Chapter 10 - Dr. Eric Schwartz
... flexible so that the neurons are capable of responding differently under different circumstances. • This adaptability enhances the possibility of integrating incoming neural signals from diverse sources and the final coordination of many parts into a smooth, purposeful movement. • It probably also a ...
... flexible so that the neurons are capable of responding differently under different circumstances. • This adaptability enhances the possibility of integrating incoming neural signals from diverse sources and the final coordination of many parts into a smooth, purposeful movement. • It probably also a ...
Development of the adolescent brain
... There seems to be a qualitative shift in the nature of thinking such that adolescents are more self-aware and self-reflective than prepubescent children. Adolescents develop a capacity to hold in mind more multidimensional concepts and are thus able to think in a more strategic manner. Empirical res ...
... There seems to be a qualitative shift in the nature of thinking such that adolescents are more self-aware and self-reflective than prepubescent children. Adolescents develop a capacity to hold in mind more multidimensional concepts and are thus able to think in a more strategic manner. Empirical res ...
Neuronal activity in dorsomedial frontal cortex and prefrontal cortex
... which only the color and shape of visual stimuli served as salient discriminative features. Each of eight stimuli was associated with a response to a different eye-movement target. The location of these stimuli varied from trial to trial but was of no behavioral relevance, and the monkeys did not pe ...
... which only the color and shape of visual stimuli served as salient discriminative features. Each of eight stimuli was associated with a response to a different eye-movement target. The location of these stimuli varied from trial to trial but was of no behavioral relevance, and the monkeys did not pe ...
Decoding the Contents of Visual Short
... were different from those used in the scanner to avoid long-term consolstimulus presentation from processes specific to short-term memory idation of the memory items. The training procedure started with a short (Sperling, 1960; Oberauer and Kliegl, 2001; Lepsien et al., 2005; Harrison exercise of th ...
... were different from those used in the scanner to avoid long-term consolstimulus presentation from processes specific to short-term memory idation of the memory items. The training procedure started with a short (Sperling, 1960; Oberauer and Kliegl, 2001; Lepsien et al., 2005; Harrison exercise of th ...
LiebermanSSSP2002REV - Sydney Symposium of Social
... The C-system. Sometimes our existing expectations in the X-system fail us. The failure can occur in one of two ways, but the result is the same in both cases: another mechanism besides the X-system is needed to guide behavior. Sometimes the task or stimulus is novel and consequently the X-system has ...
... The C-system. Sometimes our existing expectations in the X-system fail us. The failure can occur in one of two ways, but the result is the same in both cases: another mechanism besides the X-system is needed to guide behavior. Sometimes the task or stimulus is novel and consequently the X-system has ...
Current advances and pressing problems in studies of stopping
... putamen, globus pallidus, and thalamus [49]. Although some have hypothesized that a common inhibitory mechanism operates in humans and rats [50!!], comparison across species must be made with caution because STN connectivity differs between rodents and primates [51]. (2) Numerous studies identify rI ...
... putamen, globus pallidus, and thalamus [49]. Although some have hypothesized that a common inhibitory mechanism operates in humans and rats [50!!], comparison across species must be made with caution because STN connectivity differs between rodents and primates [51]. (2) Numerous studies identify rI ...
Cognitive neuroscience of self-regulation failure
... favor of bottom-up impulses, either because of a failure to engage prefrontal control areas or because of an especially strong impulse (e.g. the sight and smell of cigarettes for an abstinent smoker), then the likelihood of self-regulatory failure increases (Figure 2). Regulation of appetitive behav ...
... favor of bottom-up impulses, either because of a failure to engage prefrontal control areas or because of an especially strong impulse (e.g. the sight and smell of cigarettes for an abstinent smoker), then the likelihood of self-regulatory failure increases (Figure 2). Regulation of appetitive behav ...
How cognitive theory guides neuroscience
... The field of cognitive science studies latent, unobservable cognitive processes that generate observable behaviors. Similarly, cognitive neuroscience attempts to link latent cognitive processes with the neural mechanisms that generate them. Although neural processes are partially observable (with ima ...
... The field of cognitive science studies latent, unobservable cognitive processes that generate observable behaviors. Similarly, cognitive neuroscience attempts to link latent cognitive processes with the neural mechanisms that generate them. Although neural processes are partially observable (with ima ...
somatosensory area i
... Somatosensory association area • Brodmann’s area 5 and 7 • Parietal cortex - behind somatosensory area I • Decipher sensory information entering somatosensory area I • Receives signals from: – Somatosensory area I – Ventrobasal nuclei of thalamus – Other nuclei of thalamus – Visual and auditory cor ...
... Somatosensory association area • Brodmann’s area 5 and 7 • Parietal cortex - behind somatosensory area I • Decipher sensory information entering somatosensory area I • Receives signals from: – Somatosensory area I – Ventrobasal nuclei of thalamus – Other nuclei of thalamus – Visual and auditory cor ...
Cell loss in the motor and cingu- late cortex correlates with sympto
... phenotype (see figure). Brains from individuals with predominantly motor symptoms showed major cell loss in the motor cortex with no significant cell loss in the cingulate cortex. By contrast, brains from patients in whom mood was primarily affected showed extensive cell loss in the cingulate cortex ...
... phenotype (see figure). Brains from individuals with predominantly motor symptoms showed major cell loss in the motor cortex with no significant cell loss in the cingulate cortex. By contrast, brains from patients in whom mood was primarily affected showed extensive cell loss in the cingulate cortex ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... • “Default brain network” involves a large-scale brain network (cingulate cortex, mPFC, lateral PC), shows low activity for goal-related actions; it is active in social and emotional processing, mindwandering, daydreaming. • Activity of the default network is negatively correlated with the “action n ...
... • “Default brain network” involves a large-scale brain network (cingulate cortex, mPFC, lateral PC), shows low activity for goal-related actions; it is active in social and emotional processing, mindwandering, daydreaming. • Activity of the default network is negatively correlated with the “action n ...
Workshop program booklet
... has to solve, and propose an answer: how the nervous system ”should” optimally solve this problem given its limited amount of neural resources. Such a principled framework seems particularly important for understanding complex systems, where pure descriptive models often cannot provide satisfying an ...
... has to solve, and propose an answer: how the nervous system ”should” optimally solve this problem given its limited amount of neural resources. Such a principled framework seems particularly important for understanding complex systems, where pure descriptive models often cannot provide satisfying an ...
Slide 1
... medial cortex (MC). The solid lines in these cortical areas represent the densely packed pyramidal neurons that form a single cell layer in all three areas. S = septum; STR = striatum. C. The cellular structure of dorsal cortex. A densely packed row of pyramidal neurons forms a middle layer. Pyramid ...
... medial cortex (MC). The solid lines in these cortical areas represent the densely packed pyramidal neurons that form a single cell layer in all three areas. S = septum; STR = striatum. C. The cellular structure of dorsal cortex. A densely packed row of pyramidal neurons forms a middle layer. Pyramid ...
primary motor cortex - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... Parallel structure – signals flow between levels over multiple paths Like a company: President (association cortex) issues general commands and lower level (motor neurons and muscles) take care of details Advantage: Higher levels are left free to focsu on complex fucntions. ...
... Parallel structure – signals flow between levels over multiple paths Like a company: President (association cortex) issues general commands and lower level (motor neurons and muscles) take care of details Advantage: Higher levels are left free to focsu on complex fucntions. ...
article
... callosum, thereby involving both cortical hemispheres. In this case, sufferers often become unable to function, lose awareness of the external world, and may convulse (if the motor cortex is affected). These seizures can last several minutes, but their after-effects can last much longer. The symptom ...
... callosum, thereby involving both cortical hemispheres. In this case, sufferers often become unable to function, lose awareness of the external world, and may convulse (if the motor cortex is affected). These seizures can last several minutes, but their after-effects can last much longer. The symptom ...
Music and the Brain: Areas and Networks
... Beyond the auditory cortices, musical sounds activate distributed grey matter throughout the brain. Researchers have proposed various functional networks or pathways beyond the level of the primary auditory cortex. These functional networks subserve language and generalized auditory processing as we ...
... Beyond the auditory cortices, musical sounds activate distributed grey matter throughout the brain. Researchers have proposed various functional networks or pathways beyond the level of the primary auditory cortex. These functional networks subserve language and generalized auditory processing as we ...
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... conscience In children matures slowly and is heavily dependent on positive and negative feedback Closely linked to the emotional part of the brain (limbic system) Plays a role intuitive judgments and mood Tremendous elaboration of this region sets humans apart from other animals Language comprehensi ...
... conscience In children matures slowly and is heavily dependent on positive and negative feedback Closely linked to the emotional part of the brain (limbic system) Plays a role intuitive judgments and mood Tremendous elaboration of this region sets humans apart from other animals Language comprehensi ...
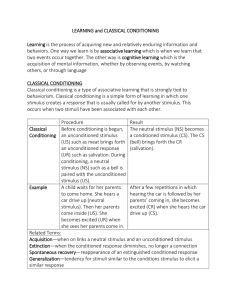
LEARNING and Classical Conditioning
... Learning is the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information and behaviors. One way we learn is by associative learning which is when we learn that two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing even ...
... Learning is the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information and behaviors. One way we learn is by associative learning which is when we learn that two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing even ...
Genardi Brodmann-Detail
... motor imagery, bimanual manipulation, and similar praxic abilities. BA5/7 may also participate in a circuit underlying imitation of motor learning. It is well established that astereognosis (or tactile agnosia: loss of the ability to recognize objects by handling them) is found in cases of damage i ...
... motor imagery, bimanual manipulation, and similar praxic abilities. BA5/7 may also participate in a circuit underlying imitation of motor learning. It is well established that astereognosis (or tactile agnosia: loss of the ability to recognize objects by handling them) is found in cases of damage i ...
DIENCEPHALON
... • important for regulation of basic functions and linkage of basic functions to more complex functions such as movement ...
... • important for regulation of basic functions and linkage of basic functions to more complex functions such as movement ...
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Structural and Functional areas of the
... stored in the brain. It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event invokes. Believed to act as an interface between limibic system, cerebum, and other sensory areas. – Clinical concerns: Autism, Depression, Narcolepsy, Posttraumatic stress disorder, and Ph ...
... stored in the brain. It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event invokes. Believed to act as an interface between limibic system, cerebum, and other sensory areas. – Clinical concerns: Autism, Depression, Narcolepsy, Posttraumatic stress disorder, and Ph ...
Neurophysiology: Sensing and categorizing
... that many reach-related neurons in M1 are tuned for the direction of the reach: they respond optimally when the monkey reaches in a particular direction, and their responses fall off gradually as the direction of reaching changes from the optimal. Salinas and Romo deliberately positioned their two o ...
... that many reach-related neurons in M1 are tuned for the direction of the reach: they respond optimally when the monkey reaches in a particular direction, and their responses fall off gradually as the direction of reaching changes from the optimal. Salinas and Romo deliberately positioned their two o ...
face-specific responses from the human inferior occipito
... pointillized faces (lower part of the inset) suggested very weak activity over the occipital cortex. Responses to the two stimulus categories also differed at the posterior channels (Fig. 2). It is suggested that this difference reflects the differential processing of simple visual features. Respons ...
... pointillized faces (lower part of the inset) suggested very weak activity over the occipital cortex. Responses to the two stimulus categories also differed at the posterior channels (Fig. 2). It is suggested that this difference reflects the differential processing of simple visual features. Respons ...
Brain Abnormalities in Murderers
... reduced integration previously observed in antisocial and violent groups. Another potential implication of poor inter-hemispheric transfer is that the right hemisphere, which is involved in the generation of negative emotions, may experience less regulation and control by the inhibitory processes of ...
... reduced integration previously observed in antisocial and violent groups. Another potential implication of poor inter-hemispheric transfer is that the right hemisphere, which is involved in the generation of negative emotions, may experience less regulation and control by the inhibitory processes of ...
Executive functions

Executive functions (also known as cognitive control and supervisory attentional system) is an umbrella term for the management (regulation, control) of cognitive processes, including working memory, reasoning, task flexibility, and problem solving as well as planning and execution.The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes, such as executive functions. The prefrontal areas of the frontal lobe are necessary but not solely sufficient for carrying out these functions.