Antibody Production and Use in Immunodetection
... antibody molecules with slightly different amino acid sequences that can further tested to find the one with the most affinity for an antigen The recombinant DNA can be engineered to encode a human antibody molecule with the binding portion of a mouse. This type of antibody is called “humanized” o ...
... antibody molecules with slightly different amino acid sequences that can further tested to find the one with the most affinity for an antigen The recombinant DNA can be engineered to encode a human antibody molecule with the binding portion of a mouse. This type of antibody is called “humanized” o ...
link
... • Antigens: foreign proteins, usually part of virus or bacteria • Antibodies: Proteins made by immune cells that “recognize” or bind with particular antigens. Original diversity of antibodyproducing cells depends on recombination of genetic sequences during cell development • Macrophages: phagocytic ...
... • Antigens: foreign proteins, usually part of virus or bacteria • Antibodies: Proteins made by immune cells that “recognize” or bind with particular antigens. Original diversity of antibodyproducing cells depends on recombination of genetic sequences during cell development • Macrophages: phagocytic ...
Document
... • It takes hours before you start having symptoms you are infected with a cold virus. • Your body’s immune response T cells start working to identify the pathogen and B cells make antibodies to immobilize it. This immobilization process can take a week and then you feel better. • Viruses can’t be ki ...
... • It takes hours before you start having symptoms you are infected with a cold virus. • Your body’s immune response T cells start working to identify the pathogen and B cells make antibodies to immobilize it. This immobilization process can take a week and then you feel better. • Viruses can’t be ki ...
overview of ebola ii study design
... Vaccines for Ebola Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-Filo in Healthy Adults, Including Elderly Subjects, HIV-infected Subjects, and Healthy Children in Three Age Strata in Africa. The sponsor, in collaboration with Bavarian Nordic GmbH (BN) and in conjunction with an Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) consor ...
... Vaccines for Ebola Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-Filo in Healthy Adults, Including Elderly Subjects, HIV-infected Subjects, and Healthy Children in Three Age Strata in Africa. The sponsor, in collaboration with Bavarian Nordic GmbH (BN) and in conjunction with an Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) consor ...
overview of ebola ii study design
... Vaccines for Ebola Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-Filo in Healthy Adults, Including Elderly Subjects, HIV-infected Subjects, and Healthy Children in Three Age Strata in Africa. The sponsor, in collaboration with Bavarian Nordic GmbH (BN) and in conjunction with an Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) consor ...
... Vaccines for Ebola Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-Filo in Healthy Adults, Including Elderly Subjects, HIV-infected Subjects, and Healthy Children in Three Age Strata in Africa. The sponsor, in collaboration with Bavarian Nordic GmbH (BN) and in conjunction with an Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) consor ...
vaccination declination form
... I understand that due to my occupational exposure to blood or other potential infectious materials I may be at risk of acquiring Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. I have been given the opportunity at Goucher College to be vaccinated with Hepatitis B vaccine, at no charge to myself. However, I decli ...
... I understand that due to my occupational exposure to blood or other potential infectious materials I may be at risk of acquiring Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. I have been given the opportunity at Goucher College to be vaccinated with Hepatitis B vaccine, at no charge to myself. However, I decli ...
Nobel Prize of physiology or medicine (1984) (4) Part I The
... will present an outline of his work concerning skin diseases. The first theory: (Specificity is predetermined) ...
... will present an outline of his work concerning skin diseases. The first theory: (Specificity is predetermined) ...
Chapter 29 Human Papilloma Virus Infection and Immunity
... directed against the strains that cause 90% of cervical cancer • Vaccine effectiveness is 90-95% in most population trials; data is only from five years of experience • Need for regular use of Pap smear continues as protection exists for only four strains ...
... directed against the strains that cause 90% of cervical cancer • Vaccine effectiveness is 90-95% in most population trials; data is only from five years of experience • Need for regular use of Pap smear continues as protection exists for only four strains ...
VACCINOLOGY
... • In order to produce an immune response, live attenuated vaccines must replicate (grow) in the vaccinated person. A relatively small dose of virus or bacteria is given, which replicates in the body and creates enough virus to stimulate an immune response. • The immune response to a live attenuated ...
... • In order to produce an immune response, live attenuated vaccines must replicate (grow) in the vaccinated person. A relatively small dose of virus or bacteria is given, which replicates in the body and creates enough virus to stimulate an immune response. • The immune response to a live attenuated ...
A41-Immune Response
... Passive vs. Active Immunity Active Immunity – body’s own immune response is activated and produces antibodies; occurs when a pathogen or a vaccination is introduced into the body; long-term effect; once you get exposed to pathogen, you retain those antibodies for awhile, explaining why some disease ...
... Passive vs. Active Immunity Active Immunity – body’s own immune response is activated and produces antibodies; occurs when a pathogen or a vaccination is introduced into the body; long-term effect; once you get exposed to pathogen, you retain those antibodies for awhile, explaining why some disease ...
You should be able to find the information necessary to answer
... 18. What are cytokines and interleukins? Provide an example of an interleukin and explain its role in the immune system. ...
... 18. What are cytokines and interleukins? Provide an example of an interleukin and explain its role in the immune system. ...
Lecture outline : Immunity This is a protective or defense mechanism
... Active and Passive Immunity • Active immunity is resistance acquired after contact with • foreign antigens, eg, microorganisims • This contact may consist of : • Clinical or subclinical infections • Immunization with live or killed infectious agents or their antigens. • Exposure to microbial product ...
... Active and Passive Immunity • Active immunity is resistance acquired after contact with • foreign antigens, eg, microorganisims • This contact may consist of : • Clinical or subclinical infections • Immunization with live or killed infectious agents or their antigens. • Exposure to microbial product ...
Interference of passive and active immunity after vaccination of pigs
... and 14 weeks of age showed antigen-specific proliferation. Similar results were observed with IFN-γ secretion after exposure to live PRV. Following exposure to the PRV a higher number of cells from vaccinated animals expressed the CD25 marker, than those from unvaccinated ones. Summarizing, MDA may ...
... and 14 weeks of age showed antigen-specific proliferation. Similar results were observed with IFN-γ secretion after exposure to live PRV. Following exposure to the PRV a higher number of cells from vaccinated animals expressed the CD25 marker, than those from unvaccinated ones. Summarizing, MDA may ...
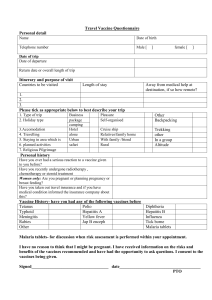
Travel Vaccination questionnaire
... Have you ever had a serious reaction to a vaccine given to you before? Have you recently undergone radiotherapy , chemotherapy or steroid treatment Women only: Are you pregnant or planning pregnancy or breast feeding? Have you taken out travel insurance and if you have medical condition informed the ...
... Have you ever had a serious reaction to a vaccine given to you before? Have you recently undergone radiotherapy , chemotherapy or steroid treatment Women only: Are you pregnant or planning pregnancy or breast feeding? Have you taken out travel insurance and if you have medical condition informed the ...
Section 18 Immunity in the Fetus and Newborn
... • A safe rule is that calves and foals should be vaccinated no earlier than 3 to 4 months of age followed by one or two revaccinations at 4-week ...
... • A safe rule is that calves and foals should be vaccinated no earlier than 3 to 4 months of age followed by one or two revaccinations at 4-week ...
International Journal of Livestock Research ISSN
... approach was used to develop a vaccine against the canine intestinal nematode Ancylostoma caninum (Miller, 1978) but it was observed that irradiation-attenuated larval vaccines developed against gastrointestinal nematodes did not protect young, susceptible stock against infection and were, therefore ...
... approach was used to develop a vaccine against the canine intestinal nematode Ancylostoma caninum (Miller, 1978) but it was observed that irradiation-attenuated larval vaccines developed against gastrointestinal nematodes did not protect young, susceptible stock against infection and were, therefore ...
Hepatitis B Form
... . Hygienists . Receptionists . Office Managers and Front Office Personnel Hepatitis B Vaccine ...
... . Hygienists . Receptionists . Office Managers and Front Office Personnel Hepatitis B Vaccine ...
Improved Sanitation - UCLA Fielding School of Public Health
... • Year-round access to vegetables and fruit (eliminates vitamin deficiency diseases such as beri beri) ...
... • Year-round access to vegetables and fruit (eliminates vitamin deficiency diseases such as beri beri) ...
Principles of Vaccination
... Lacking the gene Nef protected all monkeys for 2 years against massive dose of virus ...
... Lacking the gene Nef protected all monkeys for 2 years against massive dose of virus ...
Immune System
... • Natural passive immunity: mother passing antibodies through placenta and breast milk • Artificial passive immunity: injection of immunoglobulins in response to venom (snake bite) ...
... • Natural passive immunity: mother passing antibodies through placenta and breast milk • Artificial passive immunity: injection of immunoglobulins in response to venom (snake bite) ...
Immune System
... are coated with mucus; Mucus traps airborne pathogens & swept into the digestive system to be destroyed 3. Inflammation - Occurs when pathogens do enter the body (usually through skin); Blood vessels near wound expand; WBC leak from the vessels to invade the infected tissues; Phagocytes (wbc) engulf ...
... are coated with mucus; Mucus traps airborne pathogens & swept into the digestive system to be destroyed 3. Inflammation - Occurs when pathogens do enter the body (usually through skin); Blood vessels near wound expand; WBC leak from the vessels to invade the infected tissues; Phagocytes (wbc) engulf ...
Assignment I
... 1. What are different cells of immune system? Explain the difference between naïve and effector lymphocyte. 2. What is adaptive immunity? Give three differences between humoral and cell mediated immune response. 3. What is passive immunity? Discuss the differences between active and passive immunity ...
... 1. What are different cells of immune system? Explain the difference between naïve and effector lymphocyte. 2. What is adaptive immunity? Give three differences between humoral and cell mediated immune response. 3. What is passive immunity? Discuss the differences between active and passive immunity ...
Biology 2201
... thing that causes disease/immune response. Antigens Toxins that pathogens produce that cause harm to an organism. A foreign substance, when introduced into human body, stimulate formation of specific antibodies or sensitized lymphocytes ...
... thing that causes disease/immune response. Antigens Toxins that pathogens produce that cause harm to an organism. A foreign substance, when introduced into human body, stimulate formation of specific antibodies or sensitized lymphocytes ...