Chapter 1- Introduction to Castro Part 1
... Goals for Course • Learn nature of marine environment • Learn diversity of marine organisms • Learn ecosystems • Guide to issues in human-marine interactions • Provide info that can inform policy decisions ...
... Goals for Course • Learn nature of marine environment • Learn diversity of marine organisms • Learn ecosystems • Guide to issues in human-marine interactions • Provide info that can inform policy decisions ...
Vocabulary - USF College of Marine Science
... Species-a group of closely related organisms that can interbreed Stakeholder-one who has a share or interest, as in an enterprise Stipe-part of the kelp similar to the stem of a plant Submersible-a manned or unmanned underwater vehicle used for scientific research and military operations Substrate-s ...
... Species-a group of closely related organisms that can interbreed Stakeholder-one who has a share or interest, as in an enterprise Stipe-part of the kelp similar to the stem of a plant Submersible-a manned or unmanned underwater vehicle used for scientific research and military operations Substrate-s ...
Marine Ecosystems Vocabulary
... A water environment, from pond to ocean, in which plants and animals interact with the chemical and physical features of the environment. They contain a large diversity of organisms and include oceans, salt marshes, estuaries, lagoons, mangroves and coral reefs ...
... A water environment, from pond to ocean, in which plants and animals interact with the chemical and physical features of the environment. They contain a large diversity of organisms and include oceans, salt marshes, estuaries, lagoons, mangroves and coral reefs ...
Marine Ecology 1a
... is high in the surface mixed layer O2 decreases to a minimum at base of thermocline O2 then steadily increases with depth – Why? ...
... is high in the surface mixed layer O2 decreases to a minimum at base of thermocline O2 then steadily increases with depth – Why? ...
Lecture 5. Biology A. Taxonomy and Diversity The largest
... us is the Cladocerans which includes Daphnia, Bosmina and the Great Lakes invader, Bythotrphes. (3) copepods: small crustaceans (lobster and shrimp relatives) ranging in size from 1000 – 2000 m (1 – 2 mm). there are 10,000 species of copepods. Three orders illustrate characteristic copepod body sha ...
... us is the Cladocerans which includes Daphnia, Bosmina and the Great Lakes invader, Bythotrphes. (3) copepods: small crustaceans (lobster and shrimp relatives) ranging in size from 1000 – 2000 m (1 – 2 mm). there are 10,000 species of copepods. Three orders illustrate characteristic copepod body sha ...
Basics of biology part 2 - Jocha
... b) Explain the diffusion mechanism. What types of molecules is used for? c) Explain the osmosis mechanism. What types of molecules is used for? d) What is the source of energy that powers active transport? Why is this energy needed? What else is needed for this mechanism to work? 4. Aquatic animals ...
... b) Explain the diffusion mechanism. What types of molecules is used for? c) Explain the osmosis mechanism. What types of molecules is used for? d) What is the source of energy that powers active transport? Why is this energy needed? What else is needed for this mechanism to work? 4. Aquatic animals ...
Marine Biology
... HMS Beagle and Charles Darwin • HMS Beagle: (Her Majesty’s Ship). 5 year expedition in which Charles Darwin collected a variety of organisms, some marine and formulate his theory on origin of species by means of natural selection. ...
... HMS Beagle and Charles Darwin • HMS Beagle: (Her Majesty’s Ship). 5 year expedition in which Charles Darwin collected a variety of organisms, some marine and formulate his theory on origin of species by means of natural selection. ...
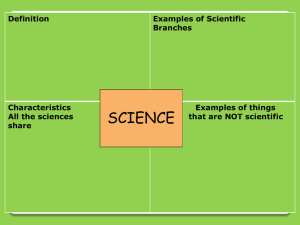
Notes #1 Nature of Science / Branches of Biology power point
... by which genetic information is passed from parents to offspring (Genes and heredity) ...
... by which genetic information is passed from parents to offspring (Genes and heredity) ...
Marine Ecosystems Test - Easy Peasy All-in
... A(n) _____ eats both plants and animals. While a(n) ______ eats only plants. (2) ...
... A(n) _____ eats both plants and animals. While a(n) ______ eats only plants. (2) ...