Evolution of low- and intermediate mass stars
... cores by a combination of the proton-proton (pp) chain (in which four protons unite to form a 4He nucleus) and the CNO tri-cycle (in which the same process is catalyzed by carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen). The former is the more important in low-mass stars, ≤1 M⊙, and the latter in more massive stars. ...
... cores by a combination of the proton-proton (pp) chain (in which four protons unite to form a 4He nucleus) and the CNO tri-cycle (in which the same process is catalyzed by carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen). The former is the more important in low-mass stars, ≤1 M⊙, and the latter in more massive stars. ...
2009 - thephysicsteacher.ie
... Why do stars and the lights of distant objects twinkle? The twinkling of stars, also known as stellar scintillation, is due to atmospheric turbulence. The turbulence of the air is caused by heat changing the density and thus the refractive index of moving pockets of air in the earth's atmosphere. Th ...
... Why do stars and the lights of distant objects twinkle? The twinkling of stars, also known as stellar scintillation, is due to atmospheric turbulence. The turbulence of the air is caused by heat changing the density and thus the refractive index of moving pockets of air in the earth's atmosphere. Th ...
Astronomy Astrophysics
... that no infrared study (beyond 1 µm) on mass segregation of M 67 has been previously made. The present approach is as well a feasibility study to explore the usefulness of the 2MASS public database for such investigations. Owing to the sky coverage which is crucial to properly take into account the ...
... that no infrared study (beyond 1 µm) on mass segregation of M 67 has been previously made. The present approach is as well a feasibility study to explore the usefulness of the 2MASS public database for such investigations. Owing to the sky coverage which is crucial to properly take into account the ...
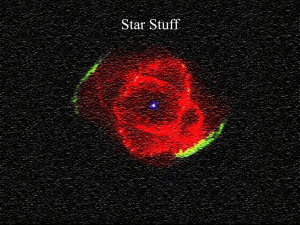
superbubbles vs super-galactic winds
... appearance of reverse shocks whenever it meets an obstacle cloud or when its thermal pressure become lower than that of the surrounding gas, as it is the case within superbubbles. There, the high pressure acquired by the swept up ISM becomes larger than that of the freely expanding ejecta (the free ...
... appearance of reverse shocks whenever it meets an obstacle cloud or when its thermal pressure become lower than that of the surrounding gas, as it is the case within superbubbles. There, the high pressure acquired by the swept up ISM becomes larger than that of the freely expanding ejecta (the free ...
Coronal Mass Ejections and Angular Momentum Loss in Young Stars
... disks? In Aarnio et al. (2010), we did not find evidence for this. Second, if there is not a star-disk link, how do the loops remain stable for the multiple rotation periods over which the X-ray flares are observed to decay? We showed in Aarnio et al. (2012) that when modeled as hot prominences, the ...
... disks? In Aarnio et al. (2010), we did not find evidence for this. Second, if there is not a star-disk link, how do the loops remain stable for the multiple rotation periods over which the X-ray flares are observed to decay? We showed in Aarnio et al. (2012) that when modeled as hot prominences, the ...
A Note on the Mixing Length Theory and Massive Star Evolution
... Figure 1 displays (in dotted lines) 3 envelope models of a 20 M with effective temperatures: 3600 K (top panels), 3900 K (middle panels) and 4200 K (lower panels). The dotted lines represent the results obtained with the convective envelope for late type supergiants following the original MLT (Vite ...
... Figure 1 displays (in dotted lines) 3 envelope models of a 20 M with effective temperatures: 3600 K (top panels), 3900 K (middle panels) and 4200 K (lower panels). The dotted lines represent the results obtained with the convective envelope for late type supergiants following the original MLT (Vite ...
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational
... apparent luminosity or brightness (what we can measure) versus their temperature produces an H-R diagram which can be compared with a H-R diagram for a clusters whose distance is known from other methods (parallax, which we discussed in module 6). And from the inverse square law for light ( light in ...
... apparent luminosity or brightness (what we can measure) versus their temperature produces an H-R diagram which can be compared with a H-R diagram for a clusters whose distance is known from other methods (parallax, which we discussed in module 6). And from the inverse square law for light ( light in ...
6. Stellar Spectra
... Nr,s/N of the lower level of the lines indicated in the upper panel against temperature T (given in units of 1000 K along the top). The pressure was taken constant at Pe = Ne k T = 131 dyne cm-2. The T-axis is adjusted to the abscissa of the upper diagram in order to obtain a correspondence between ...
... Nr,s/N of the lower level of the lines indicated in the upper panel against temperature T (given in units of 1000 K along the top). The pressure was taken constant at Pe = Ne k T = 131 dyne cm-2. The T-axis is adjusted to the abscissa of the upper diagram in order to obtain a correspondence between ...
FP11: DRAKE et al. - Astronomical Institute WWW Homepage
... We estimated the effective temperature, surface gravity, mass, luminosity, and radius of this star, as well as the inclination angle of the rotational axis. The ambipolar diffusion of hydrogen which affects much more strongly light ionized particles may enhance significantly the Li abundance and mig ...
... We estimated the effective temperature, surface gravity, mass, luminosity, and radius of this star, as well as the inclination angle of the rotational axis. The ambipolar diffusion of hydrogen which affects much more strongly light ionized particles may enhance significantly the Li abundance and mig ...
Expanding the Catalog: Considering the Importance
... begins to cool and compress due to decreased internal pressure from the end of core hydrogen burning. This compression reheats the core, causing the observed fluctuations in L and Tef f . A detailed scrutiny of the figures reveals a slight crossover that occurs in the late MS for both carbon and mag ...
... begins to cool and compress due to decreased internal pressure from the end of core hydrogen burning. This compression reheats the core, causing the observed fluctuations in L and Tef f . A detailed scrutiny of the figures reveals a slight crossover that occurs in the late MS for both carbon and mag ...
Star
... Mini Black Holes can Evaporate Mini BH produce strong tides (stellar BH don’t have strong enough tides) Lose energy by work of tidal gravity on material outside the event horizon Since energy = mass, they lose mass and get smaller Evaporate ...
... Mini Black Holes can Evaporate Mini BH produce strong tides (stellar BH don’t have strong enough tides) Lose energy by work of tidal gravity on material outside the event horizon Since energy = mass, they lose mass and get smaller Evaporate ...
Document
... potential energy into thermal energy. (2) Luminosity decreases as gravitational contraction shrinks protostar’s size, while convection remains the dominant way by which thermal energy moves from the interior to the surface. (3) Surface temperature rises and luminosity levels off when energy transpor ...
... potential energy into thermal energy. (2) Luminosity decreases as gravitational contraction shrinks protostar’s size, while convection remains the dominant way by which thermal energy moves from the interior to the surface. (3) Surface temperature rises and luminosity levels off when energy transpor ...
Model Solutions
... to us than star B, then its apparent brightness will be greater than star B. Now if both the stars are at same distance and have same mass, then star A will appear brighter if it is intrinsically bright i.e. it is hotter (blue is hotter than yellow) than star B. the size and the mass of the star doe ...
... to us than star B, then its apparent brightness will be greater than star B. Now if both the stars are at same distance and have same mass, then star A will appear brighter if it is intrinsically bright i.e. it is hotter (blue is hotter than yellow) than star B. the size and the mass of the star doe ...
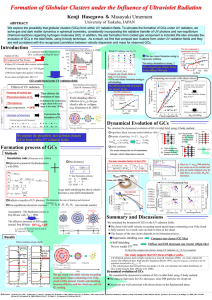
Poster - unist
... We explore the possibility that globular clusters (GCs) form within UV radiation fields. To simulate the formation of GCs under UV radiation, we solve gas and dark matter dynamics in spherical symmetry, consistently incorporating the radiative transfer of UV photons and non-equilibrium chemical reac ...
... We explore the possibility that globular clusters (GCs) form within UV radiation fields. To simulate the formation of GCs under UV radiation, we solve gas and dark matter dynamics in spherical symmetry, consistently incorporating the radiative transfer of UV photons and non-equilibrium chemical reac ...
Modeling White Dwarf Star Magnetization - Blogs at H-SC
... The evolutionary of stars generally starts with the main sequence stars. Main sequence stars go through nuclear fusion of hydrogen at the core to generate high pressure that can prevent the stars from collapsing by the gravity. When the nuclear fusion ends, main sequence stars with small mass procee ...
... The evolutionary of stars generally starts with the main sequence stars. Main sequence stars go through nuclear fusion of hydrogen at the core to generate high pressure that can prevent the stars from collapsing by the gravity. When the nuclear fusion ends, main sequence stars with small mass procee ...
Document
... the core stops. Overall contraction of the star and increase in the temperature. 2, The hydrogen shell burning stage and increase in the mass of the helium core. • The helium core starts to shrink, if its mass exceeds ~0.1 solar mass. Expansion of the envelop (evolution to the red giant) The de ...
... the core stops. Overall contraction of the star and increase in the temperature. 2, The hydrogen shell burning stage and increase in the mass of the helium core. • The helium core starts to shrink, if its mass exceeds ~0.1 solar mass. Expansion of the envelop (evolution to the red giant) The de ...
Chapter 1-3
... • neutrinos, which escape from the interior without interaction. So far, the Sun is the only (nonexploding) star from which neutrinos have been detected. • oscillations, i.e. stellar seismology. Many stars oscillate, and their frequency spectrum contains information about the speed of sound waves in ...
... • neutrinos, which escape from the interior without interaction. So far, the Sun is the only (nonexploding) star from which neutrinos have been detected. • oscillations, i.e. stellar seismology. Many stars oscillate, and their frequency spectrum contains information about the speed of sound waves in ...
Mass-radius Relations for Helium White Dwarfs
... emission, that is M-R relations of the fully degenerate helium WDs for masses greater than 0.4 M are presented. Figure 1. shows the M-R relations for helium WDs calculated by Hamada and Salpeter [5], Althaus and Benvenuto [1], Vennes et al. [11] and our results. In this figure, plus sign shows our ...
... emission, that is M-R relations of the fully degenerate helium WDs for masses greater than 0.4 M are presented. Figure 1. shows the M-R relations for helium WDs calculated by Hamada and Salpeter [5], Althaus and Benvenuto [1], Vennes et al. [11] and our results. In this figure, plus sign shows our ...
Stellar Masses
... the core H-burning phase that accounts for 90% of a star’s life. These values have been taken from stellar models computed with a composition that is initially solar. We list the stellar parameters at the beginning and end of the main-sequence lifetimes, except for the lowest-mass stars, for which w ...
... the core H-burning phase that accounts for 90% of a star’s life. These values have been taken from stellar models computed with a composition that is initially solar. We list the stellar parameters at the beginning and end of the main-sequence lifetimes, except for the lowest-mass stars, for which w ...
Can We Successfully Apply A Solar Thin-Flux
... Details of the simulation: Initial field strength of flux tube from linear stability analysis. For the solar case yields field strength of 105 G. Total flux set to 1022 Mx. Semi-implicit numerical scheme for eq. of motion of a thin, adiabatic flux tube. ...
... Details of the simulation: Initial field strength of flux tube from linear stability analysis. For the solar case yields field strength of 105 G. Total flux set to 1022 Mx. Semi-implicit numerical scheme for eq. of motion of a thin, adiabatic flux tube. ...
Disk
... outflow detection rate = 40-90% in massive YSOs (luminous IRAS sources, UC HIIs, H2O masers,…) (Osterloh et al., Beuther et al., Zhang et al., …) disks should be widespread! ...
... outflow detection rate = 40-90% in massive YSOs (luminous IRAS sources, UC HIIs, H2O masers,…) (Osterloh et al., Beuther et al., Zhang et al., …) disks should be widespread! ...
Distances
... uniform photometric properties of stars. One powerful uniformity is provided by main sequence stars, which exhibit a well-defined relationship between luminosity and surface temperature. The relative distances of two star clusters can be estimated by comparing their color-magnitude diagrams; neglect ...
... uniform photometric properties of stars. One powerful uniformity is provided by main sequence stars, which exhibit a well-defined relationship between luminosity and surface temperature. The relative distances of two star clusters can be estimated by comparing their color-magnitude diagrams; neglect ...
Compact objects for everyone: I. White dwarf stars - Rose
... and radiation creating enough pressure to oppose gravitational contraction. Thermonuclear fusion, the thermally-induced combining of nuclei as they tunnel through the Coulomb barrier, is initially responsible for supporting stars against gravitational contraction. The ultimate fate of the star depen ...
... and radiation creating enough pressure to oppose gravitational contraction. Thermonuclear fusion, the thermally-induced combining of nuclei as they tunnel through the Coulomb barrier, is initially responsible for supporting stars against gravitational contraction. The ultimate fate of the star depen ...
The First Stars in the Universe - Scientific American
... clumps are not very sensitive to the assumed cosmological conditions (for example, the exact nature of the initial density fluctuations). In fact, the predicted masses depend primarily on the physics of the hydrogen molecule and only secondarily on the cosmological model or simulation technique. One ...
... clumps are not very sensitive to the assumed cosmological conditions (for example, the exact nature of the initial density fluctuations). In fact, the predicted masses depend primarily on the physics of the hydrogen molecule and only secondarily on the cosmological model or simulation technique. One ...