Immune System - Iowa State University
... 10) During fever, your liver and spleen sequester ________and________. This inhibits the growth of ____________________. 11) Humoral immunity involves the production of___________________. 12)___ _________ __________________________________proteins are the molecules on your macrophages are used to ...
... 10) During fever, your liver and spleen sequester ________and________. This inhibits the growth of ____________________. 11) Humoral immunity involves the production of___________________. 12)___ _________ __________________________________proteins are the molecules on your macrophages are used to ...
The Characterization of Myeloid Cell Subsets in Innate and Adaptive
... subsets is still unclear. Furthermore, innate immune responses are not defined well compared to adaptive immune response against Listeria. In particular, immunity in secondary lymphoid organ such as lymph node (LN), there are much more complicated network among immune cells. Therefore I focused on t ...
... subsets is still unclear. Furthermore, innate immune responses are not defined well compared to adaptive immune response against Listeria. In particular, immunity in secondary lymphoid organ such as lymph node (LN), there are much more complicated network among immune cells. Therefore I focused on t ...
Assignment I
... 8. What are T cell and B cell receptors? Draw a schematic diagram of T cell receptor. 9. Explain the positive and negative selection of lymphocyte. 10. What are co-stimulatory molecules? Explain their role in T cell activation. 11. Discuss the CD40-CD40L interaction during T cell activation and diff ...
... 8. What are T cell and B cell receptors? Draw a schematic diagram of T cell receptor. 9. Explain the positive and negative selection of lymphocyte. 10. What are co-stimulatory molecules? Explain their role in T cell activation. 11. Discuss the CD40-CD40L interaction during T cell activation and diff ...
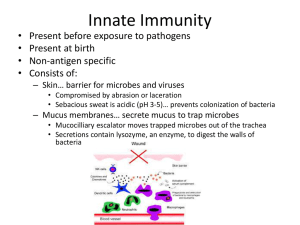
Innate Immunity - Santa Susana High School
... – Neutorphils… 60-70% of all WBCs » Attracted to infection » Sacrifice themselves after phagocytosis – Macrophages… ~5% (developed from monocytes) » Attack microbes trapped in the lymph system and various other organs – Eosinophils… active against multicellular invaders » Inject enzymes to damage or ...
... – Neutorphils… 60-70% of all WBCs » Attracted to infection » Sacrifice themselves after phagocytosis – Macrophages… ~5% (developed from monocytes) » Attack microbes trapped in the lymph system and various other organs – Eosinophils… active against multicellular invaders » Inject enzymes to damage or ...
Human Defence System
... Name two types of lymphocyte and state a role of each when viruses or other micro-organisms enter the blood. “Immunity that results from vaccination is effectively the same as the immunity that develops following an infection". Do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. ...
... Name two types of lymphocyte and state a role of each when viruses or other micro-organisms enter the blood. “Immunity that results from vaccination is effectively the same as the immunity that develops following an infection". Do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. ...
Innate Immunity and Glycobiology
... A postdoctoral fellow position is available in the Yan lab in the Department of Immunology to study molecular mechanisms of immune disorders with glycobiology defects. Research in the Yan lab covers several aspects of innate immunity including viral and bacterial evasion of innate immunity, monogeni ...
... A postdoctoral fellow position is available in the Yan lab in the Department of Immunology to study molecular mechanisms of immune disorders with glycobiology defects. Research in the Yan lab covers several aspects of innate immunity including viral and bacterial evasion of innate immunity, monogeni ...
Chapter 21 - Fundamentals of Microbiology
... d. Identify the types of T- and B-cell receptors, and assess their importance to antigen recognition. e. Explain how the clonal selection activates only those B and T cells that recognize “nonself” antigens or epitopes. f. Discuss the cellular origins of the immune system cells in the human body. g. ...
... d. Identify the types of T- and B-cell receptors, and assess their importance to antigen recognition. e. Explain how the clonal selection activates only those B and T cells that recognize “nonself” antigens or epitopes. f. Discuss the cellular origins of the immune system cells in the human body. g. ...
Immune System Quiz
... 7. What immune system disorder results from the immune system attacking loosing its ability to screen new lymphocytes for self-compatibility? A. type I diabetes B. arthritis C. multiple sclerosis D. lupus Short Answer: 8. What is the primary difference between antibodies and antigen receptors? antib ...
... 7. What immune system disorder results from the immune system attacking loosing its ability to screen new lymphocytes for self-compatibility? A. type I diabetes B. arthritis C. multiple sclerosis D. lupus Short Answer: 8. What is the primary difference between antibodies and antigen receptors? antib ...
Immune System Definition
... • Antibody production by immune cells • Antibodies are made in response to an antigen (foreign proteins) found on a foreign substance or invading organism • T (from thymus) and B (from bone marrow) cells involved in antibody production • Certain T cells activate some B cells to produce antibodies • ...
... • Antibody production by immune cells • Antibodies are made in response to an antigen (foreign proteins) found on a foreign substance or invading organism • T (from thymus) and B (from bone marrow) cells involved in antibody production • Certain T cells activate some B cells to produce antibodies • ...
Organism Physiology Immunity
... To Think About: What is the purpose of the immune system? How does the immune system function? Why do animals have a more developed immune system than other animals? 1st Learn About: Use text and prezi presentation Immunity to answer the following questions in your BILL. Ch. 43 The Immune System: Ca ...
... To Think About: What is the purpose of the immune system? How does the immune system function? Why do animals have a more developed immune system than other animals? 1st Learn About: Use text and prezi presentation Immunity to answer the following questions in your BILL. Ch. 43 The Immune System: Ca ...
دانلود
... • Type I(IFN-α,IFN-β) all immune cells and fibroblasts as an anti virus • Type II(IFN- ) T cells as a immunoregulator ...
... • Type I(IFN-α,IFN-β) all immune cells and fibroblasts as an anti virus • Type II(IFN- ) T cells as a immunoregulator ...
1 State the significance of interspecific hybridization. 1 2 What is the
... Name the different species of malarial parasite. Which of these does cause malignant tumors? What kind of immunity active or passive, is produced by vaccination? Name the disease against which BCG is given? Discuss the role of lymphoid organs in the immune response. Explain 2 different types giving ...
... Name the different species of malarial parasite. Which of these does cause malignant tumors? What kind of immunity active or passive, is produced by vaccination? Name the disease against which BCG is given? Discuss the role of lymphoid organs in the immune response. Explain 2 different types giving ...
Innate Immunity: From Flies to Humans
... Dr. Hoffmann’s research has focused on the development and the defence reactions of insects. Since 1990, he and his laboratory have explored the potent antimicrobial mechanisms of Drosophila as a paradigm for innate immune defences. In particular, the group is credited with having unravelled the rol ...
... Dr. Hoffmann’s research has focused on the development and the defence reactions of insects. Since 1990, he and his laboratory have explored the potent antimicrobial mechanisms of Drosophila as a paradigm for innate immune defences. In particular, the group is credited with having unravelled the rol ...
Document
... Protozoa: Chagas disease, Human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness), Leishmaniases. Helminth: Cysticercosis/Taeniasis, Dracunculiasis (guinea-worm disease), Echinococcosis, Foodborne trematodiases, Lymphatic filariasis, Onchocerciasis , Schistosomiasis, Soil-transmitted helminthiases. Bacter ...
... Protozoa: Chagas disease, Human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness), Leishmaniases. Helminth: Cysticercosis/Taeniasis, Dracunculiasis (guinea-worm disease), Echinococcosis, Foodborne trematodiases, Lymphatic filariasis, Onchocerciasis , Schistosomiasis, Soil-transmitted helminthiases. Bacter ...
31.4 Immunity and Technology
... 31.4 Immunity and Technology • Antiseptics kill pathogens outside of the body. – do not target specific pathogens – examples include vinegar and soap • Antibiotics kill pathogens inside the body. – target one specific bacterium or fungus – not effective against viruses ...
... 31.4 Immunity and Technology • Antiseptics kill pathogens outside of the body. – do not target specific pathogens – examples include vinegar and soap • Antibiotics kill pathogens inside the body. – target one specific bacterium or fungus – not effective against viruses ...
SG9 Immune Response
... Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Differentiate between immunity and nonspecific resistance. Contrast the four types of acquired immunity. Define antigen. Explain the function of antibodies and describe their structural and chemical characteristics. Name the function of B cells. De ...
... Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Differentiate between immunity and nonspecific resistance. Contrast the four types of acquired immunity. Define antigen. Explain the function of antibodies and describe their structural and chemical characteristics. Name the function of B cells. De ...
Microbes and diseases are risks. Children are not.
... abolish philosophical exemption from vaccines for all Vermont schoolchildren, both public and private. If passed, parents would be stripped of the right to informed consent for an invasive medical procedure on their children. Vaccines have proven risks of serious reactions, including death, which ar ...
... abolish philosophical exemption from vaccines for all Vermont schoolchildren, both public and private. If passed, parents would be stripped of the right to informed consent for an invasive medical procedure on their children. Vaccines have proven risks of serious reactions, including death, which ar ...
click - Uplift Education
... between the naïve lymphocyte and an antigen presenting cell. The _______________________ can be cytokines (such as IL-2 or IL-4) or may be interaction with a TH. 21. When B lymphocytes are activated, they divide many times. Most of the daughter cells will become _____________________________ that pr ...
... between the naïve lymphocyte and an antigen presenting cell. The _______________________ can be cytokines (such as IL-2 or IL-4) or may be interaction with a TH. 21. When B lymphocytes are activated, they divide many times. Most of the daughter cells will become _____________________________ that pr ...
The Immune System
... Transmission during incubation periods Carriers Animals to humans (rabies, Lyme disease) Soil and Water ...
... Transmission during incubation periods Carriers Animals to humans (rabies, Lyme disease) Soil and Water ...
27.4 Social Behavior
... • Social behaviors evolve when the benefits of group living outweigh its costs. – benefits: improved foraging, reproductive assistance, reduced chance of predation – costs: increased visibility, competition, disease contraction ...
... • Social behaviors evolve when the benefits of group living outweigh its costs. – benefits: improved foraging, reproductive assistance, reduced chance of predation – costs: increased visibility, competition, disease contraction ...