adults become chronic carriers of the virus. Most of these people have no symptoms but can ...
Liver infections
... pregnant mother has this marker, then 90% of the time – she will transmit the infection to the baby too! The virus is found in all body fluids (in order of concentrations): blood, serum, wound exudates, semen, saliva, vaginal fluid, urine, sweat, breast milk, faeces. Epidemiology/At risk individuals ...
... pregnant mother has this marker, then 90% of the time – she will transmit the infection to the baby too! The virus is found in all body fluids (in order of concentrations): blood, serum, wound exudates, semen, saliva, vaginal fluid, urine, sweat, breast milk, faeces. Epidemiology/At risk individuals ...
HEPATITIS The word “hepatitis” literally means “inflammation of the
... The word “hepatitis” literally means “inflammation of the liver”. Since the liver is responsible for cleaning out and processing the body’s waste products, any disease of the liver is potentially serious because it can lead to accumulation of these wastes in the body. While there are many medical co ...
... The word “hepatitis” literally means “inflammation of the liver”. Since the liver is responsible for cleaning out and processing the body’s waste products, any disease of the liver is potentially serious because it can lead to accumulation of these wastes in the body. While there are many medical co ...
View Course
... Hepatitis B is the most common cause of acute viral hepatitis. HBV is responsible for almost 80% of primary hepatocellular carcinoma cases. Approximately 400 million people worldwide are infected with HBV with an estimated 1.2 million living in the United States.5 The highest incidence of infection ...
... Hepatitis B is the most common cause of acute viral hepatitis. HBV is responsible for almost 80% of primary hepatocellular carcinoma cases. Approximately 400 million people worldwide are infected with HBV with an estimated 1.2 million living in the United States.5 The highest incidence of infection ...
Hepatitis B (and C) - Auburn School District
... blood, or other potentially infectious material such as certain bodily fluids (semen, breast milk, etc.) or tissues. ...
... blood, or other potentially infectious material such as certain bodily fluids (semen, breast milk, etc.) or tissues. ...
hepatitis B surface antigen
... • Treatment of children with HCV is under investigation. • all liver transplants are performed for end-stage hepatitis C. • no specific evidence proving that herbal relieves hepatitis symptoms or fights the virus. many herbs are toxic to the liver. ...
... • Treatment of children with HCV is under investigation. • all liver transplants are performed for end-stage hepatitis C. • no specific evidence proving that herbal relieves hepatitis symptoms or fights the virus. many herbs are toxic to the liver. ...
Infection Control
... • Hepatitis B, C & HIV/AIDS • Transmission by direct blood contact – sexual intercourse, sharing needles, needlestick injuries, razors etc. • Standard precautions only – Personal protective equipment when anticipating contact with body fluids ...
... • Hepatitis B, C & HIV/AIDS • Transmission by direct blood contact – sexual intercourse, sharing needles, needlestick injuries, razors etc. • Standard precautions only – Personal protective equipment when anticipating contact with body fluids ...
Infection Control in the School Setting
... person-to-person through the air when an infected person repeatedly comes in contact with an uninfected person. TB usually affects the lungs, ...
... person-to-person through the air when an infected person repeatedly comes in contact with an uninfected person. TB usually affects the lungs, ...
Hepatitis

Hepatitis (plural: hepatitides) is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. Hepatitis may occur with limited or no symptoms, but often leads to jaundice (a yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membrane, and conjunctiva), poor appetite, and malaise. Hepatitis is acute when it lasts less than six months and chronic when it persists longer.Acute hepatitis can be self-limiting (healing on its own), can progress to chronic hepatitis, or, rarely, can cause acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may have no symptoms, or may progress over time to fibrosis (scarring of the liver) and cirrhosis (chronic liver failure). Cirrhosis of the liver increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (a form of liver cancer).Worldwide, viral hepatitis is the most common cause of liver inflammation. Other causes include autoimmune diseases and ingestion of toxic substances (notably alcohol), certain medications (such as paracetamol), some industrial organic solvents, and plants.The term is derived from the Greek hêpar (ἧπαρ), meaning ""liver"", and the suffix -itis (-ῖτις), meaning ""inflammation"" (c. 1727).