program 1 rem program to find the sum and product of two numbers
... INPUT "Enter the radius of the circle in cm: "; Radius REM Area of a circle is 3.14 * r * r Area = 3.14 * Radius * Radius Circumference = 2 * 3.14 * Radius PRINT "Area and circumference of Circle with radius "; Radius; "are "; Area; "and "; Circumference; "respectively." END PROGRAM 4 REM To find th ...
... INPUT "Enter the radius of the circle in cm: "; Radius REM Area of a circle is 3.14 * r * r Area = 3.14 * Radius * Radius Circumference = 2 * 3.14 * Radius PRINT "Area and circumference of Circle with radius "; Radius; "are "; Area; "and "; Circumference; "respectively." END PROGRAM 4 REM To find th ...
factors - WordPress.com
... The quotient 11 is less than the divisor 13, so we stop No factors are found, therefore, 149 is a prime number (c) The following is a table of prime numbers up to the beginning of 4-digit prime numbers. ...
... The quotient 11 is less than the divisor 13, so we stop No factors are found, therefore, 149 is a prime number (c) The following is a table of prime numbers up to the beginning of 4-digit prime numbers. ...
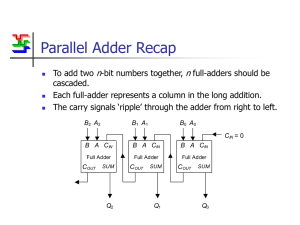
Binary Addition & Subtraction
... Subtracting 2 is equivalent to adding 6 Subtracting x is equivalent to adding 8-x ...
... Subtracting 2 is equivalent to adding 6 Subtracting x is equivalent to adding 8-x ...
Fractions (part 1) 2016
... distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers 1–100 with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. For example, express 36 + 8 as 4 (9 + 2). ...
... distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers 1–100 with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. For example, express 36 + 8 as 4 (9 + 2). ...
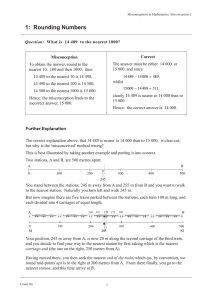
1: Rounding Numbers
... To understand why the rule works we look at its individual component parts – it is best to tackle this by applying the principal of finding something similar which we can cope with, and then working out the difference between this and the case in hand. Applying this method, we multiply first the num ...
... To understand why the rule works we look at its individual component parts – it is best to tackle this by applying the principal of finding something similar which we can cope with, and then working out the difference between this and the case in hand. Applying this method, we multiply first the num ...
2.4 BCD 2.5 Signed numbers
... • Offset Binary is where one subtracts K (usually half the largest possible number) from the representation to get the value. • Has the advantage that the number sequence from the most negative to the most positive is a simple binary progression, which makes it a natural for binary counters. • note ...
... • Offset Binary is where one subtracts K (usually half the largest possible number) from the representation to get the value. • Has the advantage that the number sequence from the most negative to the most positive is a simple binary progression, which makes it a natural for binary counters. • note ...
Elementary arithmetic
Elementary arithmetic is the simplified portion of arithmetic that includes the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It should not be confused with elementary function arithmetic.Elementary arithmetic starts with the natural numbers and the written symbols (digits) that represent them. The process for combining a pair of these numbers with the four basic operations traditionally relies on memorized results for small values of numbers, including the contents of a multiplication table to assist with multiplication and division.Elementary arithmetic also includes fractions and negative numbers, which can be represented on a number line.