Physics 2, 20 (2009) Classifying multiferroics: Mechanisms and
... and ions are responsible for the charge effects, whereas electron spins govern magnetic properties There are, however, cases where these degrees of freedom couple strongly. For example, in the new, large field of spintronics, the effects of spins on the transport properties of solids (and vice versa ...
... and ions are responsible for the charge effects, whereas electron spins govern magnetic properties There are, however, cases where these degrees of freedom couple strongly. For example, in the new, large field of spintronics, the effects of spins on the transport properties of solids (and vice versa ...
A POSSIBLE ENHANCEMENT MECHANISM OF NUCLEAR FUSION
... Hitherto, we discussed the possibility of enhanced nuclear fusions. Our discussion heavily depends on the string currents. But the state of the currents near surface severely depends on the shape of surface. To make good condition for our purpose we must make the surface skillfully. Recently, the pr ...
... Hitherto, we discussed the possibility of enhanced nuclear fusions. Our discussion heavily depends on the string currents. But the state of the currents near surface severely depends on the shape of surface. To make good condition for our purpose we must make the surface skillfully. Recently, the pr ...
Theoretical Calculation of Enthalpy of reactions involved in PZ
... done on the optimized gas phase configurations with the SM 5.4A [4] solvation model. These calculations were done by using Spartan 08. These optimized structures are used for density functional theoretical calculations by using B3LYP functional at 6-311++G (d, p) basis set level for both gaseous pha ...
... done on the optimized gas phase configurations with the SM 5.4A [4] solvation model. These calculations were done by using Spartan 08. These optimized structures are used for density functional theoretical calculations by using B3LYP functional at 6-311++G (d, p) basis set level for both gaseous pha ...
Designer materials render objects nearly invisible to
... 1–4 cm across, had lifetimes up to 8 seconds, moved at speeds of 5–30 cm/s, and decayed with no trace. The figures show one such ball, at 80-ms intervals, passing through a small gap under an electrical conductor. The experiments were done in conditions not very different from those found in nature: ...
... 1–4 cm across, had lifetimes up to 8 seconds, moved at speeds of 5–30 cm/s, and decayed with no trace. The figures show one such ball, at 80-ms intervals, passing through a small gap under an electrical conductor. The experiments were done in conditions not very different from those found in nature: ...
Topic 4: Materials - Education Umbrella
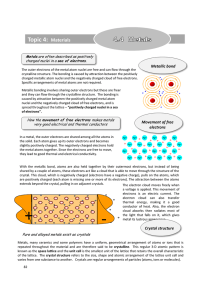
... shared by a couple of atoms, these electrons act like a cloud that is able to move through the structure of the crystal. This cloud, which is negatively charged (electrons have a negative charge), pulls on the atoms, which are positively charged (each atom is missing one or more of its electrons). T ...
... shared by a couple of atoms, these electrons act like a cloud that is able to move through the structure of the crystal. This cloud, which is negatively charged (electrons have a negative charge), pulls on the atoms, which are positively charged (each atom is missing one or more of its electrons). T ...
homework1-06 - Rose
... The directions of these two forces on the antiproton are opposite. FE points up whereas, using the right-hand rule, FB points down. Hence, ...
... The directions of these two forces on the antiproton are opposite. FE points up whereas, using the right-hand rule, FB points down. Hence, ...
Chapter 14 Nuclear Physics Applications. Home Work Solutions
... The total energy produced in full cycle is the sum of all the Q-Values of th individual reactions in the cycle: Q = Q2 + Q2 + Q3 + Q4 + Q5 + Q6 ...
... The total energy produced in full cycle is the sum of all the Q-Values of th individual reactions in the cycle: Q = Q2 + Q2 + Q3 + Q4 + Q5 + Q6 ...
Collimation and guiding of fast electrons in laser
... sources, and Fast Ignition ICF. In many of these areas a highly collimated flow of fast electrons is desirable. In the case of Fast Ignition, collimation may be crucial to the energetic viability of the scheme. Recent laser-solid experiments [7,8] indicate that the divergence of the fast electron be ...
... sources, and Fast Ignition ICF. In many of these areas a highly collimated flow of fast electrons is desirable. In the case of Fast Ignition, collimation may be crucial to the energetic viability of the scheme. Recent laser-solid experiments [7,8] indicate that the divergence of the fast electron be ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... (SEC) level to cover more advanced concepts in chemistry which are dealt with in a broad manner. Most of the concepts studied at intermediate level will not be developed to the same depth and with the same rigour as at the Advanced Matriculation level. It is hoped that a general overview of chemistr ...
... (SEC) level to cover more advanced concepts in chemistry which are dealt with in a broad manner. Most of the concepts studied at intermediate level will not be developed to the same depth and with the same rigour as at the Advanced Matriculation level. It is hoped that a general overview of chemistr ...
Document
... work related problems; realize ampere and coulomb are practically defined using this experimental setup 10 realize that weak magnetic fields around wires can be strengthened by wrapping them to make coils; describe magnetic field around coil of many loops; identify solenoid, electromagnet; realize m ...
... work related problems; realize ampere and coulomb are practically defined using this experimental setup 10 realize that weak magnetic fields around wires can be strengthened by wrapping them to make coils; describe magnetic field around coil of many loops; identify solenoid, electromagnet; realize m ...
Condensed matter physics

Condensed matter physics is a branch of physics that deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by using physical laws. In particular, these include the laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism and statistical mechanics.The most familiar condensed phases are solids and liquids, while more exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on atomic lattices, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in cold atomic systems. The study of condensed matter physics involves measuring various material properties via experimental probes along with using techniques of theoretical physics to develop mathematical models that help in understanding physical behavior.The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists identify themselves as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division at the American Physical Society. The field overlaps with chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology, and relates closely to atomic physics and biophysics. Theoretical condensed matter physics shares important concepts and techniques with theoretical particle and nuclear physics.A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography, metallurgy, elasticity, magnetism, etc., were treated as distinct areas, until the 1940s when they were grouped together as solid state physics. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquids was added to this list, forming the basis for the new, related specialty of condensed matter physics. According to physicist Phil Anderson, the term was coined by him and Volker Heine when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge from ""Solid state theory"" to ""Theory of Condensed Matter"" in 1967, as they felt it did not exclude their interests in the study of liquids, nuclear matter and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name ""condensed matter"", it had been present in Europe for some years, most prominently in the form of a journal published in English, French, and German by Springer-Verlag titled Physics of Condensed Matter, which was launched in 1963. The funding environment and Cold War politics of the 1960s and 1970s were also factors that lead some physicists to prefer the name ""condensed matter physics"", which emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, over ""solid state physics"", which was often associated with the industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics.References to ""condensed"" state can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 ""Kinetic theory of liquids"" book, Yakov Frenkel proposed that ""The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies"". As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of ""condensed bodies"".