03-30 7.1 Decimals, 7.2 Adding and Subtracting Decimals
... that each piece (cube, rod, flat,...) is 10 times the size of the last. Since each place value in a decimal is still 10 times the next, we can use base-ten blocks, but in a different way. ...
... that each piece (cube, rod, flat,...) is 10 times the size of the last. Since each place value in a decimal is still 10 times the next, we can use base-ten blocks, but in a different way. ...
Math 7 Notes – Part A: Rational Numbers Real Numbers
... Add 2 zeros to .82 so both numbers will have 4 digits to the right of the decimal point. .8032 and .8200 now both have 4 digits to the right of the decimal point (or we can say both are now expressed to the tenthousandths place). Since 8200 is larger than 8032, then .82 > .8032 Example: Compare .62 ...
... Add 2 zeros to .82 so both numbers will have 4 digits to the right of the decimal point. .8032 and .8200 now both have 4 digits to the right of the decimal point (or we can say both are now expressed to the tenthousandths place). Since 8200 is larger than 8032, then .82 > .8032 Example: Compare .62 ...
Number Theory: Links to the School Curriculum
... will, at the most, be size p – 1. For example 1/7 = 1 ÷ 7. If we carry out the division a remainder of 1 will appear on the first division, a remainder of 1 will appear again after six divisions. We call this a cycle of size six. However when we write 1/11 in decimal form, the cycle starts again aft ...
... will, at the most, be size p – 1. For example 1/7 = 1 ÷ 7. If we carry out the division a remainder of 1 will appear on the first division, a remainder of 1 will appear again after six divisions. We call this a cycle of size six. However when we write 1/11 in decimal form, the cycle starts again aft ...
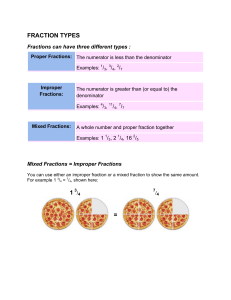
Fractions and Mixed Numbers
... If ever you get a fraction that you can still find both the numerator and the denominator in one row of your multiplication chart...do the steps again with the new numerator and denominator. This is called Reducing to Lowest Terms. ...
... If ever you get a fraction that you can still find both the numerator and the denominator in one row of your multiplication chart...do the steps again with the new numerator and denominator. This is called Reducing to Lowest Terms. ...
Rules for dividing whole numbers
... Numbers divisible by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if the last digit of the number is 0 or 5. Numbers divisible by 6: A number is divisible by 6 if it is divisible by both 2 and 3. You can use the rules above to determine if a number is divisible by 2 or 3. Example: Is the number 31254 divisible by ...
... Numbers divisible by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if the last digit of the number is 0 or 5. Numbers divisible by 6: A number is divisible by 6 if it is divisible by both 2 and 3. You can use the rules above to determine if a number is divisible by 2 or 3. Example: Is the number 31254 divisible by ...
Elementary arithmetic
Elementary arithmetic is the simplified portion of arithmetic that includes the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It should not be confused with elementary function arithmetic.Elementary arithmetic starts with the natural numbers and the written symbols (digits) that represent them. The process for combining a pair of these numbers with the four basic operations traditionally relies on memorized results for small values of numbers, including the contents of a multiplication table to assist with multiplication and division.Elementary arithmetic also includes fractions and negative numbers, which can be represented on a number line.