James Mullens, is Professor of Religious Studies
... interest that later expanded to include other endangered cultures around the world. He became especially intrigued by the possibilities for expanding human consciousness offered by religions such as Hinduism and Buddhism. After completing his MA, he traveled to India on a Shastri Institute exchange ...
... interest that later expanded to include other endangered cultures around the world. He became especially intrigued by the possibilities for expanding human consciousness offered by religions such as Hinduism and Buddhism. After completing his MA, he traveled to India on a Shastri Institute exchange ...
buddhism
... There are three principal sources of spiritual guidance recognized by Buddhists as scriptural or doctrinal authorities: Theravada Buddhism: Tripitaka — The Tripitaka is a canon of the southern schools of Buddhism written in India within 500 years of the time of the Buddha. It is divided into three s ...
... There are three principal sources of spiritual guidance recognized by Buddhists as scriptural or doctrinal authorities: Theravada Buddhism: Tripitaka — The Tripitaka is a canon of the southern schools of Buddhism written in India within 500 years of the time of the Buddha. It is divided into three s ...
Hinduism and Buddhism - individualsandsocieties
... 3. Achieving Moksha is the Goal of Life – This is union with Brahma – To achieve must free yourself from selfish desires ...
... 3. Achieving Moksha is the Goal of Life – This is union with Brahma – To achieve must free yourself from selfish desires ...
Buddhism Notes
... A religion of Asia growing out of the teaching of Buddha that suffering is inherent in life and that one can be liberated from it by mental and moral self-purification. Buddhist spiritual leader of Tibet Buddhist teachings about the cause and elimination of suffering The practice of training your mi ...
... A religion of Asia growing out of the teaching of Buddha that suffering is inherent in life and that one can be liberated from it by mental and moral self-purification. Buddhist spiritual leader of Tibet Buddhist teachings about the cause and elimination of suffering The practice of training your mi ...
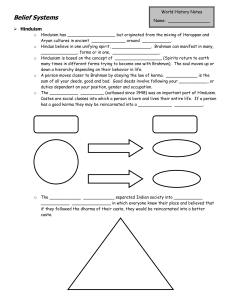
Belief Systems
... Hindus believe in one unifying spirit, _______________. Brahman can manifest in many, ______________, forms or in one, __________________. Hindusism is based on the concept of __________________ (Spirits return to earth many times in different forms trying to become one with Brahman). The soul moves ...
... Hindus believe in one unifying spirit, _______________. Brahman can manifest in many, ______________, forms or in one, __________________. Hindusism is based on the concept of __________________ (Spirits return to earth many times in different forms trying to become one with Brahman). The soul moves ...
Buddhism - deanworldhistory
... The Law of Karma • Every action results in another action • Positive actions result in good karma; negative ones lead to bad karma. • "According to the seed that’s sown, So is the fruit you reap there from, Doer of good will gather good, Doer of evil, evil reaps, Down is the seed and thou shalt tas ...
... The Law of Karma • Every action results in another action • Positive actions result in good karma; negative ones lead to bad karma. • "According to the seed that’s sown, So is the fruit you reap there from, Doer of good will gather good, Doer of evil, evil reaps, Down is the seed and thou shalt tas ...
History of Buddhism - Welcometomrfrankland
... Bhikkhu A Buddhist monk who wanders about depending upon others for his basic necessities . Bodhi A Buddhist term for the wisdom by which one attains enlightenment. Bodhisattva In Mahayana Buddhism, one who postpones attaining nirvana in order to help others achieve this goal. In Theravada Buddhism, ...
... Bhikkhu A Buddhist monk who wanders about depending upon others for his basic necessities . Bodhi A Buddhist term for the wisdom by which one attains enlightenment. Bodhisattva In Mahayana Buddhism, one who postpones attaining nirvana in order to help others achieve this goal. In Theravada Buddhism, ...
Name Class Date Two major religions, Hinduism and Buddhism
... The Buddha taught the Four Noble Truths, which explain life as suffering and give ways to cure it. The fourth truth is to follow the Eightfold Path. The Eightfold Path includes “right aspirations” and directs people in achieving the goals of a moral life and enlightenment. Buddhists strive to achiev ...
... The Buddha taught the Four Noble Truths, which explain life as suffering and give ways to cure it. The fourth truth is to follow the Eightfold Path. The Eightfold Path includes “right aspirations” and directs people in achieving the goals of a moral life and enlightenment. Buddhists strive to achiev ...
Item 8.F
... 2. Suffering comes from craving. We crave for pleasure and for things to be as they are not. We don’t accept life as it is. 3. Suffering has an end. 4. The way to end suffering can be found in the Eight-Fold Path and the Middle Way. The Middle Way rejects all extremes of thought, emotion, action, an ...
... 2. Suffering comes from craving. We crave for pleasure and for things to be as they are not. We don’t accept life as it is. 3. Suffering has an end. 4. The way to end suffering can be found in the Eight-Fold Path and the Middle Way. The Middle Way rejects all extremes of thought, emotion, action, an ...
Buddhism - Hayden Emerson
... Buddhist religion. Balanced and happy living leads to harmony with others. Suffering is a part of life because human nature, along with the world, is not perfect. ...
... Buddhist religion. Balanced and happy living leads to harmony with others. Suffering is a part of life because human nature, along with the world, is not perfect. ...
Buddhism - Hudson City Schools
... The oldest school of Buddhism. Buddhism A monastic life Focused on wisdom & meditation. ...
... The oldest school of Buddhism. Buddhism A monastic life Focused on wisdom & meditation. ...
Buddhism…
... informed look at Buddhism. Includes original comic strip expressing Buddhist teachings, an interfaith forum discussing Buddhist ideas from the perspective of other religions, and many other contributions from a wide variety of folks: http://www.dharmathecat.com/ Learn more about Tibetan Buddhism at ...
... informed look at Buddhism. Includes original comic strip expressing Buddhist teachings, an interfaith forum discussing Buddhist ideas from the perspective of other religions, and many other contributions from a wide variety of folks: http://www.dharmathecat.com/ Learn more about Tibetan Buddhism at ...
Buddhist Revision Part 1
... Left family became an ascetic gave it up reached Enlightenment. ( highest achievement) Nirvana Reincarnation ( reborn) Karma. ( the consequences of your actions) ...
... Left family became an ascetic gave it up reached Enlightenment. ( highest achievement) Nirvana Reincarnation ( reborn) Karma. ( the consequences of your actions) ...
Buddhism
... – Hell: In the hell realm, the worst place, you find the most suffering. • One day you might be walking through a forest, when all the leaves on a tree turn into razor blades and fall, cutting you into a million pieces. You cry out in pain, and your hell body resurrects, so you can be killed over an ...
... – Hell: In the hell realm, the worst place, you find the most suffering. • One day you might be walking through a forest, when all the leaves on a tree turn into razor blades and fall, cutting you into a million pieces. You cry out in pain, and your hell body resurrects, so you can be killed over an ...
Key Beliefs of Buddhism
... Because Buddhists do not believe in the soul there is no belief in reincarnation. Instead Buddhists believe that after death there is a rebirth or rebecoming of the stream of constantly changing energy and therefore some aspects of previous lives may remain, explaining child prodigies and giving ris ...
... Because Buddhists do not believe in the soul there is no belief in reincarnation. Instead Buddhists believe that after death there is a rebirth or rebecoming of the stream of constantly changing energy and therefore some aspects of previous lives may remain, explaining child prodigies and giving ris ...
BUDDHA`S TEACHINGS - Castle High School
... “For some people, religions which are based on belief in a Creator God have the most powerful effect on their ethical life and serve to motivate them to act in an ethical and sound way. However, this might not be the case for every person. For others, the Buddhist tradition, which does not emphasize ...
... “For some people, religions which are based on belief in a Creator God have the most powerful effect on their ethical life and serve to motivate them to act in an ethical and sound way. However, this might not be the case for every person. For others, the Buddhist tradition, which does not emphasize ...
4.5_Buddhism
... grasping and fixating on a self and experiences. Specifically, samsara refers to the process of cycling through one rebirth after another within the six realms of existence,[a] where each realm can be understood as physical realm or a psychological state characterized by a particular type of sufferi ...
... grasping and fixating on a self and experiences. Specifically, samsara refers to the process of cycling through one rebirth after another within the six realms of existence,[a] where each realm can be understood as physical realm or a psychological state characterized by a particular type of sufferi ...
Buddhism
... The Buddha then began to teach others that the causes of human suffering are their desires for material things. The Buddha taught that there are four noble truths and an eightfold path which will lead to enlightenment or Nirvana. ...
... The Buddha then began to teach others that the causes of human suffering are their desires for material things. The Buddha taught that there are four noble truths and an eightfold path which will lead to enlightenment or Nirvana. ...
INTRODUCTION TO BUDDHISM
... This course is an introduction to Buddhism, one of the major religions of the world. Founded by Siddgartha Gautama or the Buddha in 6th century B.C., Buddhism has spread from South Asia to other parts of Asia into a great variety of distinctive schools of thoughts. Although at the present world Asia ...
... This course is an introduction to Buddhism, one of the major religions of the world. Founded by Siddgartha Gautama or the Buddha in 6th century B.C., Buddhism has spread from South Asia to other parts of Asia into a great variety of distinctive schools of thoughts. Although at the present world Asia ...
Suffering
... • Missionaries are people who work to spread their religious beliefs. They played an important role because they traveled to distant lands to spread Buddhist teachings. ...
... • Missionaries are people who work to spread their religious beliefs. They played an important role because they traveled to distant lands to spread Buddhist teachings. ...
Aim: how did Buddhism become a major religion in Asia?
... • Founder: Siddhartha Gautama (563BCE – 483BCE), or Buddha, which means "enlightened one." • Four Noble Truths Siddhartha's philosophy of the nature of human suffering and its relation to desire is articulated by these four statements: 1. Life is full of pain and suffering. 2. Human desire causes th ...
... • Founder: Siddhartha Gautama (563BCE – 483BCE), or Buddha, which means "enlightened one." • Four Noble Truths Siddhartha's philosophy of the nature of human suffering and its relation to desire is articulated by these four statements: 1. Life is full of pain and suffering. 2. Human desire causes th ...
Buddhism
.jpeg?width=300)
Buddhism /ˈbudɪzəm/ is a nontheistic religion or philosophy (Sanskrit: dharma; Pali: धम्म dhamma) that encompasses a variety of traditions, beliefs and spiritual practices largely based on teachings attributed to Gautama Buddha, commonly known as the Buddha (""the awakened one"").According to Buddhist tradition, the Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern part of the Indian subcontinent sometime between the 6th and 4th centuries BCE. He is recognized by Buddhists as an awakened or enlightened teacher who shared his insights to help sentient beings end their suffering through the elimination of ignorance and craving. Buddhists believe that this is accomplished through the direct understanding and perception of dependent origination and the Four Noble Truths.Two major extant branches of Buddhism are generally recognized by scholars: Theravada (""The School of the Elders"") and Mahayana (""The Great Vehicle""). Theravada has a widespread following in Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia (Thailand, Burma, Laos, Cambodia, etc.). Mahayana is found throughout East Asia (China, Korea, Japan, Vietnam, Singapore, Taiwan, etc.) and includes the traditions of Pure Land, Zen, Nichiren Buddhism, Shingon, and Tiantai (Tendai). Vajrayana, a body of teachings attributed to Indian siddhas, may be viewed as a third branch or merely a part of Mahayana. Tibetan Buddhism, as practiced in Tibet, Bhutan, Nepal, the Himalayan region of India, Kalmykia, Mongolia and surrounding areas, preserves the Vajrayana teachings of eighth century India. Buddhists number between an estimated 488 million and 535 million, making it one of the world's major religions.In Theravada Buddhism, the ultimate goal is the attainment of the sublime state of Nirvana, achieved by practicing the Noble Eightfold Path (also known as the Middle Way), thus escaping what is seen as a cycle of suffering and rebirth. Mahayana Buddhism instead aspires to Buddhahood via the bodhisattva path, a state wherein one remains in this cycle to help other beings reach awakening. Tibetan Buddhism aspires to Buddhahood or rainbow body.Buddhist schools vary on the exact nature of the path to liberation, the importance and canonicity of various teachings and scriptures, and especially their respective practices. One consistent belief held by all Buddhist schools is the lack of a creator deity. The foundations of Buddhist tradition and practice are the Three Jewels: the Buddha, the Dharma (the teachings), and the Sangha (the community). Taking ""refuge in the triple gem"" has traditionally been a declaration and commitment to being on the Buddhist path, and in general distinguishes a Buddhist from a non-Buddhist. Other practices may include following ethical precepts; support of the monastic community; renouncing conventional living and becoming a monastic; the development of mindfulness and practice of meditation; cultivation of higher wisdom and discernment; study of scriptures; devotional practices; ceremonies; and in the Mahayana tradition, invocation of buddhas and bodhisattvas.