Development of the Brain
... eyes to the human brain Route of visual input to the two hemispheres of the brain. Note that the left hemisphere is connected to the left half of each retina and thus gets visual input from the right half of the world; the opposite is true of the right hemisphere. ...
... eyes to the human brain Route of visual input to the two hemispheres of the brain. Note that the left hemisphere is connected to the left half of each retina and thus gets visual input from the right half of the world; the opposite is true of the right hemisphere. ...
No Slide Title
... Sensations and location of body parts Unilateral Neglect - can sense the neglected side but fail to to attend to it. ...
... Sensations and location of body parts Unilateral Neglect - can sense the neglected side but fail to to attend to it. ...
Information Processing and Other Models of Human Learning
... But only 60 percent of left handed people have language functions in the left hemisphere Right hemisphere: spatial and holistic thought In normal populations, a division of labor ...
... But only 60 percent of left handed people have language functions in the left hemisphere Right hemisphere: spatial and holistic thought In normal populations, a division of labor ...
Chapter 14 - FacultyWeb
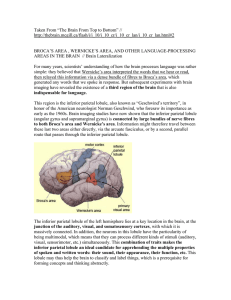
... Wernike’s area in the parietal lobe General interpretive area of the temporal lobe Primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe Broca’s area in the frontal lobe ...
... Wernike’s area in the parietal lobe General interpretive area of the temporal lobe Primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe Broca’s area in the frontal lobe ...
Motivation and Emotion
... – Develop emotional preference for stimuli to which have been unknowingly exposed . ...
... – Develop emotional preference for stimuli to which have been unknowingly exposed . ...
LeDoux outlines his theory of emotions and memory
... LeDoux has worked mostly with rats, pairing foot shock with a tone. He started with the assumption that the brain somehow pairs the tone and the shock in memory, thereby making the tone a harbinger of threat. The tone alone then triggers a fear response: It activates the autonomic nervous system, wh ...
... LeDoux has worked mostly with rats, pairing foot shock with a tone. He started with the assumption that the brain somehow pairs the tone and the shock in memory, thereby making the tone a harbinger of threat. The tone alone then triggers a fear response: It activates the autonomic nervous system, wh ...
Document
... A mirror neuron is a neuron that fires both when an animal acts and when the animal observes the same action performed by another.[1][2][3] Thus, the neuron "mirrors" the behavior of the other, as though the observer were itself acting. Such neurons have been directly observed in primatespecies.[4] ...
... A mirror neuron is a neuron that fires both when an animal acts and when the animal observes the same action performed by another.[1][2][3] Thus, the neuron "mirrors" the behavior of the other, as though the observer were itself acting. Such neurons have been directly observed in primatespecies.[4] ...
Language Processing in the Brain
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
Who You Know: Prominent Psychologists (Word Associations
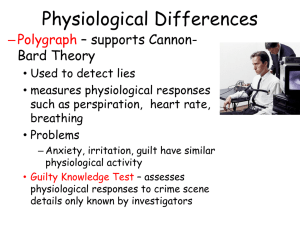
... Cannon-Bard – emotion is the result of the perception of a stimulus that causes both physiological changes and subjective feelings (physiological change and emotional response occur simultaneously) Schacter (Stanley) – two-factor theory re: emotion; need to have a cognitive label coupled with a phys ...
... Cannon-Bard – emotion is the result of the perception of a stimulus that causes both physiological changes and subjective feelings (physiological change and emotional response occur simultaneously) Schacter (Stanley) – two-factor theory re: emotion; need to have a cognitive label coupled with a phys ...
psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... 12. The thalamus receives information from the sensory neurons and routes it to the higher brain regions that control the senses. The thalamus can be said to function functions like________ switchboard. 14. Discuss the control of voluntary movement. 15. Judging and planning are enabled by the____ l ...
... 12. The thalamus receives information from the sensory neurons and routes it to the higher brain regions that control the senses. The thalamus can be said to function functions like________ switchboard. 14. Discuss the control of voluntary movement. 15. Judging and planning are enabled by the____ l ...
The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
... The brain stem & medulla The brain stem begins where the spinal cord enters the skull swelling slightly, forming the medulla. Here lies the controls for your heartbeat & ...
... The brain stem & medulla The brain stem begins where the spinal cord enters the skull swelling slightly, forming the medulla. Here lies the controls for your heartbeat & ...
Chapter 2 Notes
... Hemispheric specialization: Some cortical functions are localized to a particular hemisphere of the brain ...
... Hemispheric specialization: Some cortical functions are localized to a particular hemisphere of the brain ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... HORMONES CLOSELY ASSOCIATED WITH STRESS ARE PRODUCED BY WHAT GLAND? Adreanal ...
... HORMONES CLOSELY ASSOCIATED WITH STRESS ARE PRODUCED BY WHAT GLAND? Adreanal ...
Chapter 12 – Motivation and Emotion
... Moods – Affective responses that are typically longer-lasting than emotions and less likely to have a specific object or target Display rules – Cultural rules that govern the expression of emotion Dimensional view of emotions is concerned with “more this” and “less that” while classification is more ...
... Moods – Affective responses that are typically longer-lasting than emotions and less likely to have a specific object or target Display rules – Cultural rules that govern the expression of emotion Dimensional view of emotions is concerned with “more this” and “less that” while classification is more ...
Neural Basis of Emotion
... • Neurons at the pole of the temporal lobe below the cortex on the medial side • Greek name for almond shape • Has 3 nuclei, basolateral, corticomedial and central • Afferents from all lobes of neocortex & hippocampus and cingulate gyrus ...
... • Neurons at the pole of the temporal lobe below the cortex on the medial side • Greek name for almond shape • Has 3 nuclei, basolateral, corticomedial and central • Afferents from all lobes of neocortex & hippocampus and cingulate gyrus ...
The Human Brain
... below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
... below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
File
... Cerebrum, the part of the brain that lies just beneath the skull, it divided into the right and left cerebral hemispheres. It is responsible for many activities such as calculation, contemplation, learning, emotions and memory A thick band of axons known as corpus callosum enables the right and left ...
... Cerebrum, the part of the brain that lies just beneath the skull, it divided into the right and left cerebral hemispheres. It is responsible for many activities such as calculation, contemplation, learning, emotions and memory A thick band of axons known as corpus callosum enables the right and left ...
{ How Neurosciences help us to understand some (psycho)therapeutic processes
... Vital to cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision-making, empathy, and emotion. ACC is involved in the processing of the affective dimension of pain responsible for rendering new memories permanent. ...
... Vital to cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision-making, empathy, and emotion. ACC is involved in the processing of the affective dimension of pain responsible for rendering new memories permanent. ...
AJA Teaching - Neuroscience
... Conditions in the uterus can give rise to life-long changes in genetic material. People in their sixties who were conceived during the Hunger Winter of 1944-45 in the Netherlands have been found to have a different molecular setting for a gene which influences growth. Researchers from the LUMC are ...
... Conditions in the uterus can give rise to life-long changes in genetic material. People in their sixties who were conceived during the Hunger Winter of 1944-45 in the Netherlands have been found to have a different molecular setting for a gene which influences growth. Researchers from the LUMC are ...
myers Chapter 02 review game
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
Brain Anatomy “Science erases what was previously true.”
... • The anterior cingulate is a neural alarm system that signals when something is wrong or when an autonomic process should get conscious attention. It is particularly active during physical and social pain, probably carrying the emotional component. It also fires when others experience pain (em ...
... • The anterior cingulate is a neural alarm system that signals when something is wrong or when an autonomic process should get conscious attention. It is particularly active during physical and social pain, probably carrying the emotional component. It also fires when others experience pain (em ...
The Scientific Method - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
Review Sheet 1 scientific method and neurobiology
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
Slide ()
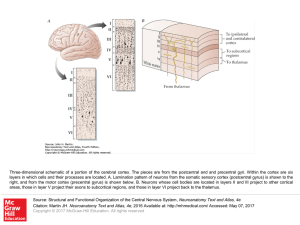
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...