Mathematics Summer Session: Transition Math Chapter 1 Notes
... then add the numerator. Keep the same denominator. So, 2 ½ would become (2 x 2 + 1)/2 = 5/2. Lesson 1-8: Throw a negative sign in front of any of the positive whole numbers, and you have negative numbers. Unlike positive numbers, the closer a negative number is to zero, the bigger it is. So, -.0001 ...
... then add the numerator. Keep the same denominator. So, 2 ½ would become (2 x 2 + 1)/2 = 5/2. Lesson 1-8: Throw a negative sign in front of any of the positive whole numbers, and you have negative numbers. Unlike positive numbers, the closer a negative number is to zero, the bigger it is. So, -.0001 ...
huddersfield nov 2015
... checked it out with a range of numbers tested it widely; thrashed it in fact done reversing (inverses) to get back to the starting number built algebraic expressions with ‘m’ for a million ...
... checked it out with a range of numbers tested it widely; thrashed it in fact done reversing (inverses) to get back to the starting number built algebraic expressions with ‘m’ for a million ...
Name
... 1.1 I can compare, order, and locate real numbers on a number line. Rewrite each statement with <, >, or = to make a true statement. ...
... 1.1 I can compare, order, and locate real numbers on a number line. Rewrite each statement with <, >, or = to make a true statement. ...
Floating-Point Representation and Approximation Errors
... the problem exactly, the solution may be meaningless • ill-conditioned problems are close to ill-posed problems: there exist small perturbations which make the problem unsolvable in exact arithmetic. ...
... the problem exactly, the solution may be meaningless • ill-conditioned problems are close to ill-posed problems: there exist small perturbations which make the problem unsolvable in exact arithmetic. ...
maths-SOW-year-9 - Barbara Priestman Academy
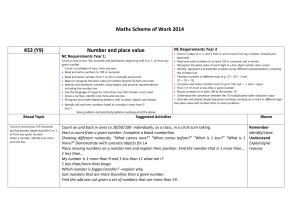
... Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count in multiples of twos, fives and tens Read and write numbers to 100 in numerals Read and write numbers from 1 to 20 in numerals and words Begin to recognise the place value of numbers beyond 2 ...
... Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Count in multiples of twos, fives and tens Read and write numbers to 100 in numerals Read and write numbers from 1 to 20 in numerals and words Begin to recognise the place value of numbers beyond 2 ...
Square Roots via Newton`s Method
... with existence and correctness of the solutions (as in analysis), but with the time (and other computational resources, e.g. memory) required to compute the result. • We are also concerned with accuracy of the results, because in practice we only ever have approximate answers: – Some algorithms may ...
... with existence and correctness of the solutions (as in analysis), but with the time (and other computational resources, e.g. memory) required to compute the result. • We are also concerned with accuracy of the results, because in practice we only ever have approximate answers: – Some algorithms may ...