Introductory Psychology
... cases, make a “diagnosis” concerning where you believe brain damage has occurred. Case 1: A 56-year-old female has suffered a recent stroke. She speaks in a curious manner resembling fluent English but the phrases make no sense. You find that she comprehends your verbal or written instructions perfe ...
... cases, make a “diagnosis” concerning where you believe brain damage has occurred. Case 1: A 56-year-old female has suffered a recent stroke. She speaks in a curious manner resembling fluent English but the phrases make no sense. You find that she comprehends your verbal or written instructions perfe ...
Brain 2012 - student version
... Information from the left half of your field of vision goes to your right hemisphere, and information from the right half of your visual field goes to your left hemisphere, which usually controls speech. (Note, however, that each eye receives sensory information from both the right and left visual f ...
... Information from the left half of your field of vision goes to your right hemisphere, and information from the right half of your visual field goes to your left hemisphere, which usually controls speech. (Note, however, that each eye receives sensory information from both the right and left visual f ...
General PLTW Document
... sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and cold throughout the body. A specialized structure within the brain is the thalamus. With the exception of smell, the thalamus acts as a relay station for all the ...
... sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and cold throughout the body. A specialized structure within the brain is the thalamus. With the exception of smell, the thalamus acts as a relay station for all the ...
Lecture 6C
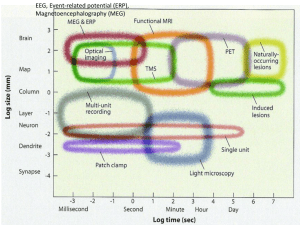
... – Injecting radioactive substance into the bloodstream, which is taken up by active parts of the brain. – Advantages: ability to track changing activity in the brain, fast – Disadvantages: expensive, requires sophisticated staff, must be near a cyclotron, relatively slow ...
... – Injecting radioactive substance into the bloodstream, which is taken up by active parts of the brain. – Advantages: ability to track changing activity in the brain, fast – Disadvantages: expensive, requires sophisticated staff, must be near a cyclotron, relatively slow ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory because decreased amounts of it in the brain are associated with the disease, Alzheimers. Neurotransmit ...
... neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory because decreased amounts of it in the brain are associated with the disease, Alzheimers. Neurotransmit ...
Ms. Setzer-The Brain!
... Split Brain Patients With the corpus callosum severed, objects (apple) presented in the right visual field can be named. Objects (pencil) in the left visual field cannot. ...
... Split Brain Patients With the corpus callosum severed, objects (apple) presented in the right visual field can be named. Objects (pencil) in the left visual field cannot. ...
1. What different types of attention exist? Name and describe at least
... a so called priority map of vistual stimuli. A priority map is a map of locations where attention should be directed based on stimulus salience and cognitive input. A related concept is the salience map; this maps the exogenous attention features of a stimulus scenario. A priority map can be through ...
... a so called priority map of vistual stimuli. A priority map is a map of locations where attention should be directed based on stimulus salience and cognitive input. A related concept is the salience map; this maps the exogenous attention features of a stimulus scenario. A priority map can be through ...
The Nervous System
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body ...
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body ...
How Does the Brain Learn Through Music?
... “ States should review their curriculum guidelines to ensure that they encourage adequate attention to and time for art and music, and should consider including measures of knowledge and skills in art and music among the multiple measures used for NCLB accountability.” ...
... “ States should review their curriculum guidelines to ensure that they encourage adequate attention to and time for art and music, and should consider including measures of knowledge and skills in art and music among the multiple measures used for NCLB accountability.” ...
A Data Mining Survey of the Allen Brain Atlas
... (on the order of 1,000 in a mouse and 10,000 in a human per system) that control fundamental behaviors by interacting with many areas of the brain, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and frontal cortex. When a biological organism experiences an important event in the environment, the activation of ...
... (on the order of 1,000 in a mouse and 10,000 in a human per system) that control fundamental behaviors by interacting with many areas of the brain, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and frontal cortex. When a biological organism experiences an important event in the environment, the activation of ...
Four Ways Analytics Think Like You
... power increasingly intelligent machines that perform advanced human tasks. It’s not science fiction —AI analytics are already used in many business applications. Here are four examples of analytics that imitate the way you think, and how they are used. ...
... power increasingly intelligent machines that perform advanced human tasks. It’s not science fiction —AI analytics are already used in many business applications. Here are four examples of analytics that imitate the way you think, and how they are used. ...
The Nervous System
... signal transmitted by a neuron • As signals move from one neuron to another, they must cross the synapse. This is the transition zone between two neurons (a very small gap) ...
... signal transmitted by a neuron • As signals move from one neuron to another, they must cross the synapse. This is the transition zone between two neurons (a very small gap) ...
Neurocognition Cognitive Neuroscience/neuropsychology
... functions,m such as motor activitiy, are associated with a specific area of the brain Aggregate Field Theory - functions also distributed in other brain areas Currently believed it is a little of both ...
... functions,m such as motor activitiy, are associated with a specific area of the brain Aggregate Field Theory - functions also distributed in other brain areas Currently believed it is a little of both ...
The Brain and the Nervous System
... Convoluted (folded, wrinkled) structure enables more tissue to fit The cortex provides flexibility in behavior Divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 paired lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal ...
... Convoluted (folded, wrinkled) structure enables more tissue to fit The cortex provides flexibility in behavior Divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 paired lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal ...
HOW CHILDREN LEARN pp
... 2 TYPES OF PERIODS IN WIRING THAT ARE CRITICAL TO LEARNING 1) CRITICAL PERIOD –THESE AR TIMES WHEN SOME PART OF THE BODY IS VULNERABLE TO A LACK OF STIMULATION. EX: BABY BORN WITH CATARACTS THAT ARE NOT REMOVED WITHING A FEW MONTHS WILL FOREVER BE BLIND BECAUSE THE VISION NEURONS DIE. 2) SENSITI ...
... 2 TYPES OF PERIODS IN WIRING THAT ARE CRITICAL TO LEARNING 1) CRITICAL PERIOD –THESE AR TIMES WHEN SOME PART OF THE BODY IS VULNERABLE TO A LACK OF STIMULATION. EX: BABY BORN WITH CATARACTS THAT ARE NOT REMOVED WITHING A FEW MONTHS WILL FOREVER BE BLIND BECAUSE THE VISION NEURONS DIE. 2) SENSITI ...
Neuro-transmitters
... synapses” (are naturally stimulated by the drug nicotine). Therefore, nicotine acts as an acetylcholine agonist. Has the effects of: ...
... synapses” (are naturally stimulated by the drug nicotine). Therefore, nicotine acts as an acetylcholine agonist. Has the effects of: ...
02_Neuroscience
... Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) 1. Pros: • High spatial sensitivity • Down to the mm! ...
... Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) 1. Pros: • High spatial sensitivity • Down to the mm! ...
Plasticity and Functional Recovery of the Brain After
... who have suffered brain trauma. The fact that we know that spontaneous brain recovery slows down after a few weeks, means that we are aware of when it may be necessary to start physical therapy to maintain improvements in functioning. Although the brain has the ability to fix itself to a certain ext ...
... who have suffered brain trauma. The fact that we know that spontaneous brain recovery slows down after a few weeks, means that we are aware of when it may be necessary to start physical therapy to maintain improvements in functioning. Although the brain has the ability to fix itself to a certain ext ...
Neuroscience
... Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles. Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. ...
... Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles. Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production. ...
mapping the brain - Scholastic Heads Up
... MRI scans of the brain have shown that people who have been using drugs for a long time have a smaller prefrontal cortex than people who have not been using drugs. The prefrontal cortex is the area where decision making occurs. ...
... MRI scans of the brain have shown that people who have been using drugs for a long time have a smaller prefrontal cortex than people who have not been using drugs. The prefrontal cortex is the area where decision making occurs. ...
Slides
... and varies in thickness from ~1-4 mm • The CORTEX is divided into 5 “lobes” (4 are named after the cranial bones which overlie them) ...
... and varies in thickness from ~1-4 mm • The CORTEX is divided into 5 “lobes” (4 are named after the cranial bones which overlie them) ...
Neuroanatomy - Kelley Kline
... medulla. Both pons & medulla form reticular formation & raphe system. ...
... medulla. Both pons & medulla form reticular formation & raphe system. ...
Nervous System
... Nerve • A group of neurons (specifically their axons) that are bundled together anywhere except the brain/spinal cord, is termed a nerve ...
... Nerve • A group of neurons (specifically their axons) that are bundled together anywhere except the brain/spinal cord, is termed a nerve ...