Viral Vaccines - Molecular Immunology
... • Infects human cells but some do not replicate • Better presentation of antigen • Generate T cell response Minuses •Can cause bad reactions •Can be problems with pre-exisiting immunity to virus •Often can only accommodate one or two antigens ...
... • Infects human cells but some do not replicate • Better presentation of antigen • Generate T cell response Minuses •Can cause bad reactions •Can be problems with pre-exisiting immunity to virus •Often can only accommodate one or two antigens ...
Antibody Kills 91% of HIV Strains
... this goal. One potential pitfall: There is evidence that Donor 45's cells took months or possibly even years to create the powerful antibodies. That means scientists might have to give repeated booster shots or devise other ways to speed up this process. Finally, there are experimental methods that ...
... this goal. One potential pitfall: There is evidence that Donor 45's cells took months or possibly even years to create the powerful antibodies. That means scientists might have to give repeated booster shots or devise other ways to speed up this process. Finally, there are experimental methods that ...
Annex I1/3 to the Certificate Νο 820
... Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA), anti-doublestranded DNA antibodies (anti-dsDNA), anti-extractable nuclear antigens antibodies (ENA) (SS-A, SS-B, RNP, Sm), antiscleroderma-70 antibodies (antitopoisomerase I) (Scl-70), anti-cardiolipin antibodies (anti-phospholipid), anti-β2glycoprotein I antibodies (an ...
... Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA), anti-doublestranded DNA antibodies (anti-dsDNA), anti-extractable nuclear antigens antibodies (ENA) (SS-A, SS-B, RNP, Sm), antiscleroderma-70 antibodies (antitopoisomerase I) (Scl-70), anti-cardiolipin antibodies (anti-phospholipid), anti-β2glycoprotein I antibodies (an ...
Pharmaceutical interventions
... Relatively better hygiene, nutritional status and availability of drugs for treating secondary complications might mitigate health impact ...
... Relatively better hygiene, nutritional status and availability of drugs for treating secondary complications might mitigate health impact ...
BIOL 495: Introduction to Immunology
... Specific immunities are referred to as our Adaptive immunity for which there are 2 branches: Humoral immunity Cell-mediated immunity ...
... Specific immunities are referred to as our Adaptive immunity for which there are 2 branches: Humoral immunity Cell-mediated immunity ...
Chapter 43 – Immune System
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? ...
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? ...
The Immune Response
... • The T-cells then bind to B-cells causing them to divide and produce plasma cells and memory B cells • Plasma cells secrete antibodies • Memory B cells and antibodies stay in the bloodstream and attack and mark the antigens quickly for destruction by macrophages the next time they enter the body • ...
... • The T-cells then bind to B-cells causing them to divide and produce plasma cells and memory B cells • Plasma cells secrete antibodies • Memory B cells and antibodies stay in the bloodstream and attack and mark the antigens quickly for destruction by macrophages the next time they enter the body • ...
31.4 Immunity and Technology
... – examples include vinegar and soap • Antibiotics kill pathogens inside the body. – target one specific bacterium or fungus – not effective against viruses ...
... – examples include vinegar and soap • Antibiotics kill pathogens inside the body. – target one specific bacterium or fungus – not effective against viruses ...
Immunity
... Phagocytes and Granulocytes Phagocytes are large white cells that can engulf and digest foreign invaders. They include monocytes, which circulate in the blood, and macrophages, which are found in tissues throughout the body, as well as neutrophils, cells that circulate in the blood but move into tis ...
... Phagocytes and Granulocytes Phagocytes are large white cells that can engulf and digest foreign invaders. They include monocytes, which circulate in the blood, and macrophages, which are found in tissues throughout the body, as well as neutrophils, cells that circulate in the blood but move into tis ...
TEST immune 2012 markscheme
... right ventricle has thinner walls than left ventricle / vice versa; atrio-ventricular valves / tricuspid and bicuspid valves — shown between atria and ventricles; aorta and pulmonary artery — shown leaving the appropriate ventricle with semilunar valves shown; pulmonary vein and vena cava — shown en ...
... right ventricle has thinner walls than left ventricle / vice versa; atrio-ventricular valves / tricuspid and bicuspid valves — shown between atria and ventricles; aorta and pulmonary artery — shown leaving the appropriate ventricle with semilunar valves shown; pulmonary vein and vena cava — shown en ...
Hermans HRC66 2006 (PDF 103kb)
... and tuberculosis, but that appropriately designed vaccines may be used in the future as effective therapies for a number of common disease conditions. “There is accumulating evidence that vaccines can be used therapeutically to treat conditions like cancer, allergy and autoimmune disease. For all of ...
... and tuberculosis, but that appropriately designed vaccines may be used in the future as effective therapies for a number of common disease conditions. “There is accumulating evidence that vaccines can be used therapeutically to treat conditions like cancer, allergy and autoimmune disease. For all of ...
Immunology - PharmaEuphoria
... Based upon the ability of antigens to carry out their functions, antigens are of two types complete antigens Incomplete antigens (haptens) A complete antigen is able to induce antibody formation & produce a specific and observable reaction with the antibody so produced. Haptens are substances which ...
... Based upon the ability of antigens to carry out their functions, antigens are of two types complete antigens Incomplete antigens (haptens) A complete antigen is able to induce antibody formation & produce a specific and observable reaction with the antibody so produced. Haptens are substances which ...
Specific Responses
... • An individual produces a supply of antibodies • Body produces antibodies as a result of infection, infection is stopped • Can be brought on by Immunization • Use of vaccination to expand cloning of B and T Cells • Most often are the pathogens themselves ...
... • An individual produces a supply of antibodies • Body produces antibodies as a result of infection, infection is stopped • Can be brought on by Immunization • Use of vaccination to expand cloning of B and T Cells • Most often are the pathogens themselves ...
Immune System
... • The Immune system must have the ability to distinguish between self and non-self molecules • Self Molecules- components of an organism’s body that can be distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Autoimmunity- immune reaction against self molecules • Non-self Molecules- recognize ...
... • The Immune system must have the ability to distinguish between self and non-self molecules • Self Molecules- components of an organism’s body that can be distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Autoimmunity- immune reaction against self molecules • Non-self Molecules- recognize ...
Functional genomics as a tool to define a molecular signature of
... FMDV vaccines • Inactivated virus vaccines • No cross-protection between serotypes • Multivalent vaccines to provide protection against the different serotypes • Challenge tests are needed to establish a PD50 (50% protective dose) value or protection • Challenge experiments requires appropriate bio ...
... FMDV vaccines • Inactivated virus vaccines • No cross-protection between serotypes • Multivalent vaccines to provide protection against the different serotypes • Challenge tests are needed to establish a PD50 (50% protective dose) value or protection • Challenge experiments requires appropriate bio ...
`immunisation` and `vaccine-preventable diseases`.
... disease (DHA 2012). It may have been the strength of the child’s immune system or lack of exposure to the wild virus that resulted in protection from disease. Proof that a vaccine provides protection needs to be obtained from controlled clinical trials with statistically significant numbers of vacci ...
... disease (DHA 2012). It may have been the strength of the child’s immune system or lack of exposure to the wild virus that resulted in protection from disease. Proof that a vaccine provides protection needs to be obtained from controlled clinical trials with statistically significant numbers of vacci ...
INMUNOLOGIA MOLECULAR
... • produce mAbs in vitro or with ascites • harvest culture media (supernatant) – in vitro material is less concentrated and contains bovine serum • ascites are tumors grown in peritoneal cavity – ascites fluid and sera contain high [mAb] – minor contamination with mouse IgG ...
... • produce mAbs in vitro or with ascites • harvest culture media (supernatant) – in vitro material is less concentrated and contains bovine serum • ascites are tumors grown in peritoneal cavity – ascites fluid and sera contain high [mAb] – minor contamination with mouse IgG ...
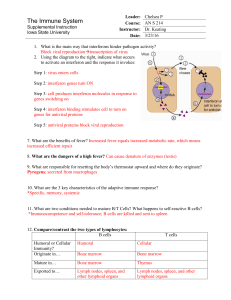
Title - Iowa State University
... 4: Subsequent challenge by same antigen 5: Secreted antibody molecules results in more rapid response 16. What is the purpose of creating memory cells? Memory cells recognize infection faster ...
... 4: Subsequent challenge by same antigen 5: Secreted antibody molecules results in more rapid response 16. What is the purpose of creating memory cells? Memory cells recognize infection faster ...
New Technologies in Vaccines
... with lowered capability to reproduce in humans. • Since Jenner’s time, live, attenuated vaccines have been developed for many other diseases, especially those caused by viruses. • In the United States, common live, attenuated vaccines including ...
... with lowered capability to reproduce in humans. • Since Jenner’s time, live, attenuated vaccines have been developed for many other diseases, especially those caused by viruses. • In the United States, common live, attenuated vaccines including ...
The Human Immune response
... are medicines that kill bacteria or fungi. Although vaccines are given to prevent illness caused by viruses, antibiotics are administered after a person is sick. They cure the disease. • Vaccines prevent viral infections. There is no treatment for viral infections, like there is for bacterial infect ...
... are medicines that kill bacteria or fungi. Although vaccines are given to prevent illness caused by viruses, antibiotics are administered after a person is sick. They cure the disease. • Vaccines prevent viral infections. There is no treatment for viral infections, like there is for bacterial infect ...
The antibody in real life
... The antibody in real life B-cells are specific white blood cells that produce antibodies (antibodies are long chain protein molecules) and these antibodies are able to attach to foreign elements within the blood, in classical immunology this attachment is often described as a lock and key mechanism. ...
... The antibody in real life B-cells are specific white blood cells that produce antibodies (antibodies are long chain protein molecules) and these antibodies are able to attach to foreign elements within the blood, in classical immunology this attachment is often described as a lock and key mechanism. ...
Expansion of in vitro potency testing: Case Study with Serovar Hardjo
... Split Hardjo into types • Hardjo-bovis isolated around the world • Hardjo type prajitno UK, Africa and ...
... Split Hardjo into types • Hardjo-bovis isolated around the world • Hardjo type prajitno UK, Africa and ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 17. What are antibodies? Discuss the various classes and their distribution. 18. Describe the principle and process of complement fixation and Western blot. 19. Write in detail on the primary and secondary lymphoid organs. 20. Give an account on the production and HAT selection of hybridoma cells. ...
... 17. What are antibodies? Discuss the various classes and their distribution. 18. Describe the principle and process of complement fixation and Western blot. 19. Write in detail on the primary and secondary lymphoid organs. 20. Give an account on the production and HAT selection of hybridoma cells. ...
Purposes and uses of epidemiology The ultimate purpose of
... Live vaccines (not used currently due to infection risk). Live, attenuated vaccines Killed or inactivated vaccines Toxoid vaccines Others Conjugate vaccines DNA vaccines Recombinant vector vaccines Live, attenuated vaccines: Live, attenuated vaccines contain a version of the living mi ...
... Live vaccines (not used currently due to infection risk). Live, attenuated vaccines Killed or inactivated vaccines Toxoid vaccines Others Conjugate vaccines DNA vaccines Recombinant vector vaccines Live, attenuated vaccines: Live, attenuated vaccines contain a version of the living mi ...