Chapter 4
... – Each block contains a number of columns equal to the number of electrons that can occupy that subshell • The s-block has 2 columns, because a maximum of 2 electrons can occupy the single orbital in an s-subshell. • The p-block has 6 columns, because a maximum of 6 electrons can occupy the three ...
... – Each block contains a number of columns equal to the number of electrons that can occupy that subshell • The s-block has 2 columns, because a maximum of 2 electrons can occupy the single orbital in an s-subshell. • The p-block has 6 columns, because a maximum of 6 electrons can occupy the three ...
The relation between the ( hypothetical) intrinsic vibrational motion
... The set of results indicates the following. If the intrinsic vibration-rotation motion of fundamental particles exists in nature, such motion must trap quantized amounts of magnetic flux, which is required by gauge invariance of the theory. The values of the flux depend on the actual charge of the p ...
... The set of results indicates the following. If the intrinsic vibration-rotation motion of fundamental particles exists in nature, such motion must trap quantized amounts of magnetic flux, which is required by gauge invariance of the theory. The values of the flux depend on the actual charge of the p ...
EMF 1994 Assignment 4
... (b) Does the electron gain or lose potential energy in moving to the new position? (c) How much potential energy is gained or lost? Express the answer both in electron Volts and Joules. Hints: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) ...
... (b) Does the electron gain or lose potential energy in moving to the new position? (c) How much potential energy is gained or lost? Express the answer both in electron Volts and Joules. Hints: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) ...
6. Quantum Electrodynamics
... ~ This the local, physical, gauge invariant objects E is fine for the free classical theory: Maxwell’s equations ~ and B. ~ But it is were, after all, first written in terms of E not possible to describe certain quantum phenomena, such as the Aharonov-Bohm effect, without using the gauge potential A ...
... ~ This the local, physical, gauge invariant objects E is fine for the free classical theory: Maxwell’s equations ~ and B. ~ But it is were, after all, first written in terms of E not possible to describe certain quantum phenomena, such as the Aharonov-Bohm effect, without using the gauge potential A ...
Quantum Fields and Fundamental Geometry
... ● Propagating mass and rest mass ● Inertia, gravity and the Higgs ● Geometries for weak and strong interactions ● Curvilinear description of elementary particles ● Particle transmutation ...
... ● Propagating mass and rest mass ● Inertia, gravity and the Higgs ● Geometries for weak and strong interactions ● Curvilinear description of elementary particles ● Particle transmutation ...
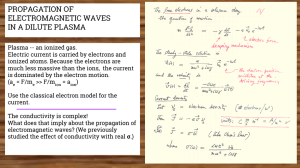
PROPAGATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN A DILUTE PLASMA
... It’s not simply that ne is small, because σ is proportional to ne . What we mean is that collisions are rare. Then γ is small, i.e., iωγ << mω2. ...
... It’s not simply that ne is small, because σ is proportional to ne . What we mean is that collisions are rare. Then γ is small, i.e., iωγ << mω2. ...
Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields
... Suppose a particle with charge q and mass m moves with velocity vector v. If a force F acts in the same direction as the velocity v then the particle continues to move in the same direction, but it speeds up. This is what an electric field can do to charged particles. We can describe it a bit differ ...
... Suppose a particle with charge q and mass m moves with velocity vector v. If a force F acts in the same direction as the velocity v then the particle continues to move in the same direction, but it speeds up. This is what an electric field can do to charged particles. We can describe it a bit differ ...
Quantum Mechanics II, Ex 4730
... Given a spherical shell with radius R and a particle with mass M and charge e. Notice that the standard variables which show the particle are (θ, φ, Lx, Ly, Lz) In this question we have to assume that the particle can be excited from ground state to first energy level but not beyond so the state spa ...
... Given a spherical shell with radius R and a particle with mass M and charge e. Notice that the standard variables which show the particle are (θ, φ, Lx, Ly, Lz) In this question we have to assume that the particle can be excited from ground state to first energy level but not beyond so the state spa ...
WP1
... to visualize in classical mechanical terms. Some concepts defy common sense, e.g. a) superposition (of states, quantum systems can be in more than one discrete state at a time) b) non-locality (spooky action at a distance) c) non determinism (QM is essentially stochastic) d) non reality (some “inter ...
... to visualize in classical mechanical terms. Some concepts defy common sense, e.g. a) superposition (of states, quantum systems can be in more than one discrete state at a time) b) non-locality (spooky action at a distance) c) non determinism (QM is essentially stochastic) d) non reality (some “inter ...
CHAPTER 1: The Birth of Modern Physics
... Establishes heat as energy Introduces the concept of internal energy Creates temperature as a measure of internal energy Generates limitations of the energy processes that cannot take place ...
... Establishes heat as energy Introduces the concept of internal energy Creates temperature as a measure of internal energy Generates limitations of the energy processes that cannot take place ...
Environmental Physics for Freshman Geography Students
... where q1 and q2 are the amounts of electric charge (measured in coulombs, C), r is the distance between them (measured in m), and K is Coulomb’s electrostatic constant (= 8.99 x 109 kg m3 s-2 C-2). The introduction of electric charges into the simple world of mechanics requires the use of a new dime ...
... where q1 and q2 are the amounts of electric charge (measured in coulombs, C), r is the distance between them (measured in m), and K is Coulomb’s electrostatic constant (= 8.99 x 109 kg m3 s-2 C-2). The introduction of electric charges into the simple world of mechanics requires the use of a new dime ...