Lab 1
... Group: Cyanobacteria The cyanobacteria are aerobic, photoautotrophic bacteria. They were once called blue-green algae but they are made up of prokaryotic cellas and are not a true algae. They have unicellular, colonial and filamentous forms. They contain the pigment phycocyanin which give them their ...
... Group: Cyanobacteria The cyanobacteria are aerobic, photoautotrophic bacteria. They were once called blue-green algae but they are made up of prokaryotic cellas and are not a true algae. They have unicellular, colonial and filamentous forms. They contain the pigment phycocyanin which give them their ...
sample
... 11. Taxis refers to the ability of many bacteria to move toward favorable conditions (positive taxis) or away from unfavorable conditions (negative taxis). Only motile bacteria are capable of taxis. In an almost all cases, motile bacteria rely on flagella. 12. Almost all bacteria are protected from ...
... 11. Taxis refers to the ability of many bacteria to move toward favorable conditions (positive taxis) or away from unfavorable conditions (negative taxis). Only motile bacteria are capable of taxis. In an almost all cases, motile bacteria rely on flagella. 12. Almost all bacteria are protected from ...
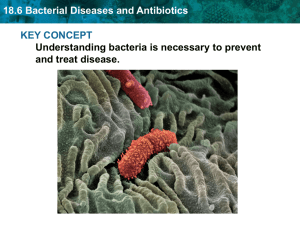
18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics KEY CONCEPT
... • Antibiotics may stop bacterial cell wall formation. ...
... • Antibiotics may stop bacterial cell wall formation. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... - Adds to theory that chloroplasts may have originated from cells living within the cells of other organisms. ...
... - Adds to theory that chloroplasts may have originated from cells living within the cells of other organisms. ...
Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses
... thick internal wall enclosing DNA and portion of cytoplasm. Can remain dormant for months or years ...
... thick internal wall enclosing DNA and portion of cytoplasm. Can remain dormant for months or years ...
ch17
... has relatively little protein associated with it. Replication and translation is similar to eukaryotes. Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules found in bacteria. ...
... has relatively little protein associated with it. Replication and translation is similar to eukaryotes. Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules found in bacteria. ...
Module 8 – Diversity of Microbial World
... requirements for growth characters like carbon and nitrogen sources, cell wall constituents, general nutritional type, energy sources, optimum growth temperature, Motility. 3. Ecology:- These are taxonomically valuable because even very closely related microorganisms can differ considerably with res ...
... requirements for growth characters like carbon and nitrogen sources, cell wall constituents, general nutritional type, energy sources, optimum growth temperature, Motility. 3. Ecology:- These are taxonomically valuable because even very closely related microorganisms can differ considerably with res ...
Chapter 27 Prokaryotes
... more complex. They have a peptidoglycan layer surrounded by the plasma membrane and an outer membrane. - Gram-negative bacteria are typically more resistant to host immune defenses and antibiotics. Note that the two types of bacteria can be stained to determine which is gram-negative (pink) and gram ...
... more complex. They have a peptidoglycan layer surrounded by the plasma membrane and an outer membrane. - Gram-negative bacteria are typically more resistant to host immune defenses and antibiotics. Note that the two types of bacteria can be stained to determine which is gram-negative (pink) and gram ...
Document
... more complex. They have a peptidoglycan layer surrounded by the plasma membrane and an outer membrane. - Gram-negative bacteria are typically more resistant to host immune defenses and antibiotics. Note that the two types of bacteria can be stained to determine which is gram-negative (pink) and gram ...
... more complex. They have a peptidoglycan layer surrounded by the plasma membrane and an outer membrane. - Gram-negative bacteria are typically more resistant to host immune defenses and antibiotics. Note that the two types of bacteria can be stained to determine which is gram-negative (pink) and gram ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Bacterial Cells and Gram Staining
... 2.) Strep throat is caused by streptococcus bacteria. When you go to the doctor with a sore throat, they swab your throat and have you wait for the results of the "culture" to see if you have strep throat. What does the "culture" look like if you have strep throat? 3.) Some bacterial infections are ...
... 2.) Strep throat is caused by streptococcus bacteria. When you go to the doctor with a sore throat, they swab your throat and have you wait for the results of the "culture" to see if you have strep throat. What does the "culture" look like if you have strep throat? 3.) Some bacterial infections are ...
Microbiology Laboratories Report on Training Visit
... The principle of the method is the isolation (extraction) of microorganisms from the environment, the dilution of MO in appropriate medium and smears the cell suspension on surface of Petri dishes. Microorganisms growing on agar (Petri dishes, Petri plates) media form masses of cells called colonies ...
... The principle of the method is the isolation (extraction) of microorganisms from the environment, the dilution of MO in appropriate medium and smears the cell suspension on surface of Petri dishes. Microorganisms growing on agar (Petri dishes, Petri plates) media form masses of cells called colonies ...
food safety multimedia training hot words and definitions
... the food poisoning caused by toxins excreted by these microorganisms. They grow fast in moist foods high in protein, and are commonly spread by infected workers and workers with poor hygiene habits. The improper holding and storing of foods enables staph to grow to hazardous levels. ...
... the food poisoning caused by toxins excreted by these microorganisms. They grow fast in moist foods high in protein, and are commonly spread by infected workers and workers with poor hygiene habits. The improper holding and storing of foods enables staph to grow to hazardous levels. ...
Slide - Smith Lab
... • Human neutrophil peptides 1-3 (alpha-defensins) are found in human tears at 0.2-1µg/ml • hBD-2 made by ocular epithelium – induced by LPS via TLR4 and LTA and lipoproteins through TLR2 – not detected in normal tear film • LL-37 another antimicrobial peptide was detected in ocular cells and upregul ...
... • Human neutrophil peptides 1-3 (alpha-defensins) are found in human tears at 0.2-1µg/ml • hBD-2 made by ocular epithelium – induced by LPS via TLR4 and LTA and lipoproteins through TLR2 – not detected in normal tear film • LL-37 another antimicrobial peptide was detected in ocular cells and upregul ...
Methods of Food Preservation
... 3.2. Preservation by low water activity (aw) Water activity can be reduced by partial removal of the water (drying, reverse osmosis, concentration) or by adding substances which increase the osmotic pressure of the food or media such as sugars, ethanol, glycerol, salts, etc. (Booth, 1998). The major ...
... 3.2. Preservation by low water activity (aw) Water activity can be reduced by partial removal of the water (drying, reverse osmosis, concentration) or by adding substances which increase the osmotic pressure of the food or media such as sugars, ethanol, glycerol, salts, etc. (Booth, 1998). The major ...
Bacteria: Part II
... the Great Salt Lake and the Dead Sea, These organisms use salt to generate ATP. ...
... the Great Salt Lake and the Dead Sea, These organisms use salt to generate ATP. ...
27 - GEOCITIES.ws
... THE WORLD OF PROKARYOTES They're (almost) everywhere an overview of prokaryotic life 1. Describe the many unique characteristics of prokaryotes. Explain why it might be said that prokaryotes are the most successful organisms ever to live. a. Most ancient, small, anucleate b. Only major taxon found e ...
... THE WORLD OF PROKARYOTES They're (almost) everywhere an overview of prokaryotic life 1. Describe the many unique characteristics of prokaryotes. Explain why it might be said that prokaryotes are the most successful organisms ever to live. a. Most ancient, small, anucleate b. Only major taxon found e ...
Extinction of microbes: evidence and potential consequences
... Extinction is a principle of evolution and well over 99% of the species that have ever lived have become extinct. It is often said that we lose about 1 species per day; however, this is just a guesstimate. Nevertheless, we seem at present to be living in a period of mass extinction, the 6th of its k ...
... Extinction is a principle of evolution and well over 99% of the species that have ever lived have become extinct. It is often said that we lose about 1 species per day; however, this is just a guesstimate. Nevertheless, we seem at present to be living in a period of mass extinction, the 6th of its k ...
Bacteria
... ______ 3. What two kingdoms of living things do bacteria belong to? a. Eubacteria and Archaebacteria b. Fungi and Animalia c. Archaebacteria and Fungi d. Protista and Plantae ______ 4. Eubacteria and Archaebacteria contain a. all of the forms of life on Earth. b. the oldest forms of life on Earth. c ...
... ______ 3. What two kingdoms of living things do bacteria belong to? a. Eubacteria and Archaebacteria b. Fungi and Animalia c. Archaebacteria and Fungi d. Protista and Plantae ______ 4. Eubacteria and Archaebacteria contain a. all of the forms of life on Earth. b. the oldest forms of life on Earth. c ...
When is LB used?
... Microbiology Susceptibility (MS) Domain • The MS domain is designed to store any findings related to the organisms found and submitted in MB. This will usually consist of susceptibility testing results, but can also be other organism-related findings such as extent of growth of an organism. • All c ...
... Microbiology Susceptibility (MS) Domain • The MS domain is designed to store any findings related to the organisms found and submitted in MB. This will usually consist of susceptibility testing results, but can also be other organism-related findings such as extent of growth of an organism. • All c ...
Bacteria
... microbiology, API's give accurate identification results, have extensive databases and are standardized, easy-to-use test systems. The products comprise strips that generally contain 20 miniature biochemical tests. Currently, there are 16 identification products covering almost all bacterial groups ...
... microbiology, API's give accurate identification results, have extensive databases and are standardized, easy-to-use test systems. The products comprise strips that generally contain 20 miniature biochemical tests. Currently, there are 16 identification products covering almost all bacterial groups ...
Customizable Antimicrobial Peptides Case # 1210 Overview Technology Contact
... Dr. Rickey Hicks and East Carolina University have developed a platform of novel synthetic antimicrobial peptides customized to treat a wide variety of bacterial, fungal and/or viral infections. This novel method alters the physicochemical properties of antimicrobial peptides to increase selectivity ...
... Dr. Rickey Hicks and East Carolina University have developed a platform of novel synthetic antimicrobial peptides customized to treat a wide variety of bacterial, fungal and/or viral infections. This novel method alters the physicochemical properties of antimicrobial peptides to increase selectivity ...
Module II
... We are familiar with the term “spores” from the fungi. Fungal spores are, so to speak, the seeds of the fungus, whereas bacterial spores are something very different and have absolutely nothing in common with fungal spores. Some bacteria can change into spores. Under unfavourable living conditions, ...
... We are familiar with the term “spores” from the fungi. Fungal spores are, so to speak, the seeds of the fungus, whereas bacterial spores are something very different and have absolutely nothing in common with fungal spores. Some bacteria can change into spores. Under unfavourable living conditions, ...
Bacterial Classification, Structure and Function
... Molecular subtyping: Sometimes it is necessary to determine whether strains from the same species are the same or different. For example if there is an outbreak of infections that appear due to the same bacterial species, the hospital epidemiologist will want to know if all of the infections are due ...
... Molecular subtyping: Sometimes it is necessary to determine whether strains from the same species are the same or different. For example if there is an outbreak of infections that appear due to the same bacterial species, the hospital epidemiologist will want to know if all of the infections are due ...
Bacterial Classification, Structure and Function
... The classification of bacteria serves a variety of different functions. Because of this variety, bacteria may be grouped using many different typing schemes. The critical feature for all these classification systems is an organism identified by one individual (scientist, clinician, epidemiologist), ...
... The classification of bacteria serves a variety of different functions. Because of this variety, bacteria may be grouped using many different typing schemes. The critical feature for all these classification systems is an organism identified by one individual (scientist, clinician, epidemiologist), ...
Bacteria Webquest - Mansfield Legacy
... Please visit the following websites: http://www.cellsalive.com/pen.htm http://whyfiles.org/2012/bacteria-social-critters/ http://www.microbiologybytes.com/video/endospores.html 24. What is penicillin? How does it work? 25. What is a plasmid? How does this allow for antibiotic resistance? 26. How can ...
... Please visit the following websites: http://www.cellsalive.com/pen.htm http://whyfiles.org/2012/bacteria-social-critters/ http://www.microbiologybytes.com/video/endospores.html 24. What is penicillin? How does it work? 25. What is a plasmid? How does this allow for antibiotic resistance? 26. How can ...
Microorganism

A microorganism (from the Greek: μικρός, mikros, ""small"" and ὀργανισμός, organismós, ""organism"") is a microscopic living organism, which may be single celled or multicellular. The study of microorganisms is called microbiology, a subject that began with the discovery of microorganisms in 1674 by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, using a microscope of his own design.Microorganisms are very diverse and include all the bacteria and archaea and almost all the protozoa. They also include some fungi, algae, and certain animals, such as rotifers. Many macroscopic animals and plants have microscopic juvenile stages. Some microbiologists also classify viruses (and viroids) as microorganisms, but others consider these as nonliving.Microorganisms live in every part of the biosphere, including soil, hot springs, ""seven miles deep"" in the ocean, ""40 miles high"" in the atmosphere and inside rocks far down within the Earth's crust (see also endolith). Microorganisms, under certain test conditions, have been observed to thrive in the vacuum of outer space. The total amount of soil and subsurface bacterial carbon is estimated as 5 x 1017 g, or the ""weight of the United Kingdom"". The mass of prokaryote microorganisms — which includes bacteria and archaea, but not the nucleated eukaryote microorganisms — may be as much as 0.8 trillion tons of carbon (of the total biosphere mass, estimated at between 1 and 4 trillion tons). On 17 March 2013, researchers reported data that suggested microbial life forms thrive in the Mariana Trench. the deepest spot in the Earth's oceans. Other researchers reported related studies that microorganisms thrive inside rocks up to 580 m (1,900 ft; 0.36 mi) below the sea floor under 2,590 m (8,500 ft; 1.61 mi) of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States, as well as 2,400 m (7,900 ft; 1.5 mi) beneath the seabed off Japan. On 20 August 2014, scientists confirmed the existence of microorganisms living 800 m (2,600 ft; 0.50 mi) below the ice of Antarctica. According to one researcher,""You can find microbes everywhere — they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are.""Microorganisms are crucial to nutrient recycling in ecosystems as they act as decomposers. As some microorganisms can fix nitrogen, they are a vital part of the nitrogen cycle, and recent studies indicate that airborne microorganisms may play a role in precipitation and weather. Microorganisms are also exploited in biotechnology, both in traditional food and beverage preparation, and in modern technologies based on genetic engineering. A small proportion of microorganisms are pathogenic and cause disease and even death in plants and animals. Microorganisms are often referred to as microbes, but this is usually used in reference to pathogens.