Part 1: Mongols Part 2: Aztecs
... • They migrated to central Mexico from the northwest in the middle of the 13th Century • They had a reputation for kidnapping women and seizing land cultivated by ...
... • They migrated to central Mexico from the northwest in the middle of the 13th Century • They had a reputation for kidnapping women and seizing land cultivated by ...
Warm-up #7 What were some cultural advances
... Warm-up #7 • What were some cultural advances made by the Aztecs? • Why did the Aztec empire fall? ...
... Warm-up #7 • What were some cultural advances made by the Aztecs? • Why did the Aztec empire fall? ...
Part 1: Mongols Part 2: Aztecs
... • They migrated to central Mexico from the northwest in the middle of the 13th Century • They had a reputation for kidnapping women and seizing land cultivated by ...
... • They migrated to central Mexico from the northwest in the middle of the 13th Century • They had a reputation for kidnapping women and seizing land cultivated by ...
Latin American Civilizations
... Every Spring and Fall equinox, the sun hits the pyramid just perfectly that a snake is formed on the edge of the staircase. The head is down on the bottom of the staircase. Architects still aren’t exactly sure of how the Mayans figured out how to build this. ...
... Every Spring and Fall equinox, the sun hits the pyramid just perfectly that a snake is formed on the edge of the staircase. The head is down on the bottom of the staircase. Architects still aren’t exactly sure of how the Mayans figured out how to build this. ...
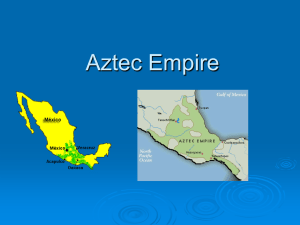
Aztec Empire
... Aztecs called themselves Mexica (meh-shee-ka) Skilled warriors, one ruler ruled over Aztec Empire. Under the leader Monteczuma they expanded to 1/3 of Mexico- Mostly in South. Population of 25 million at peak. Grew stronger through war, tribute, and trade. Tribute– The Aztecs made neighboring tribes ...
... Aztecs called themselves Mexica (meh-shee-ka) Skilled warriors, one ruler ruled over Aztec Empire. Under the leader Monteczuma they expanded to 1/3 of Mexico- Mostly in South. Population of 25 million at peak. Grew stronger through war, tribute, and trade. Tribute– The Aztecs made neighboring tribes ...
Document 1: Mayan Mathematics
... Document 9: Machu Picchu Embedded within a dramatic landscape at the meeting point between the Peruvian Andes and the Amazon Basin, the Historic Sanctuary of Machu Picchu is among the greatest artistic, architectural and land use achievements anywhere and the most significant tangible legacy of the ...
... Document 9: Machu Picchu Embedded within a dramatic landscape at the meeting point between the Peruvian Andes and the Amazon Basin, the Historic Sanctuary of Machu Picchu is among the greatest artistic, architectural and land use achievements anywhere and the most significant tangible legacy of the ...
Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, Incan PP File
... made up the noble class O Soldiers, merchants and farmers who owned land made up the Commoners O At the bottom it was the captured people who were enslaved ...
... made up the noble class O Soldiers, merchants and farmers who owned land made up the Commoners O At the bottom it was the captured people who were enslaved ...
Aztec Empire Informational Text
... travel. There were neighborhoods throughout the city. Each had its own temple, school, land, and council for government. More than 200,000 people walked about Tenochtitlan every day. Some lived in the city's neighborhoods. Others came from the countryside to the bustling3 marketplace to trade their ...
... travel. There were neighborhoods throughout the city. Each had its own temple, school, land, and council for government. More than 200,000 people walked about Tenochtitlan every day. Some lived in the city's neighborhoods. Others came from the countryside to the bustling3 marketplace to trade their ...
Michael M ppt - snoopyloveshistory
... Andes • The Incas were polytheistic-belief in many gods • They did not have written language, but had spoken language (used knots as messages) • They also practiced animal sacrifice, and on special occasions human sacrifice • The Incas were taken over by the Pizarro and the Spanish in 1531 because t ...
... Andes • The Incas were polytheistic-belief in many gods • They did not have written language, but had spoken language (used knots as messages) • They also practiced animal sacrifice, and on special occasions human sacrifice • The Incas were taken over by the Pizarro and the Spanish in 1531 because t ...
Mesoamerican Civilizations
... divided into 18 months with 20 days each with 5 extra days at the end. A Lunar calendar and a Calendar based on the movement of the Planet Venus. This was a sacred calendar with 260 days and 13 weeks of 20 days each. The Mayan calendar says our present world was created in 3114 B.C. and the current ...
... divided into 18 months with 20 days each with 5 extra days at the end. A Lunar calendar and a Calendar based on the movement of the Planet Venus. This was a sacred calendar with 260 days and 13 weeks of 20 days each. The Mayan calendar says our present world was created in 3114 B.C. and the current ...
Slide 1
... • This calendar defines a year of 18 months, each of 20 days, and five extra days, 365 days in total. These extra days were considered unlucky and so very little was done on them. Each year had a name and number combination as did the days in the The Tonalpohualli but this time there were only 52 su ...
... • This calendar defines a year of 18 months, each of 20 days, and five extra days, 365 days in total. These extra days were considered unlucky and so very little was done on them. Each year had a name and number combination as did the days in the The Tonalpohualli but this time there were only 52 su ...
Native American Civilizations Presentation
... marshy Lake Texcoco, was drained and cultivated by the Aztecs and became the thriving civilization upon whose remains the modern cities of Mexico are now built. ...
... marshy Lake Texcoco, was drained and cultivated by the Aztecs and became the thriving civilization upon whose remains the modern cities of Mexico are now built. ...
Native American Civilizations Presentation
... marshy Lake Texcoco, was drained and cultivated by the Aztecs and became the thriving civilization upon whose remains the modern cities of Mexico are now built. ...
... marshy Lake Texcoco, was drained and cultivated by the Aztecs and became the thriving civilization upon whose remains the modern cities of Mexico are now built. ...
Mesoamerica Study Guide - local
... _____ 22. This was devastating to the Aztecs. The Spanish unknowingly brought it with them, which helped them conquer the Aztecs. _____ 23. When the Spanish leader arrived, the Aztecs believed that he was this _____ 24. The Aztec capital city was built on one of these ...
... _____ 22. This was devastating to the Aztecs. The Spanish unknowingly brought it with them, which helped them conquer the Aztecs. _____ 23. When the Spanish leader arrived, the Aztecs believed that he was this _____ 24. The Aztec capital city was built on one of these ...
Name Class Date People first came to the Americas from Asia
... 900, the Maya abandoned most of their cities, possibly because of frequent warfare or over-farming. Aztec civilization began in the Valley of Mexico. The Aztecs founded Tenochtitlán, their capital city, in A.D. 1325. Because it was located on an island in a lake, they found ingenious ways to create ...
... 900, the Maya abandoned most of their cities, possibly because of frequent warfare or over-farming. Aztec civilization began in the Valley of Mexico. The Aztecs founded Tenochtitlán, their capital city, in A.D. 1325. Because it was located on an island in a lake, they found ingenious ways to create ...
Lsn 21 Mongols and A..
... • They migrated to central Mexico from the northwest in the middle of the 13th Century • They had a reputation for kidnapping women and seizing land cultivated by ...
... • They migrated to central Mexico from the northwest in the middle of the 13th Century • They had a reputation for kidnapping women and seizing land cultivated by ...
HIS101Lsn20Mongolsan..
... • They migrated to central Mexico from the northwest in the middle of the 13th Century • They had a reputation for kidnapping women and seizing land cultivated by ...
... • They migrated to central Mexico from the northwest in the middle of the 13th Century • They had a reputation for kidnapping women and seizing land cultivated by ...
Aztec sacrifice - Mrs. Bloom Social Studies
... The overwhelming majority of the sacrificed captives apparently were consumed. A principal -- and sometimes only -- objective of Aztec war expeditions was to capture prisoners for sacrifice. While some might be sacrificed and eaten on the field of battle, most were taken to home communities or to t ...
... The overwhelming majority of the sacrificed captives apparently were consumed. A principal -- and sometimes only -- objective of Aztec war expeditions was to capture prisoners for sacrifice. While some might be sacrificed and eaten on the field of battle, most were taken to home communities or to t ...
Los Aztecas - Espanol THS
... The reasons for the human sacrifices are still not clear. Many historians believe that the Aztec used these human sacrifices to frighten their enemies. Most of the people sacrificed by the Aztec were captives of war. The Aztec believed that sacrificing an enemy warrior especially pleased their gods ...
... The reasons for the human sacrifices are still not clear. Many historians believe that the Aztec used these human sacrifices to frighten their enemies. Most of the people sacrificed by the Aztec were captives of war. The Aztec believed that sacrificing an enemy warrior especially pleased their gods ...
Wld - Maples Elementary School
... 10. What are three advantages of the Valley of Mexico attracting people to settle there? 11. What is obsidian? 12. According to the Aztec, who was the god of the sun and warfare? 13. Aztecs often demanded tribute from their conquered subjects in the form of what products? 14. What are the three clas ...
... 10. What are three advantages of the Valley of Mexico attracting people to settle there? 11. What is obsidian? 12. According to the Aztec, who was the god of the sun and warfare? 13. Aztecs often demanded tribute from their conquered subjects in the form of what products? 14. What are the three clas ...
Mesoamerica 2016 Power Point
... The birth of civilized man may have begun in Asia and spread to Africa and beyond but in the middle (meso) land that joins the two American continents (North & South America) there were ...
... The birth of civilized man may have begun in Asia and spread to Africa and beyond but in the middle (meso) land that joins the two American continents (North & South America) there were ...
Aztec Empire

The Mexica Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance (Nahuatl: Ēxcān Tlahtōlōyān, [ˈjéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥]) began as an alliance of three Nahua ""altepetl"" city-states: Mexico-Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan. These three city-states ruled the area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until they were defeated by the combined forces of the Spanish conquistadores and their native allies under Hernán Cortés in 1521.The Triple Alliance was formed from the victorious faction in a civil war fought between the city of Azcapotzalco and its former tributary provinces. Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, Tenochtitlan quickly established itself as the dominant partner militarily. By the time the Spanish arrived in 1520, the lands of the Alliance were effectively ruled from Tenochtitlan, and the other partners in the alliance had assumed subsidiary roles.The alliance waged wars of conquest and expanded rapidly after its formation. At its height, the alliance controlled most of central Mexico as well as some more distant territories within Mesoamerica such as the Xoconochco province, an Aztec exclave near the present-day Guatemalan border. Aztec rule has been described by scholars as ""hegemonic"" or ""indirect"". Rulers of conquered cities were left in power so long as they agreed to pay semi-annual tribute to the alliance as well as supplying military support for the Aztec war efforts. In return, the imperial authority offered protection and political stability as well as facilitating an integrated economic network of diverse lands and peoples with significant local autonomy despite their tributary status.