Rule 1. - Thutong
... Exercise 9. During the summer months, one ice cream truck visits Jeannette's neighbourhood every 4 days and another ice cream truck visits her neighbourhood every 5 days. If both trucks visited today, when is the next time both trucks will visit on the same day? ...
... Exercise 9. During the summer months, one ice cream truck visits Jeannette's neighbourhood every 4 days and another ice cream truck visits her neighbourhood every 5 days. If both trucks visited today, when is the next time both trucks will visit on the same day? ...
Class IX TO X
... ECONOMICS 1. Make an assignment on sectors of Indian Economy with suitable pictures (Refer page-19) 2. Learn question answers of Chapter – 1 Story of Village Palampur. ...
... ECONOMICS 1. Make an assignment on sectors of Indian Economy with suitable pictures (Refer page-19) 2. Learn question answers of Chapter – 1 Story of Village Palampur. ...
Significant Figures
... In carrying out calculations, the general rule is that the accuracy of a calculated result is limited by the least accurate measurement involved in the calculation. (1) In addition and subtraction, the result is rounded off to the last common digit occurring furthest to the right in all components. ...
... In carrying out calculations, the general rule is that the accuracy of a calculated result is limited by the least accurate measurement involved in the calculation. (1) In addition and subtraction, the result is rounded off to the last common digit occurring furthest to the right in all components. ...
Week 3 Solutions, Jan 21 st
... Each element of X is in exactly one of these sets. The element 1 could be in any of the four sets, the element 2 could be in any of the four sets and the element 3 could be in any of the four sets. Each assignment of elements to sets uniquely generates a ‘triple’ (A, B, C) e.g. if 1, 2, 3 were all i ...
... Each element of X is in exactly one of these sets. The element 1 could be in any of the four sets, the element 2 could be in any of the four sets and the element 3 could be in any of the four sets. Each assignment of elements to sets uniquely generates a ‘triple’ (A, B, C) e.g. if 1, 2, 3 were all i ...
2-1
... and d are integers and d 0. Any fraction can be written as a decimal by dividing the numerator by the denominator. If the division ends or terminates, because the remainder is zero, then the decimal is a terminating decimal. ...
... and d are integers and d 0. Any fraction can be written as a decimal by dividing the numerator by the denominator. If the division ends or terminates, because the remainder is zero, then the decimal is a terminating decimal. ...
SigFig ppt - Ms. Dougalas
... 1. Write down the given amount. Don’t forget the units! 2. Multiply by a fraction. 3. Use the fraction as a conversion factor. Determine if the top or the bottom should be the same unit as the given so that it will cancel. 4. Put a unit on the opposite side that will be the new unit. If you don’t kn ...
... 1. Write down the given amount. Don’t forget the units! 2. Multiply by a fraction. 3. Use the fraction as a conversion factor. Determine if the top or the bottom should be the same unit as the given so that it will cancel. 4. Put a unit on the opposite side that will be the new unit. If you don’t kn ...
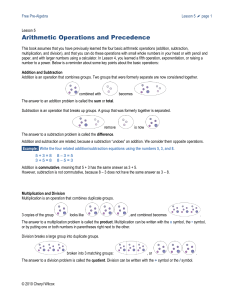
Elementary arithmetic
Elementary arithmetic is the simplified portion of arithmetic that includes the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It should not be confused with elementary function arithmetic.Elementary arithmetic starts with the natural numbers and the written symbols (digits) that represent them. The process for combining a pair of these numbers with the four basic operations traditionally relies on memorized results for small values of numbers, including the contents of a multiplication table to assist with multiplication and division.Elementary arithmetic also includes fractions and negative numbers, which can be represented on a number line.