Explanation - Fort Bend ISD
... The force of air resistance is also acting on the coffee filter and is comparable in size to the weight. ...
... The force of air resistance is also acting on the coffee filter and is comparable in size to the weight. ...
AP 1 Midterm Review
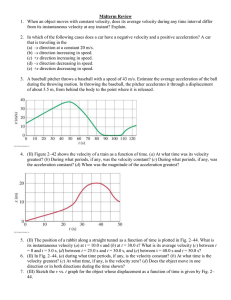
... 8. Which of the following situations is impossible? (a) An object has velocity directed east and acceleration directed west. (b) An object has velocity directed east and acceleration directed east. (c) An object has zero velocity but non-zero acceleration. (d) An object has constant non-zero accele ...
... 8. Which of the following situations is impossible? (a) An object has velocity directed east and acceleration directed west. (b) An object has velocity directed east and acceleration directed east. (c) An object has zero velocity but non-zero acceleration. (d) An object has constant non-zero accele ...
Summary of Chapters 1-3 Equations of motion for a uniformly acclerating object
... or a big spaceship (air-track unnecessary) These springs can be taken anywhere in the universe and used to measure the mass of any cart. Also, the stretching of these springs can be used to define the unit of force. ...
... or a big spaceship (air-track unnecessary) These springs can be taken anywhere in the universe and used to measure the mass of any cart. Also, the stretching of these springs can be used to define the unit of force. ...
Newtons` Second Law
... Newton’s 1st law If the total “resultant” force acting on an object is zero, then the object will either remain at rest or it would move along a line with a constant velocity. ...
... Newton’s 1st law If the total “resultant” force acting on an object is zero, then the object will either remain at rest or it would move along a line with a constant velocity. ...
Slides 69-70 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. ...
... 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. ...
Test 2 Review
... Changing Motion and Turning. According to Newton's First Law, an object in motion continues moving in a straight line unless it is acted on by a force. Planets orbit the sun in an almost circular path. They are not violating Newton's First Law. They are obeying Newton's Second Law. The sun is exerti ...
... Changing Motion and Turning. According to Newton's First Law, an object in motion continues moving in a straight line unless it is acted on by a force. Planets orbit the sun in an almost circular path. They are not violating Newton's First Law. They are obeying Newton's Second Law. The sun is exerti ...
Description of Motion in One Dimension
... Describe the concepts of gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. If an object of mass m is lifted to a certain height h above the surface of the earth then the work done is mgh and the object now has a potential energy equal to the work done mgh (force = mg, displacement = h). F ...
... Describe the concepts of gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. If an object of mass m is lifted to a certain height h above the surface of the earth then the work done is mgh and the object now has a potential energy equal to the work done mgh (force = mg, displacement = h). F ...
7th gd Forces
... The Nature of Force • A force is a push or a pull. • Like velocity and acceleration, a force is described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts. • The strength of a force is measured in the SI ...
... The Nature of Force • A force is a push or a pull. • Like velocity and acceleration, a force is described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts. • The strength of a force is measured in the SI ...
Physics Chapters 456 (Due on October 24)
... a. Yes, because there is a net force acting on the wagon. b. Yes, because there is a time delay between action and reaction. c. No, because the forces cancel each other. d. Yes, because the horse's pull on the wagon is larger than the wagon's pull on the horse. ____ 70. A large truck and a small car ...
... a. Yes, because there is a net force acting on the wagon. b. Yes, because there is a time delay between action and reaction. c. No, because the forces cancel each other. d. Yes, because the horse's pull on the wagon is larger than the wagon's pull on the horse. ____ 70. A large truck and a small car ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... 6. Enter 5000 kg for m1, 1000 kg for m2, and 0.1 meters as the distance. Your Fg should be 0.03335 N, as shown in the example at right. If it is, good! If not, fix your formula. 7. Have Mr. Holland check your Fg calculator. Teacher initials____ 8. Add in a section that will calculate acceleration v ...
... 6. Enter 5000 kg for m1, 1000 kg for m2, and 0.1 meters as the distance. Your Fg should be 0.03335 N, as shown in the example at right. If it is, good! If not, fix your formula. 7. Have Mr. Holland check your Fg calculator. Teacher initials____ 8. Add in a section that will calculate acceleration v ...
grade 9 physics notes
... When a cannonball is fired from a cannon, the cannon exerts a force on the cannonball and the cannonball exerts an equal and opposite force on the cannon. However, the cannon being more massive, recoils with less speed, but the cannonball moves faster by Newton's second law of motion which states th ...
... When a cannonball is fired from a cannon, the cannon exerts a force on the cannonball and the cannonball exerts an equal and opposite force on the cannon. However, the cannon being more massive, recoils with less speed, but the cannonball moves faster by Newton's second law of motion which states th ...
Chapter 6 - TeacherWeb
... Objects fall to the ground at the same rate _______________________________________________________________ because the acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects Objects accelerate towards earth at a ________________ rate of acceleration constant 9.8 m/s/s second equal to _____________ ...
... Objects fall to the ground at the same rate _______________________________________________________________ because the acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects Objects accelerate towards earth at a ________________ rate of acceleration constant 9.8 m/s/s second equal to _____________ ...
Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is usually taken to be the force on the object due to gravity. Weight is a vector whose magnitude (a scalar quantity), often denoted by an italic letter W, is the product of the mass m of the object and the magnitude of the local gravitational acceleration g; thus: W = mg. The unit of measurement for weight is that of force, which in the International System of Units (SI) is the newton. For example, an object with a mass of one kilogram has a weight of about 9.8 newtons on the surface of the Earth, and about one-sixth as much on the Moon. In this sense of weight, a body can be weightless only if it is far away (in principle infinitely far away) from any other mass. Although weight and mass are scientifically distinct quantities, the terms are often confused with each other in everyday use.There is also a rival tradition within Newtonian physics and engineering which sees weight as that which is measured when one uses scales. There the weight is a measure of the magnitude of the reaction force exerted on a body. Typically, in measuring an object's weight, the object is placed on scales at rest with respect to the earth, but the definition can be extended to other states of motion. Thus, in a state of free fall, the weight would be zero. In this second sense of weight, terrestrial objects can be weightless. Ignoring air resistance, the famous apple falling from the tree, on its way to meet the ground near Isaac Newton, is weightless.Further complications in elucidating the various concepts of weight have to do with the theory of relativity according to which gravity is modelled as a consequence of the curvature of spacetime. In the teaching community, a considerable debate has existed for over half a century on how to define weight for their students. The current situation is that a multiple set of concepts co-exist and find use in their various contexts.