Review Sheet Filled Out
... Can’t tell where an electron is at any moment in time – the uncertainty principle There’s more – the list could be long! ...
... Can’t tell where an electron is at any moment in time – the uncertainty principle There’s more – the list could be long! ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
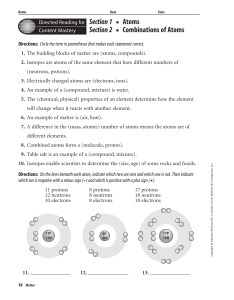
... 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an element determine how the element will change when it reacts with another element. 6. An example of matter is (air, heat). 7. A difference in the (mass, atomic) number of atoms means the atoms are of ...
... 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an element determine how the element will change when it reacts with another element. 6. An example of matter is (air, heat). 7. A difference in the (mass, atomic) number of atoms means the atoms are of ...
The History of Quantum Mechanics
... quantum state) provided the reason for electrons in atoms being arranged in shells with the maximum number of electrons being 2, 8, 18, 32… etc, from the first to the nth shell. This principle is significant for the fact that it explains why matter occupies space exclusively for itself and does no ...
... quantum state) provided the reason for electrons in atoms being arranged in shells with the maximum number of electrons being 2, 8, 18, 32… etc, from the first to the nth shell. This principle is significant for the fact that it explains why matter occupies space exclusively for itself and does no ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... FIRST SEMESTER – NOVEMBER 2010 PH 1812 - ELECTRODYNAMICS Date : 30-10-10 Time : 1:00 - 4:00 ...
... FIRST SEMESTER – NOVEMBER 2010 PH 1812 - ELECTRODYNAMICS Date : 30-10-10 Time : 1:00 - 4:00 ...
bio and abstract
... A revolution in electronics is in view, with the comtemporary evolution of the two novel disciplines, spintronics and molecular electronics. A fundamental link between these two fields can be established using molecular magnetic materials and, in particular, single-molecule magnets, which combine t ...
... A revolution in electronics is in view, with the comtemporary evolution of the two novel disciplines, spintronics and molecular electronics. A fundamental link between these two fields can be established using molecular magnetic materials and, in particular, single-molecule magnets, which combine t ...
Document
... quantum state) provided the reason for electrons in atoms being arranged in shells with the maximum number of electrons being 2, 8, 18, 32… etc, from the first to the nth shell. This principle is significant for the fact that it explains why matter occupies space exclusively for itself and does no ...
... quantum state) provided the reason for electrons in atoms being arranged in shells with the maximum number of electrons being 2, 8, 18, 32… etc, from the first to the nth shell. This principle is significant for the fact that it explains why matter occupies space exclusively for itself and does no ...
1 Electrons in Atoms
... molecular bonds: the spectrum of bonds between the two extremes of atomic bonding. polar molecules: many molecules having dissimilar atoms may have electric dipole moments and are thus polar. van der Waals bond : an interaction between the electric dipole moments of two atoms or molecules. hydrogen ...
... molecular bonds: the spectrum of bonds between the two extremes of atomic bonding. polar molecules: many molecules having dissimilar atoms may have electric dipole moments and are thus polar. van der Waals bond : an interaction between the electric dipole moments of two atoms or molecules. hydrogen ...
Andrew York
... The study of topological quantum fluids has emerged over the last decade or so as an interesting application of Quantum Field Theory. The Hall fluid is an example of one such fluid, and describes a system in which a collection of electrons move in a plane in the presence of a magnetic field B direc ...
... The study of topological quantum fluids has emerged over the last decade or so as an interesting application of Quantum Field Theory. The Hall fluid is an example of one such fluid, and describes a system in which a collection of electrons move in a plane in the presence of a magnetic field B direc ...
Minh Binh Nguyen Talk Announcement
... Artificial low dimensional systems such as quantum dots, quantum wires, and quantum wells have been significantly broadening mankind's knowledge and experience on the quantum nano-world. However, in many cases, going toward low dimensionality requires to sacrifice a degree of freedom which is an int ...
... Artificial low dimensional systems such as quantum dots, quantum wires, and quantum wells have been significantly broadening mankind's knowledge and experience on the quantum nano-world. However, in many cases, going toward low dimensionality requires to sacrifice a degree of freedom which is an int ...
Consider the following solution to the hydrogen atom problem
... magnetic field, a result known as the Paschen-Bach effect is realized. In the PaschenBach effect the perturbation produced by the external magnetic field is large enough so that spin-orbit coupling can be ignored, but smaller than the Coulomb interaction, so the Paschen-Bach can be treated as a pert ...
... magnetic field, a result known as the Paschen-Bach effect is realized. In the PaschenBach effect the perturbation produced by the external magnetic field is large enough so that spin-orbit coupling can be ignored, but smaller than the Coulomb interaction, so the Paschen-Bach can be treated as a pert ...
Chemistry is a material science
... change. Substances undergoing a physical change may have an alter state of matter or changed shape, but never a change in ___________ of the matter itself. When H2O(l) as a liquid freezes it is H2O(s) as a solid, but there is no change is the fixed ________ of H:O in H2O. This indicates there is not ...
... change. Substances undergoing a physical change may have an alter state of matter or changed shape, but never a change in ___________ of the matter itself. When H2O(l) as a liquid freezes it is H2O(s) as a solid, but there is no change is the fixed ________ of H:O in H2O. This indicates there is not ...
T. Dammak - TU-MRS
... We have prepared new semiconductor (C4H16N3)CuCl5 crystals which are self-assembled organic–inorganic hybrid materials. The grown crystals have been studied by X-ray diffraction, infrared absorption and Raman scattering. We found that the title compound, abbreviated 2C6PbBr4, crystallises in a two-d ...
... We have prepared new semiconductor (C4H16N3)CuCl5 crystals which are self-assembled organic–inorganic hybrid materials. The grown crystals have been studied by X-ray diffraction, infrared absorption and Raman scattering. We found that the title compound, abbreviated 2C6PbBr4, crystallises in a two-d ...
2016_Goswami_Partha_physicsgoswami@gmail
... coupling(RSOC), and the exchange coupling. We report the effect of the non-magnetic impurity scattering on stand-alone, mono-layer silicene (MLS) first taking into account intra- and inter-valley scattering processes. Our investigation have shown that, as long as the impurity strength parameter V 0 ...
... coupling(RSOC), and the exchange coupling. We report the effect of the non-magnetic impurity scattering on stand-alone, mono-layer silicene (MLS) first taking into account intra- and inter-valley scattering processes. Our investigation have shown that, as long as the impurity strength parameter V 0 ...
matter unified - Swedish Association for New Physics
... Hopefully this issue is more distinct and clear in its performance. The new web address is: ...
... Hopefully this issue is more distinct and clear in its performance. The new web address is: ...
Condensed matter physics

Condensed matter physics is a branch of physics that deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by using physical laws. In particular, these include the laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism and statistical mechanics.The most familiar condensed phases are solids and liquids, while more exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on atomic lattices, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in cold atomic systems. The study of condensed matter physics involves measuring various material properties via experimental probes along with using techniques of theoretical physics to develop mathematical models that help in understanding physical behavior.The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists identify themselves as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division at the American Physical Society. The field overlaps with chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology, and relates closely to atomic physics and biophysics. Theoretical condensed matter physics shares important concepts and techniques with theoretical particle and nuclear physics.A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography, metallurgy, elasticity, magnetism, etc., were treated as distinct areas, until the 1940s when they were grouped together as solid state physics. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquids was added to this list, forming the basis for the new, related specialty of condensed matter physics. According to physicist Phil Anderson, the term was coined by him and Volker Heine when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge from ""Solid state theory"" to ""Theory of Condensed Matter"" in 1967, as they felt it did not exclude their interests in the study of liquids, nuclear matter and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name ""condensed matter"", it had been present in Europe for some years, most prominently in the form of a journal published in English, French, and German by Springer-Verlag titled Physics of Condensed Matter, which was launched in 1963. The funding environment and Cold War politics of the 1960s and 1970s were also factors that lead some physicists to prefer the name ""condensed matter physics"", which emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, over ""solid state physics"", which was often associated with the industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics.References to ""condensed"" state can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 ""Kinetic theory of liquids"" book, Yakov Frenkel proposed that ""The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies"". As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of ""condensed bodies"".