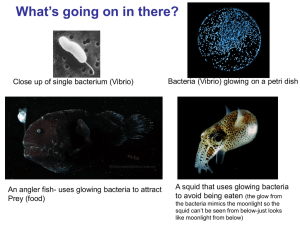
Diseases
... • Physical and chemical barrier against microbes • Moist areas have greater number of bacteria ...
... • Physical and chemical barrier against microbes • Moist areas have greater number of bacteria ...
Infection Control
... Divide into two new cells – mitosis Inactive (spore forming stage)-form spherical spores with tough outer covering for protection-cannot be harmed by disinfectants When conditions are favorable they grow and reproduce. ...
... Divide into two new cells – mitosis Inactive (spore forming stage)-form spherical spores with tough outer covering for protection-cannot be harmed by disinfectants When conditions are favorable they grow and reproduce. ...
Scientific American, February 2010, p
... Most bacteria are well-behaved companions. Indeed, if you are ever feeling lonely, remember that the trillions of microbes living in and on the average human body outnumber the human cells by a ratio of 10 to one. Of all the tens of thousands of known bacterial species, only about 100 are renegades ...
... Most bacteria are well-behaved companions. Indeed, if you are ever feeling lonely, remember that the trillions of microbes living in and on the average human body outnumber the human cells by a ratio of 10 to one. Of all the tens of thousands of known bacterial species, only about 100 are renegades ...
Bacteria and Germs
... – Pathogens – microbes that cause disease • Botulism – improperly canned foods • E. coli – improperly cooked beef • Salmonella – improperly cooked chicken ...
... – Pathogens – microbes that cause disease • Botulism – improperly canned foods • E. coli – improperly cooked beef • Salmonella – improperly cooked chicken ...
Adaptations and Traits of Organisms Final assessment
... 1. An example of a fossil is the preserved remains from a prehistoric organism that have been preserved inside rock. 2. An example of a fossil is an old, rigid unchanging person ...
... 1. An example of a fossil is the preserved remains from a prehistoric organism that have been preserved inside rock. 2. An example of a fossil is an old, rigid unchanging person ...
Homeostasis and Control Systems
... is carried from the core to the surface of the body, maintaining core temperature. Extremities can turn blue and feel cold and can even be damaged (frostbite). ...
... is carried from the core to the surface of the body, maintaining core temperature. Extremities can turn blue and feel cold and can even be damaged (frostbite). ...
Microbe Math
... 1. Ask students for examples of decay they have seen, such as food left in the refrigerator too long or a dead animal in the yard. Explain that bacteria and fungi cause most of the decay. 2. Explain that an individual bacterium is far too small to be seen by our eyes alone; most are about 1/1000 of ...
... 1. Ask students for examples of decay they have seen, such as food left in the refrigerator too long or a dead animal in the yard. Explain that bacteria and fungi cause most of the decay. 2. Explain that an individual bacterium is far too small to be seen by our eyes alone; most are about 1/1000 of ...
Active Reading Example and Exercise
... shoes. Foot and shoe cleanliness will also affect bacterial growth, since bacteria will grow at an exponential rate and be significantly worse if they're already present. Crevices created by long toenails or lots of body hair will also create extra surface area on which bacteria can proliferate. The ...
... shoes. Foot and shoe cleanliness will also affect bacterial growth, since bacteria will grow at an exponential rate and be significantly worse if they're already present. Crevices created by long toenails or lots of body hair will also create extra surface area on which bacteria can proliferate. The ...
Skin Infections - Derby GP Specialty Training Programme
... normally present on the skin. For example: Staphylococcus epidermidis and yeasts The presence of bacteria does not automatically lead to a skin infection ...
... normally present on the skin. For example: Staphylococcus epidermidis and yeasts The presence of bacteria does not automatically lead to a skin infection ...
university of cambridge
... The fee covers the cost of all meals (except the evening meal on Wednesday 7th December 2016 and lunch on Friday 9th December 2016) accommodation from Monday 5th December 2016 to Friday 9th December 2016. A wine reception on Monday evening, Walking Tour of Cambridge on the Wednesday afternoon and a ...
... The fee covers the cost of all meals (except the evening meal on Wednesday 7th December 2016 and lunch on Friday 9th December 2016) accommodation from Monday 5th December 2016 to Friday 9th December 2016. A wine reception on Monday evening, Walking Tour of Cambridge on the Wednesday afternoon and a ...
Study Guide Answers
... the sun somewhat protective? Exposure to UV radiation causes melanocytes to increase melanin production. Melanin covers the nuclei of cells and absorbs UV radiation. 22.When a person has severe burns, what are the two most life-threatening concerns? Fluid loss and infection 23.Which part of the skin ...
... the sun somewhat protective? Exposure to UV radiation causes melanocytes to increase melanin production. Melanin covers the nuclei of cells and absorbs UV radiation. 22.When a person has severe burns, what are the two most life-threatening concerns? Fluid loss and infection 23.Which part of the skin ...
Bacterial Infections
... Bacteria as pathogens Some bacteria which gain their energy from other organisms can act as pathogens The negative effects on the host are generally either from toxins produced by the bacteria or from chemicals released by damaged cells ...
... Bacteria as pathogens Some bacteria which gain their energy from other organisms can act as pathogens The negative effects on the host are generally either from toxins produced by the bacteria or from chemicals released by damaged cells ...
Immune System-
... Phagocytes move to lungs and engulf bacteria Bacteria survive and breed inside phagocyte Tubercles form in lungs—small, rounded swellings containing infected phagocytes First infection is usually not severe Re-infection results in chronic TB which gradually destroys the lung tissue Fever, loss of ap ...
... Phagocytes move to lungs and engulf bacteria Bacteria survive and breed inside phagocyte Tubercles form in lungs—small, rounded swellings containing infected phagocytes First infection is usually not severe Re-infection results in chronic TB which gradually destroys the lung tissue Fever, loss of ap ...
Chapter 6
... therefore can be a source of infection of others. ● It is most frequently used in reference to a person with an asymptomatic infection or to someone who has recovered from a disease but continues to carry the organism and may shed it for a long period. ...
... therefore can be a source of infection of others. ● It is most frequently used in reference to a person with an asymptomatic infection or to someone who has recovered from a disease but continues to carry the organism and may shed it for a long period. ...
tutorial 1 File
... 2. Living organisms are classified into distinct groups. Compare the traditional classification system with the modern classification system that led to the formation of the three domain system. 3. What are the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? ...
... 2. Living organisms are classified into distinct groups. Compare the traditional classification system with the modern classification system that led to the formation of the three domain system. 3. What are the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? ...
Gram-Negative Bacteria - Mrs. Yu`s Science Classes
... Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting peptidoglycan, which is present in a thick layer in Gram-positive bacteria ...
... Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting peptidoglycan, which is present in a thick layer in Gram-positive bacteria ...
Label the Skin Anatomy Diagram
... hair follicle - a tube-shaped sheath that sebaceous gland - a small, sack-shaped surrounds the part of the hair that is under gland that releases oily (fatty) liquids onto the skin. It is located in the epidermis and the hair follicle (the oil lubricated and the dermis. The hair is nourished by the ...
... hair follicle - a tube-shaped sheath that sebaceous gland - a small, sack-shaped surrounds the part of the hair that is under gland that releases oily (fatty) liquids onto the skin. It is located in the epidermis and the hair follicle (the oil lubricated and the dermis. The hair is nourished by the ...
Skin flora

The skin flora, more properly referred to as the skin microbiota, are the microorganisms which reside on the skin. Most research has been upon those that reside upon the 2 square metres of human skin, cf. the human microbiome. The skin microbiome refer to their genomes.Many of them are bacteria of which there are around 1000 species upon human skin from 19 phyla. The total number of bacteria on an average human has been estimated at 1012 (1 trillion). Most are found in the superficial layers of the epidermis and the upper parts of hair follicles.Skin flora is usually non-pathogenic, and either commensal (are not harmful to their host) or mutualistic (offer a benefit). The benefits bacteria can offer include preventing transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface, either by competing for nutrients, secreting chemicals against them, or stimulating the skin's immune system. However, resident microbes can cause skin diseases and enter the blood system creating life-threatening diseases particularly in immunosuppressed people.A major nonhuman skin flora is Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a chytrid and non-hyphal zoosporic fungus that causes chytridiomycosis, an infectious disease thought to be responsible for the decline in amphibian populations.