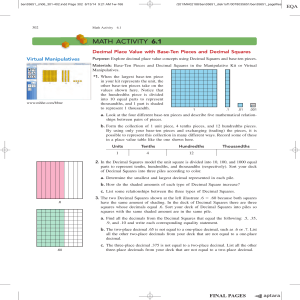
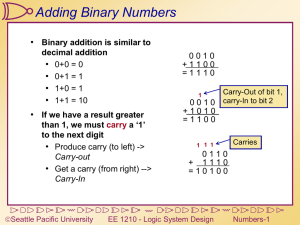
a > -2
... An inequality is a mathematical sentence formed by placing an inequality symbol between two expressions. The solution of an inequality is the set of numbers that you can substitute for the variable to make the inequality true. The graph of an inequality in one variable is the set of points on a numb ...
... An inequality is a mathematical sentence formed by placing an inequality symbol between two expressions. The solution of an inequality is the set of numbers that you can substitute for the variable to make the inequality true. The graph of an inequality in one variable is the set of points on a numb ...
Lecture 5: Control Structure (Iteration)
... The program must process 10 test results. A countercontrolled loop will be used. Two counters can be used—one to count the number of students who passed the exam and one to count the number of students who failed the exam. Each test result is a number—either a 1 or a 2. If the number is not a ...
... The program must process 10 test results. A countercontrolled loop will be used. Two counters can be used—one to count the number of students who passed the exam and one to count the number of students who failed the exam. Each test result is a number—either a 1 or a 2. If the number is not a ...
Who Wants to be a Millionaire
... Question 14 If a row of 10p pieces was put together edge to edge to form a line 25 m long how much would it be worth roughly!? ...
... Question 14 If a row of 10p pieces was put together edge to edge to form a line 25 m long how much would it be worth roughly!? ...