Biology Study Guide
... Classification: (Chap 17) Describe Linnaeus’ system of binomial nomenclature. List the seven levels of biological classification from simple to complex. Name the six kingdoms and identify the following for each: prokaryote/eukaryote, sexual/asexual reproduction, autotrophic/heterotrophic. What is a ...
... Classification: (Chap 17) Describe Linnaeus’ system of binomial nomenclature. List the seven levels of biological classification from simple to complex. Name the six kingdoms and identify the following for each: prokaryote/eukaryote, sexual/asexual reproduction, autotrophic/heterotrophic. What is a ...
I. Introduction to class
... Genetic recombination contributes to an organism’s genetic diversity. In eucaryotes recombination occurs during meiosis through a process called crossing over. In procaryotes there are several different mechanisms of genetic recombination: Transformation, conjugation, and transduction In all ...
... Genetic recombination contributes to an organism’s genetic diversity. In eucaryotes recombination occurs during meiosis through a process called crossing over. In procaryotes there are several different mechanisms of genetic recombination: Transformation, conjugation, and transduction In all ...
AP Biology
... REPRODUCTION 14. Describe binary fission. Is this a sexual or asexual form of reproduction? ...
... REPRODUCTION 14. Describe binary fission. Is this a sexual or asexual form of reproduction? ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there - EvergreenStateCollege-Home
... The active lac repressor is a tetramer of four LacI+ monomers, each of which can bind to an operator sequence to block the opening of the double helix for transcription. One tetramer can bind two operator sequences and cause the DNA between the operators to “kink” or “loop” When the repressor inter ...
... The active lac repressor is a tetramer of four LacI+ monomers, each of which can bind to an operator sequence to block the opening of the double helix for transcription. One tetramer can bind two operator sequences and cause the DNA between the operators to “kink” or “loop” When the repressor inter ...
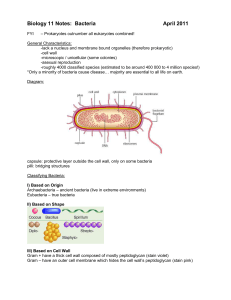
DNA. Structures of bacteria
... • A fragment of exogenous naked bacterial DNA are taken up and absorbed into recipient cells. • Common in Haemophilus influenzae & ...
... • A fragment of exogenous naked bacterial DNA are taken up and absorbed into recipient cells. • Common in Haemophilus influenzae & ...
Document
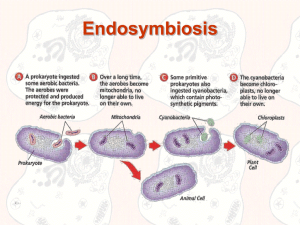
... “Why worry about life in space (astrobiology, etc.) when terrestrial microbes can provide clues as to the origins and evolution of eukaryotic differentiation?” ...
... “Why worry about life in space (astrobiology, etc.) when terrestrial microbes can provide clues as to the origins and evolution of eukaryotic differentiation?” ...
Chapter 8: Microbial Genetics
... In eucaryotes recombination occurs during meiosis through a process called crossing over. over. In procaryotes there are several different mechanisms of genetic recombination: Transformation Transformation,, conjugation conjugation,, and transduction In all cases, it involves a DNA donor and a DNA r ...
... In eucaryotes recombination occurs during meiosis through a process called crossing over. over. In procaryotes there are several different mechanisms of genetic recombination: Transformation Transformation,, conjugation conjugation,, and transduction In all cases, it involves a DNA donor and a DNA r ...
Assessing evolutionary relationships among
... than from Bacteria. Best-match methods have also been used to suggest distinct origins for different genetic elements within species such as Deinococcus radiodurans and Vibrio cholerae [6•,13] and to identify likely organellar genes in nuclear genomes of eukaryotes [14]. The main advantage of best-m ...
... than from Bacteria. Best-match methods have also been used to suggest distinct origins for different genetic elements within species such as Deinococcus radiodurans and Vibrio cholerae [6•,13] and to identify likely organellar genes in nuclear genomes of eukaryotes [14]. The main advantage of best-m ...
Questions from the Audience
... 1. Staphylococcus aureus is (type of organism) 2. Staphylococcus aureus grows in (pattern) 3. What color is Staphylococcus aureus? 4. What is a commensal? 5. Which type of infection is LEAST LIKELY with Staphylococcus aureus? 6. A facultative anaerobe lives 7. Penicillin works by 8. Resistance to an ...
... 1. Staphylococcus aureus is (type of organism) 2. Staphylococcus aureus grows in (pattern) 3. What color is Staphylococcus aureus? 4. What is a commensal? 5. Which type of infection is LEAST LIKELY with Staphylococcus aureus? 6. A facultative anaerobe lives 7. Penicillin works by 8. Resistance to an ...
Rodriguez, Brianna M.
... In class we discussed DNA replication and how our genes sometimes mutate. However, we really didn’t discuss much on how microbes themselves can mutate. While microbial mutations are rare, they do occur, about every one to ten million DNA bases. However, we must take into consideration the fact that ...
... In class we discussed DNA replication and how our genes sometimes mutate. However, we really didn’t discuss much on how microbes themselves can mutate. While microbial mutations are rare, they do occur, about every one to ten million DNA bases. However, we must take into consideration the fact that ...
Evolution and Diversification of Life
... • Simple things came first • Complexity accumulates slowly through trial and error via many known mechanisms ...
... • Simple things came first • Complexity accumulates slowly through trial and error via many known mechanisms ...
1 Discover the World of Microbes, Bacteria, Archaea - Wiley-VCH
... Section 1 Batch and continuous culture 1. What is the difference between generation time g and doubling time td? g is the time required for doubling the number of cells, whereas td is the time required for doubling the cell mass. 2. Describe the characteristic feature of the logarithmic growth phase ...
... Section 1 Batch and continuous culture 1. What is the difference between generation time g and doubling time td? g is the time required for doubling the number of cells, whereas td is the time required for doubling the cell mass. 2. Describe the characteristic feature of the logarithmic growth phase ...
Bacteria Notes Pre AP Teacher 14-15
... b. does not take up stain, prevented by lipid layer around cell wall: Gram 2. antibiotic used to cure bacterial infection depends on: Gram + or Gram 3. harder to treat: Gram - have more complex cell walls to impede entry of antibiotics D. Causes disease: 1. destroys cells – of infected organisms by ...
... b. does not take up stain, prevented by lipid layer around cell wall: Gram 2. antibiotic used to cure bacterial infection depends on: Gram + or Gram 3. harder to treat: Gram - have more complex cell walls to impede entry of antibiotics D. Causes disease: 1. destroys cells – of infected organisms by ...
Powerpoint File - Centre for Microbial Diseases and Immunity
... As more genomes from bacterial pathogens are sequenced, it is becoming apparent that a significant proportion of virulence factors are encoded in clusters of genes, termed Pathogenicity Islands (reviewed in 1). These islands and other genomic islands, tend to have atypical guanine and cytosine conte ...
... As more genomes from bacterial pathogens are sequenced, it is becoming apparent that a significant proportion of virulence factors are encoded in clusters of genes, termed Pathogenicity Islands (reviewed in 1). These islands and other genomic islands, tend to have atypical guanine and cytosine conte ...
Transport in Plants
... Changes in gene frequency occur from one generation to the next with small populations Sources of genetic drift: founder effect and bottleneck effect ...
... Changes in gene frequency occur from one generation to the next with small populations Sources of genetic drift: founder effect and bottleneck effect ...
The Development of Gene Probes for Coliforms and Other Micro
... Gene probe is the term used to describe a novel molecular biological technique which detects pieces of genetic material specific to a speciesor group of organisms. It has been proposed that gene probes should allow the detection of specific microorganisms with greater speedand certainty than traditi ...
... Gene probe is the term used to describe a novel molecular biological technique which detects pieces of genetic material specific to a speciesor group of organisms. It has been proposed that gene probes should allow the detection of specific microorganisms with greater speedand certainty than traditi ...
Folie 1
... 1 Department of Biology and CESAM, University of Aveiro, 3810 Aveiro, Portugal 2 Medinfar– Pharmaceutical Products SA, Amadora, 2700 Venda Nova, Portugal 3 Institut für Chemie, Technische Universität Berlin, 10623 Berlin, Germany ...
... 1 Department of Biology and CESAM, University of Aveiro, 3810 Aveiro, Portugal 2 Medinfar– Pharmaceutical Products SA, Amadora, 2700 Venda Nova, Portugal 3 Institut für Chemie, Technische Universität Berlin, 10623 Berlin, Germany ...
Module 2 Evolution review A website and some wikispaces have
... B. a change in the coat-color genes of deer predator species C. an increase in coat-color diversity in the population D. an increase in the number of genes for coat color in the population 4. Two continental plates collide and begin to build up a mountain range. Gradually, a species of lizards becom ...
... B. a change in the coat-color genes of deer predator species C. an increase in coat-color diversity in the population D. an increase in the number of genes for coat color in the population 4. Two continental plates collide and begin to build up a mountain range. Gradually, a species of lizards becom ...
30Biotech2007print
... _______ new chromosome into organism organism _______ new gene as if it were its own organism _______ gene as if it were its own _____________________________________: Regents Biology Remember: we all use the same genetic code! ...
... _______ new chromosome into organism organism _______ new gene as if it were its own organism _______ gene as if it were its own _____________________________________: Regents Biology Remember: we all use the same genetic code! ...
Horizontal gene transfer

Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) refers to the transfer of genes between organisms in a manner other than traditional reproduction. Also termed lateral gene transfer (LGT), it contrasts with vertical transfer, the transmission of genes from the parental generation to offspring via sexual or asexual reproduction. HGT has been shown to be an important factor in the evolution of many organisms.Horizontal gene transfer is the primary reason for bacterial antibiotic resistance, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. This horizontal gene transfer often involves temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes that are responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various mechanisms (e.g., via F-pilus), subsequently arming the antibiotic resistant genes' recipient against antibiotics, which is becoming a medical challenge to deal with.Most thinking in genetics has focused upon vertical transfer, but there is a growing awareness that horizontal gene transfer is a highly significant phenomenon and among single-celled organisms perhaps the dominant form of genetic transfer.Artificial horizontal gene transfer is a form of genetic engineering.