myths about the rabies vaccine • 100.6 kb
... “I tell practitioners that vaccines are drugs, albeit biological drugs. I remind them that they would not consider it good medicine to give an unnecessary pharmaceutical drug on a recurring basis. I think it is even worse to give a vaccine, or biological drug, that isn’t necessary. The possible adve ...
... “I tell practitioners that vaccines are drugs, albeit biological drugs. I remind them that they would not consider it good medicine to give an unnecessary pharmaceutical drug on a recurring basis. I think it is even worse to give a vaccine, or biological drug, that isn’t necessary. The possible adve ...
Vaccines Learning Module | Vaccine Education Center
... Are the most effective means of controlling infectious diseases. ...
... Are the most effective means of controlling infectious diseases. ...
31.4 Immunity and Technology KEY CONCEPT help keep a person healthy.
... Vaccines artificially produce acquired immunity. • Vaccines also control pathogens and disease. – given to prevent illness – contain the antigen of a weakened pathogen ...
... Vaccines artificially produce acquired immunity. • Vaccines also control pathogens and disease. – given to prevent illness – contain the antigen of a weakened pathogen ...
IMMUNISATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? File
... This is a recording of a live lecture. It may contain errors of fact or presentation which cannot be corrected after the event, and should not therefore be regarded as a definitive source of information. Due to issues of copyright and other considerations, some sections of the lecture as delivered a ...
... This is a recording of a live lecture. It may contain errors of fact or presentation which cannot be corrected after the event, and should not therefore be regarded as a definitive source of information. Due to issues of copyright and other considerations, some sections of the lecture as delivered a ...
Immunological Defence Mechanisms Against Biological
... Vaccines can be very effective: cases of smallpox (extinction of the disease: non more cases of smallpox exist on earth for the success of global vaccine campaigns) and of polyo (near extinction of disease, except in some nomad populations and in critical areas of today’s world, like Syria and also, ...
... Vaccines can be very effective: cases of smallpox (extinction of the disease: non more cases of smallpox exist on earth for the success of global vaccine campaigns) and of polyo (near extinction of disease, except in some nomad populations and in critical areas of today’s world, like Syria and also, ...
Immunity
... The baby has her/his immunity from the mother but it only lasts a few months because the baby hasn't developed his/her own immunity. ...
... The baby has her/his immunity from the mother but it only lasts a few months because the baby hasn't developed his/her own immunity. ...
Immunologic Disorders
... Principles of Immunization • Immunization:is the process that an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an agent. – Active immunity – Passive immunity ...
... Principles of Immunization • Immunization:is the process that an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an agent. – Active immunity – Passive immunity ...
File
... Active immunity is where the body cells are stimulated so that they make their own antibodies. The vaccine may cause some of the milder symptoms of the disease to appear, but the person will be protected from a serious attack. Passive immunity, which does not last as long as active immunity, is ach ...
... Active immunity is where the body cells are stimulated so that they make their own antibodies. The vaccine may cause some of the milder symptoms of the disease to appear, but the person will be protected from a serious attack. Passive immunity, which does not last as long as active immunity, is ach ...
IMMUNITY- humoral immunity, or antibody
... ii. Passive- antibodies come from serum of an immune individual (not always human) 1. immediate protection 2. short lived protection 3. mother/ fetus d. Antibodies- also known as "Ig"s (for immunoglobulins). Secreted by plasma cells or by activated B-cells i. Basic structure 1. "variable" region - a ...
... ii. Passive- antibodies come from serum of an immune individual (not always human) 1. immediate protection 2. short lived protection 3. mother/ fetus d. Antibodies- also known as "Ig"s (for immunoglobulins). Secreted by plasma cells or by activated B-cells i. Basic structure 1. "variable" region - a ...
Summary - Discontools
... hyopneumoniae . A better understanding of genetics would enable the development of improved vaccines, diagnostics and control strategies. Continued molecular improvements and knowledge of the mycoplasma genome will also be important to understand the way in which they can regulate the immune respons ...
... hyopneumoniae . A better understanding of genetics would enable the development of improved vaccines, diagnostics and control strategies. Continued molecular improvements and knowledge of the mycoplasma genome will also be important to understand the way in which they can regulate the immune respons ...
Vaxart`s Tablet Vaccine for H1N1 Influenza Generates Protective
... could compete with that of any of the currently marketed vaccines, even without taking into account the convenience and logistical advantages of our room-temperature stable and user-friendly tablet. In addition, our tablet vaccine could significantly increase vaccination rates, currently at about 45 ...
... could compete with that of any of the currently marketed vaccines, even without taking into account the convenience and logistical advantages of our room-temperature stable and user-friendly tablet. In addition, our tablet vaccine could significantly increase vaccination rates, currently at about 45 ...
IB280 SEMINAR Dr. France-Isabelle Auzanneau, Professor, Department of Chemistry, University of Guelph
... Professor, Department of Chemistry, University of Guelph Tumor Associated Carbohydrate antigens: Synthetic chemistry and molecular modelling studies Carbohydrates constitute the most abundant class of natural products. In addition to being a source of energy, numerous oligo- and poly- saccharides ha ...
... Professor, Department of Chemistry, University of Guelph Tumor Associated Carbohydrate antigens: Synthetic chemistry and molecular modelling studies Carbohydrates constitute the most abundant class of natural products. In addition to being a source of energy, numerous oligo- and poly- saccharides ha ...
Immunity II
... Describe how the flu vaccine protects the human body. In your answer be sure to: • Identify the substance in the flu vaccine that stimulates immunity (1) • State how the human immune system reacts to the vaccine (1) • State one reason the flu vaccine does not protect from viral diseases such as meas ...
... Describe how the flu vaccine protects the human body. In your answer be sure to: • Identify the substance in the flu vaccine that stimulates immunity (1) • State how the human immune system reacts to the vaccine (1) • State one reason the flu vaccine does not protect from viral diseases such as meas ...
Vaccinations - New Hope Veterinary Clinic
... – Live disease-causing organism is treated in a way such that it induces an immune response without causing disease – Modern technology has made this very safe ...
... – Live disease-causing organism is treated in a way such that it induces an immune response without causing disease – Modern technology has made this very safe ...
Chapter 3
... 3.8 Inactivated vaccines and toxoids Inactivated vaccines and toxoids injected into a person who does not have prior exposure to the antigen produce a primary antibody response. IgM antibody is produced initially followed by IgG antibody. Two or more injections are usually required initially with th ...
... 3.8 Inactivated vaccines and toxoids Inactivated vaccines and toxoids injected into a person who does not have prior exposure to the antigen produce a primary antibody response. IgM antibody is produced initially followed by IgG antibody. Two or more injections are usually required initially with th ...
56. Novel immunological approaches for emergency FMD vaccines
... Vaccination has the potential to reduce large-scaling culling to control future FMD outbreaks in Europe. Due to the rapidity of FMDV replication and spread, the development of vaccine formulations inducing early protection is critical for an emergency scenario. Our strategy is to stimulate innate an ...
... Vaccination has the potential to reduce large-scaling culling to control future FMD outbreaks in Europe. Due to the rapidity of FMDV replication and spread, the development of vaccine formulations inducing early protection is critical for an emergency scenario. Our strategy is to stimulate innate an ...
12.2 Review Questions What happens when serum containing B
... 1. What happens when serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells carrying the B antigen? Will the same thing happen if serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells containing A antigen? Explain your answer. 2. What is serology and what is its most widespread application? I ...
... 1. What happens when serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells carrying the B antigen? Will the same thing happen if serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells containing A antigen? Explain your answer. 2. What is serology and what is its most widespread application? I ...
葉才明
... • CD4 antigen is the main receptor for HIV entry: The viral envelope glycoprotein gp120 binds to CD4 • Immune dysfunction results from the direct effects of HIV and impairment of CD4 T cells • Antibody response appears to be ineffective in controlling HIV ...
... • CD4 antigen is the main receptor for HIV entry: The viral envelope glycoprotein gp120 binds to CD4 • Immune dysfunction results from the direct effects of HIV and impairment of CD4 T cells • Antibody response appears to be ineffective in controlling HIV ...
Acquired immunity
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
Study Guide For Immune System Test, Chapter 40
... 1. What are the functions of B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and macrophages? 2. What is the difference between an antigen and an antibody? 3. How does acquired immunity work in a natural way (chicken pox) and when a vaccine is used (polio)? 4. What is the difference between a virus cell and a bacteri ...
... 1. What are the functions of B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and macrophages? 2. What is the difference between an antigen and an antibody? 3. How does acquired immunity work in a natural way (chicken pox) and when a vaccine is used (polio)? 4. What is the difference between a virus cell and a bacteri ...
Development of an enhanced bovine viral diarrhea virus subunit
... for one year (Fig. 3a). Negative control animals did not develop Nabs against BVDV in all the time points analyzed; therefore, BVDV circulation throughout the experiment was discarded. Furthermore, only the animals from the positive control group showed anti NS3 antibodies, highlighting the ability ...
... for one year (Fig. 3a). Negative control animals did not develop Nabs against BVDV in all the time points analyzed; therefore, BVDV circulation throughout the experiment was discarded. Furthermore, only the animals from the positive control group showed anti NS3 antibodies, highlighting the ability ...
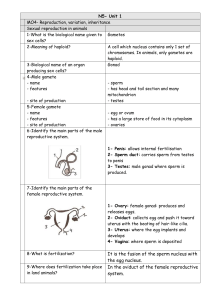
N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual
... releases eggs. 2- Oviduct: collects egg and push it toward uterus with the beating of hair-like cilia. 3- Uterus: where the egg implants and ...
... releases eggs. 2- Oviduct: collects egg and push it toward uterus with the beating of hair-like cilia. 3- Uterus: where the egg implants and ...
Bacteria vs. Viruses
... D. Primary and Secondary Immune Responses 1. The second time you are infected by a pathogen (foreign invader), your immune system works faster to fight it. WHY? ...
... D. Primary and Secondary Immune Responses 1. The second time you are infected by a pathogen (foreign invader), your immune system works faster to fight it. WHY? ...
An immune system is a collection of mechanisms within an organism
... Passive immunity is usually short-term, lasting between a few days and several months. Newborn infants have no prior exposure to microbes and are particularly vulnerable to infection. Several layers of passive protection are provided by the mother. During pregnancy, a particular type of antibody, ca ...
... Passive immunity is usually short-term, lasting between a few days and several months. Newborn infants have no prior exposure to microbes and are particularly vulnerable to infection. Several layers of passive protection are provided by the mother. During pregnancy, a particular type of antibody, ca ...