Institute of Marine Science
... The Institute of Marine Science conducts marine science studies in the world’s oceans, with special emphasis on Arctic and Pacific sub-Arctic waters. The faculty provide expertise in chemical, geological and physical oceanography and marine biology. Instruction is carried out through a minor in mari ...
... The Institute of Marine Science conducts marine science studies in the world’s oceans, with special emphasis on Arctic and Pacific sub-Arctic waters. The faculty provide expertise in chemical, geological and physical oceanography and marine biology. Instruction is carried out through a minor in mari ...
Bahamas - Campbell Scientific
... Most marine organisms live and grow in open systems in which ocean currents link mangrove forests, sea grass beds, coral reefs, and open oceans in an interconnected system of marine habitats. The queen conch, spiny lobster and Nassau grouper move among these habitats during their life cycles, hatchi ...
... Most marine organisms live and grow in open systems in which ocean currents link mangrove forests, sea grass beds, coral reefs, and open oceans in an interconnected system of marine habitats. The queen conch, spiny lobster and Nassau grouper move among these habitats during their life cycles, hatchi ...
Document
... Coral animals live as solitary or colonial forms and secrete a hard external skeleton of calcium carbonate. Each polyp generation builds on the skeletal remains of earlier generations to form skeletons that we call coral. ...
... Coral animals live as solitary or colonial forms and secrete a hard external skeleton of calcium carbonate. Each polyp generation builds on the skeletal remains of earlier generations to form skeletons that we call coral. ...
Oceanography Final Study Guide
... 20. What ships were built just for marine science work? 21. What did submersibles and self-contained diving contribute to the study of the ocean? 22. What types of submersibles have been used for underwater research? 23. What are the advantages and disadvantages of submersibles compared to scuba? 24 ...
... 20. What ships were built just for marine science work? 21. What did submersibles and self-contained diving contribute to the study of the ocean? 22. What types of submersibles have been used for underwater research? 23. What are the advantages and disadvantages of submersibles compared to scuba? 24 ...
Feature Summary
... fleshy macroalgae were dominant in many of the healthy reefs of the region, often forming expansive meadows spanning acres and serving as critical habitats for numerous invertebrates and juvenile fishes. Macroalgae occupied as much as or even more surface area than live reef corals in 46% of the sit ...
... fleshy macroalgae were dominant in many of the healthy reefs of the region, often forming expansive meadows spanning acres and serving as critical habitats for numerous invertebrates and juvenile fishes. Macroalgae occupied as much as or even more surface area than live reef corals in 46% of the sit ...
Virus and Heterotrophic Microplankton
... prokaryotes, although this has not been firmly established yet. Prokaryotes are divided into two major groups, Bacteria and Archaea. Most of the oceanic prokaryotes are not yet culturable, thus their metabolic pathways are largely unknown. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that most of the marine Bacte ...
... prokaryotes, although this has not been firmly established yet. Prokaryotes are divided into two major groups, Bacteria and Archaea. Most of the oceanic prokaryotes are not yet culturable, thus their metabolic pathways are largely unknown. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that most of the marine Bacte ...
North Atlantic coastal ecosystems at threat due to climate change
... Marine Biological Association as part of the UK Ocean Acidification Research Programme. It involved more than 20 international partners including Plymouth University, the Marine Biological Association of the UK and the Natural History Museum, and has been published in the scientific journal Ecology ...
... Marine Biological Association as part of the UK Ocean Acidification Research Programme. It involved more than 20 international partners including Plymouth University, the Marine Biological Association of the UK and the Natural History Museum, and has been published in the scientific journal Ecology ...
Marine pollution A case study of oceanic pollution and how it affects
... ton of krill”.3 Biosphere is the circle of life that includes all living things in the air, land and water. The biosphere includes biotic factors such as living plants and animals it also includes abiotic (non-living) factors such as soil, water, temperature, light and salinity. Together they functi ...
... ton of krill”.3 Biosphere is the circle of life that includes all living things in the air, land and water. The biosphere includes biotic factors such as living plants and animals it also includes abiotic (non-living) factors such as soil, water, temperature, light and salinity. Together they functi ...
Guilini Katja and Ann Vanreusel ECOLOGY OF DIFFERENT DEEP-SEA ENVIRONMENTS
... Photoautotrophs fix carbon dioxide and assimilate inorganic nutrients in the euphotic ocean layer. 10-30% of the converted carbon sinks out of the surface waters, either directly as organic particles or indirectly after being eaten by marine animals. This material undergoes microbial degradation on ...
... Photoautotrophs fix carbon dioxide and assimilate inorganic nutrients in the euphotic ocean layer. 10-30% of the converted carbon sinks out of the surface waters, either directly as organic particles or indirectly after being eaten by marine animals. This material undergoes microbial degradation on ...
Chapter 1 - Hatboro-Horsham School District
... • Beginnings of modern marine science – Challenger expedition exploring world’s oceans • 4,700 new species collected and described • significance of plankton receives attention marine studies in the United States • expeditions of Alexander Agassiz • funding of the first marine biology laboratory: An ...
... • Beginnings of modern marine science – Challenger expedition exploring world’s oceans • 4,700 new species collected and described • significance of plankton receives attention marine studies in the United States • expeditions of Alexander Agassiz • funding of the first marine biology laboratory: An ...
File
... continental shelf, which extends out about 300 km. • This zone contains the nutrients carried into oceans and rivers. • This zone is shallow so therefore light reaches all the way to the ocean floor. • Organisms such as algae, fish, mussels, crabs, barnacles, oysters, worms, and sea cucumbers live h ...
... continental shelf, which extends out about 300 km. • This zone contains the nutrients carried into oceans and rivers. • This zone is shallow so therefore light reaches all the way to the ocean floor. • Organisms such as algae, fish, mussels, crabs, barnacles, oysters, worms, and sea cucumbers live h ...
Chapter 23 Paleozoic, Mesozoic, & Cenozoic Eras
... • During Carbonifierous Period southeastern Laurentia collided with Gondwana – Gondwana = large landmass that eventually ...
... • During Carbonifierous Period southeastern Laurentia collided with Gondwana – Gondwana = large landmass that eventually ...
Document
... Most aquatic species have gills with thin, feathery extensions that have an extensive surface area in contact with water. For example, insects have tracheal systems, branched air ducts leading into the interior from pores in the cuticle. Evidence shows that arthropods diverged early in their histo ...
... Most aquatic species have gills with thin, feathery extensions that have an extensive surface area in contact with water. For example, insects have tracheal systems, branched air ducts leading into the interior from pores in the cuticle. Evidence shows that arthropods diverged early in their histo ...
Ch16ReadingStudyGuide
... *microscopic ___________________constitute the base of the marine food __________ in the pelagic zone *____________________found in the uppermost reaches of ocean waters are billions and billions of these tiny photosynthetic ____________, protists, and _____________________; _______________________, ...
... *microscopic ___________________constitute the base of the marine food __________ in the pelagic zone *____________________found in the uppermost reaches of ocean waters are billions and billions of these tiny photosynthetic ____________, protists, and _____________________; _______________________, ...
Diversity Lab Presentation
... Mushrooms, molds, and other types of fungi are the most abundant saprophytes. Certain types of bacteria, some seed plants, and some orchids are also saprophytes. Saprophytes produce enzymes that break down organic matter into absorbable nutrients. Most saprophytic seed plants derive their food in co ...
... Mushrooms, molds, and other types of fungi are the most abundant saprophytes. Certain types of bacteria, some seed plants, and some orchids are also saprophytes. Saprophytes produce enzymes that break down organic matter into absorbable nutrients. Most saprophytic seed plants derive their food in co ...
Animal Diversity Background
... Background: Arthropods are by far the most numerous and diverse of all animals, with more than 1 million known species. Marine, freshwater, or terrestrial forms are found in every conceivable habitat due to their high degree of evolutionarily adaptability and their great mobility, including for some ...
... Background: Arthropods are by far the most numerous and diverse of all animals, with more than 1 million known species. Marine, freshwater, or terrestrial forms are found in every conceivable habitat due to their high degree of evolutionarily adaptability and their great mobility, including for some ...
DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS
... The Animal Kingdom is divided in several phyla mainly on the basis of the cell organisation, symmetry, presence or absence of notochord and body cavity. Animals are arranged progressively from simple single-celled protozoans to highly complex mammals. Given below are some of the main characteristic ...
... The Animal Kingdom is divided in several phyla mainly on the basis of the cell organisation, symmetry, presence or absence of notochord and body cavity. Animals are arranged progressively from simple single-celled protozoans to highly complex mammals. Given below are some of the main characteristic ...
Public Comments on the U.S. Commission on Ocean Policy’s Preliminary Report
... decade. While we find the information in Chapter 18 of the Commission's Preliminary Report "Reducing Marine Debris," to be extremely valuable, we believe the most significant component of marine debris has been completely overlooked. Both pre and post-consumer plastic particulates in our oceans outw ...
... decade. While we find the information in Chapter 18 of the Commission's Preliminary Report "Reducing Marine Debris," to be extremely valuable, we believe the most significant component of marine debris has been completely overlooked. Both pre and post-consumer plastic particulates in our oceans outw ...
Evolution of bilateral symmetry
... horny material that is rich in protein – the inner layer of the shell consists of pearly material that is used as mother-of-pearl • pearls are formed in clams and oysters when a foreign object becomes lodged between the mantle and the inner shell • the mantle coats the foreign object with layer upon ...
... horny material that is rich in protein – the inner layer of the shell consists of pearly material that is used as mother-of-pearl • pearls are formed in clams and oysters when a foreign object becomes lodged between the mantle and the inner shell • the mantle coats the foreign object with layer upon ...
Binomial Nomenclature- system of assigning 2 names to every species
... Virus: Not a living cell, but rather a protein coat (called a capsid) surrounding genetic material Genetic material can be DNA or RNA. Viruses infect host cells in 2 ways: Lytic cycle - virus injects genes, cell reads genes and follows directions which tell it to make new viruses, viruses leave the ...
... Virus: Not a living cell, but rather a protein coat (called a capsid) surrounding genetic material Genetic material can be DNA or RNA. Viruses infect host cells in 2 ways: Lytic cycle - virus injects genes, cell reads genes and follows directions which tell it to make new viruses, viruses leave the ...
Southeast Asia`s Seas:global treasures of biodiversity—in peril
... Overfishing is also the most pervasive threat to reef health, putting 64% of the Southeast Asia’s reefs at risk. Although some remote reefs remain in pristine condition, destructive fishing practices are now threatening many of them. Climate Change: Altering our Oceans Carbon emissions on land are ...
... Overfishing is also the most pervasive threat to reef health, putting 64% of the Southeast Asia’s reefs at risk. Although some remote reefs remain in pristine condition, destructive fishing practices are now threatening many of them. Climate Change: Altering our Oceans Carbon emissions on land are ...
Precambrian Marine Microbes
... Objectives: 1. Know the dates of the Precambrian time period 2. Understand the ecological role of the primary producers of the Precambrian. 3. Understand how the marine organisms of the Precambrian changed the physical aspects of our planet. ...
... Objectives: 1. Know the dates of the Precambrian time period 2. Understand the ecological role of the primary producers of the Precambrian. 3. Understand how the marine organisms of the Precambrian changed the physical aspects of our planet. ...
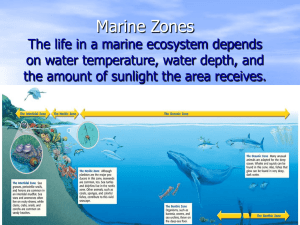
Marine Zones The life in a marine ecosystem depends on water
... deepest parts of the benthic zone do not get any sunlight. They are also very cold. Animals, such as fishes, worms, and crabs, have special adaptations to the deep, dark water. Many of these organisms get food by eating material that sinks from above. Some organisms, such as bacteria, get energy fro ...
... deepest parts of the benthic zone do not get any sunlight. They are also very cold. Animals, such as fishes, worms, and crabs, have special adaptations to the deep, dark water. Many of these organisms get food by eating material that sinks from above. Some organisms, such as bacteria, get energy fro ...