Types of Numbers - English for Maths
... divided into N, produced whole numbers. The factors/divisors of a number N, less the number itself, are referred to as the aliquot parts, aliquot divisors, or proper divisors, of the number.) Equivalently, N is also abundant if the sum, S(N), of "all" its divisors is greater than 2N. From the follow ...
... divided into N, produced whole numbers. The factors/divisors of a number N, less the number itself, are referred to as the aliquot parts, aliquot divisors, or proper divisors, of the number.) Equivalently, N is also abundant if the sum, S(N), of "all" its divisors is greater than 2N. From the follow ...
Chapter 6
... are integers and b 0. Two rational numbers are equal if and only if they can be represented by equivalent fractions. • Pg 355 ex. • What is not a rational number? ...
... are integers and b 0. Two rational numbers are equal if and only if they can be represented by equivalent fractions. • Pg 355 ex. • What is not a rational number? ...
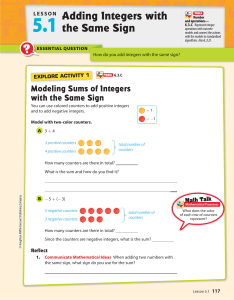
5.1 Adding Integers with the Same Sign
... 24. Multistep On Monday, Jan made withdrawals of $25, $45, and $75 from her savings account. On the same day, her twin sister Julie made withdrawals of $35, $55, and $65 from her savings account. a. Write a sum of negative integers to show Jan’s withdrawals on Monday. Find the total amount Jan withd ...
... 24. Multistep On Monday, Jan made withdrawals of $25, $45, and $75 from her savings account. On the same day, her twin sister Julie made withdrawals of $35, $55, and $65 from her savings account. a. Write a sum of negative integers to show Jan’s withdrawals on Monday. Find the total amount Jan withd ...
Chapter 1 - Pearson Education
... To round 72,304 to the nearest thousand, observe that the digit in the hundreds place is 3. Since the digit is less than 5, we do not add 1 to the digit in the thousands place. The number 72,304 rounded to the nearest thousand is 72,000. ...
... To round 72,304 to the nearest thousand, observe that the digit in the hundreds place is 3. Since the digit is less than 5, we do not add 1 to the digit in the thousands place. The number 72,304 rounded to the nearest thousand is 72,000. ...
Analyzing and Comparing Montgomery Multiplication Algorithms
... Roughly speaking, we may organize the algorithms based on two factors. The rst factor is whether multiplication and reduction are separated or integrated. In the separated approach, we rst multiply a and b, then perform a Montgomery reduction. In the integrated approach, we alternate between mult ...
... Roughly speaking, we may organize the algorithms based on two factors. The rst factor is whether multiplication and reduction are separated or integrated. In the separated approach, we rst multiply a and b, then perform a Montgomery reduction. In the integrated approach, we alternate between mult ...
Lesson 13 - UnboundEd
... hundredths. The second solution shows decomposing 100 to take out 10 to make 1. They then added 9 ones with the 1 they made from 6 tenths and 4 tenths to get 10 ones and 13 hundredths. The third solution shows converting tenths to hundredths in one step. Then, they decomposed the hundredths to m ...
... hundredths. The second solution shows decomposing 100 to take out 10 to make 1. They then added 9 ones with the 1 they made from 6 tenths and 4 tenths to get 10 ones and 13 hundredths. The third solution shows converting tenths to hundredths in one step. Then, they decomposed the hundredths to m ...
How do we teach your child`s math
... extend the diagonal lines down and add up each diagonal section; starting from right to left. First addition is 2, then 9 + 1 + 2 = 12; so write down 2 and carry 1 to the next column, then add 9 + 1 + 8 and carried 1 = 19, carry 1 over then add 6 + carried 1 = 7. Then read numbers eg 7922 ! ...
... extend the diagonal lines down and add up each diagonal section; starting from right to left. First addition is 2, then 9 + 1 + 2 = 12; so write down 2 and carry 1 to the next column, then add 9 + 1 + 8 and carried 1 = 19, carry 1 over then add 6 + carried 1 = 7. Then read numbers eg 7922 ! ...
ppt
... Binary numbers • Digits are 1 and 0 (a binary digit is called a bit) 1 = true 0 = false • MSB –most significant bit • LSB –least significant bit • Bit numbering: ...
... Binary numbers • Digits are 1 and 0 (a binary digit is called a bit) 1 = true 0 = false • MSB –most significant bit • LSB –least significant bit • Bit numbering: ...
Chapter 1 Digital Systems and Numbers System
... Example. Using 2’s complement, subtract: (A) (1010)2 from (1101)2 , (B) (1101)2 from (1010)2. Solution. The 1’s complement of 1010 is 0101.The 2’s complement is 0101 + 1 = 0110. We will add it to ...
... Example. Using 2’s complement, subtract: (A) (1010)2 from (1101)2 , (B) (1101)2 from (1010)2. Solution. The 1’s complement of 1010 is 0101.The 2’s complement is 0101 + 1 = 0110. We will add it to ...
GCF
... Greatest Common Factor (GCF) – The largest number that is a factor for 2 or more numbers. Multiple – The product of a number and any other whole number. Least Common Multiple (LCM) – The smallest number that is a multiple of 2 or more numbers. Factor Tree – A diagram used to decompose a composite nu ...
... Greatest Common Factor (GCF) – The largest number that is a factor for 2 or more numbers. Multiple – The product of a number and any other whole number. Least Common Multiple (LCM) – The smallest number that is a multiple of 2 or more numbers. Factor Tree – A diagram used to decompose a composite nu ...
Topic 10 powerpoint
... Deciding Where to Start Sample: Kim has 142 cotton balls and is making a snowman craft that uses 3 cotton balls per snowman. How many crafts will Kim make? How many cotton balls will Kim have left? • What division problem can solve this? • Divide hundreds. How many hundreds can you put in a group? ...
... Deciding Where to Start Sample: Kim has 142 cotton balls and is making a snowman craft that uses 3 cotton balls per snowman. How many crafts will Kim make? How many cotton balls will Kim have left? • What division problem can solve this? • Divide hundreds. How many hundreds can you put in a group? ...
Elementary arithmetic
Elementary arithmetic is the simplified portion of arithmetic that includes the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It should not be confused with elementary function arithmetic.Elementary arithmetic starts with the natural numbers and the written symbols (digits) that represent them. The process for combining a pair of these numbers with the four basic operations traditionally relies on memorized results for small values of numbers, including the contents of a multiplication table to assist with multiplication and division.Elementary arithmetic also includes fractions and negative numbers, which can be represented on a number line.