PDF Version of module
... Now that we are working in the rational numbers – the integers together with all positive and negative fractions – we finally have a system that is closed under all four operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division (except by zero). They are also closed under the operation of tak ...
... Now that we are working in the rational numbers – the integers together with all positive and negative fractions – we finally have a system that is closed under all four operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division (except by zero). They are also closed under the operation of tak ...
Test - Mu Alpha Theta
... Start with any positive integer (ex. 4,229,301) and count the number of even digits, E, the number of odd digits, O, and their sum, E + O. Create a new number by concatenating the three values (in the order E, O, E+O) into one number and dropping any leading 0’s (for our example it would be 437). Fo ...
... Start with any positive integer (ex. 4,229,301) and count the number of even digits, E, the number of odd digits, O, and their sum, E + O. Create a new number by concatenating the three values (in the order E, O, E+O) into one number and dropping any leading 0’s (for our example it would be 437). Fo ...
Math Unit 2 Study Guide
... Math Unit 8 Study Guide Math Unit 8 Test is soon! To be ready for the test, be sure you can do the following types of problems. Your math journal and all the Study Links from Unit 8 will also help you prepare. Determine if mixed numbers and fractions are equivalent (ex: 1 ½ is equal to 3/2) Multiply ...
... Math Unit 8 Study Guide Math Unit 8 Test is soon! To be ready for the test, be sure you can do the following types of problems. Your math journal and all the Study Links from Unit 8 will also help you prepare. Determine if mixed numbers and fractions are equivalent (ex: 1 ½ is equal to 3/2) Multiply ...
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ALGORITHMS
... complete quotient α0 = 1/(α − a). This method is called the basic method. In the course of this process precision is lost, and one has to take precautions to stop before the partial quotients become incorrect. Lehmer [6] gives a safe stopping-criterion, and a trick to reduce the amount of multi-leng ...
... complete quotient α0 = 1/(α − a). This method is called the basic method. In the course of this process precision is lost, and one has to take precautions to stop before the partial quotients become incorrect. Lehmer [6] gives a safe stopping-criterion, and a trick to reduce the amount of multi-leng ...
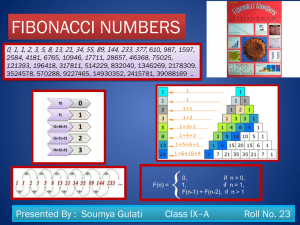
25 soumya gulati-finalmath project-fa3-fibonacci
... Multiply the two middle or inner numbers (here 2 x 3 = 6); Double the result ( 6 x 2 = 12). [SIDE a] a = 2 Fn+1 x Fn+2 Multiply together the two outer numbers ( 1 x 5 = 5). [SIDE b] b = F n x Fn+3 The hypotenuse is found by adding together the squares of the inner two numbers (here 22=4 and 32=9 and ...
... Multiply the two middle or inner numbers (here 2 x 3 = 6); Double the result ( 6 x 2 = 12). [SIDE a] a = 2 Fn+1 x Fn+2 Multiply together the two outer numbers ( 1 x 5 = 5). [SIDE b] b = F n x Fn+3 The hypotenuse is found by adding together the squares of the inner two numbers (here 22=4 and 32=9 and ...