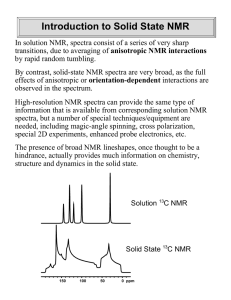
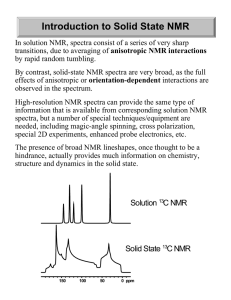
Introduction to Solid State NMR
... Origins of Solid-State NMR Original NMR experiments focused on 1H and 19F NMR, for reasons of sensitivity. However, anisotropies in the local fields of the protons broadened the 1H NMR spectra such that no spectral lines could be resolved. The only cases where useful spectra could be obtained was f ...
... Origins of Solid-State NMR Original NMR experiments focused on 1H and 19F NMR, for reasons of sensitivity. However, anisotropies in the local fields of the protons broadened the 1H NMR spectra such that no spectral lines could be resolved. The only cases where useful spectra could be obtained was f ...
Solid State NMR
... Origins of Solid-State NMR Original NMR experiments focused on 1H and 19F NMR, for reasons of sensitivity. However, anisotropies in the local fields of the protons broadened the 1H NMR spectra such that no spectral lines could be resolved. The only cases where useful spectra could be obtained was f ...
... Origins of Solid-State NMR Original NMR experiments focused on 1H and 19F NMR, for reasons of sensitivity. However, anisotropies in the local fields of the protons broadened the 1H NMR spectra such that no spectral lines could be resolved. The only cases where useful spectra could be obtained was f ...
Widening the Axion Window via Kinetic and Stückelberg Mixings
... PACS numbers: 14.80.Va, 11.25.Wx, 95.35.+d, 98.80.Cq ...
... PACS numbers: 14.80.Va, 11.25.Wx, 95.35.+d, 98.80.Cq ...
Photo-Fragmentation of Lithium Atoms Studied with MOTReMi
... The exact description of the triple ionization of Li (as well as the double ionization of Li by electron impact) involving three free electrons today is beyond the capability of even advanced computation methods which are able to handle only up to two continuum electrons [Res99,Bra02]. Therefore, l ...
... The exact description of the triple ionization of Li (as well as the double ionization of Li by electron impact) involving three free electrons today is beyond the capability of even advanced computation methods which are able to handle only up to two continuum electrons [Res99,Bra02]. Therefore, l ...
Collected Scientific Papers - SN Bose National Centre for Basic
... was made. They were to be immutable entities. But the photon was clearly an entity which could be created or destroyed. Where does a photon come from and where does it go? And how can we really understand creation and destruction? What is the implication of strict identity of photons? In what sense ...
... was made. They were to be immutable entities. But the photon was clearly an entity which could be created or destroyed. Where does a photon come from and where does it go? And how can we really understand creation and destruction? What is the implication of strict identity of photons? In what sense ...
What can electron paramagnetic resonance tell us about the Si/SiO2
... an unsophisticated observer on earth that the sun is in a circular orbit about the earth.! The nucleus thus generates a local magnetic field which would scale with the electron’s orbital angular momentum, r3p, and with the nuclear charge. One would thus correctly surmise that spin-orbit coupling int ...
... an unsophisticated observer on earth that the sun is in a circular orbit about the earth.! The nucleus thus generates a local magnetic field which would scale with the electron’s orbital angular momentum, r3p, and with the nuclear charge. One would thus correctly surmise that spin-orbit coupling int ...
Magnetic fields of charged particles in motion
... see that the magnetic forces exerted on the top and bottom sides cause a torque that tends to rotate the loop as indicated in Figure 28.10. When the current loop is oriented with its magnetic dipole moment parallel to the magnetic field, all four sides experience a magnetic force (Figure 28.11), How ...
... see that the magnetic forces exerted on the top and bottom sides cause a torque that tends to rotate the loop as indicated in Figure 28.10. When the current loop is oriented with its magnetic dipole moment parallel to the magnetic field, all four sides experience a magnetic force (Figure 28.11), How ...
... which describes the interface of superconducting and non superconducting regions. In type-I materials lc < this term is positive and such boundaries are not advantageous to superconductivity. However, in type-II materials lc > 1/4i, the interface term is negative, and the system benefits from norma ...
Nonlocal optical response in metallic nanostructures
... Recently, interest in the hydrodynamic model was rekindled when a finite-element numerical implementation of the hydrodynamic equations was presented [87–89], which was subsequently utilized to study the plasmonic cylindrical dimer [88], surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy [90], and waveguiding in m ...
... Recently, interest in the hydrodynamic model was rekindled when a finite-element numerical implementation of the hydrodynamic equations was presented [87–89], which was subsequently utilized to study the plasmonic cylindrical dimer [88], surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy [90], and waveguiding in m ...
UNIVERSITY OF BUCHAREST FACULTY OF CHEMISTRY
... The goals of this PhD Thesis were the design and synthesis of new compartmental and non-compartmental Schiff-base ligands which can be used to synthesize new binuclear and polynuclear complexes exhibiting interesting magnetic and luminescence properties. The achievement of our objectives was realize ...
... The goals of this PhD Thesis were the design and synthesis of new compartmental and non-compartmental Schiff-base ligands which can be used to synthesize new binuclear and polynuclear complexes exhibiting interesting magnetic and luminescence properties. The achievement of our objectives was realize ...
A Maxwellian Perspective on Particle Acceleration
... has ceased to interact with the drive fields. In general, the total electromagnetic field energy can have been reduced only if a component of the radiation fields of the electron continues to occupy the same volume as the drive fields (until possible absorption of these fields by matter). The radiation fi ...
... has ceased to interact with the drive fields. In general, the total electromagnetic field energy can have been reduced only if a component of the radiation fields of the electron continues to occupy the same volume as the drive fields (until possible absorption of these fields by matter). The radiation fi ...
Solution Processed Group VI Transition Metal Dichalcogenides: A
... and X a chalcogen atom of sulfur, selenium or tellurium (S, Se or Te). As such over forty different varieties may be realised, covering the full array of electronic properties from insulators and semiconductors through to metals and superconductors, depending on the combination of M and X.[1] TMD mo ...
... and X a chalcogen atom of sulfur, selenium or tellurium (S, Se or Te). As such over forty different varieties may be realised, covering the full array of electronic properties from insulators and semiconductors through to metals and superconductors, depending on the combination of M and X.[1] TMD mo ...
Ion Beam Neutralization
... electron. The mobile electrons rapidly enter the beam volume. Low-energy electrons can follow high-energy ions to neutralize a beam propagating into free space. Also the technology to generate electrons is straightforward compared with the complexity of ion sources (Chapter 7). There are two ways to ...
... electron. The mobile electrons rapidly enter the beam volume. Low-energy electrons can follow high-energy ions to neutralize a beam propagating into free space. Also the technology to generate electrons is straightforward compared with the complexity of ion sources (Chapter 7). There are two ways to ...
Spin diffusion equation for nonuniform driving field
... found to be nonzero. This is understood from the way the spin current vanishes in the bulk, when exact cancellation occurs between two terms, one related to spin polarization and the other related to the driving field. The exact cancellation no longer holds near the electrode interfaces when the ...
... found to be nonzero. This is understood from the way the spin current vanishes in the bulk, when exact cancellation occurs between two terms, one related to spin polarization and the other related to the driving field. The exact cancellation no longer holds near the electrode interfaces when the ...
spectroscopic analysis of dna strands influenced by magnetic field
... In recent years, the number of research related to biological sensing devices has increased tremendously. Investigations related to environmental effects on DNA involve multidisciplinary studies and are actively pursued due to its novelty. Studies on the behavior of some optical parameters of DNA un ...
... In recent years, the number of research related to biological sensing devices has increased tremendously. Investigations related to environmental effects on DNA involve multidisciplinary studies and are actively pursued due to its novelty. Studies on the behavior of some optical parameters of DNA un ...
Introduction to Neutron Scattering
... the neutron and the nucleus. Fortunately the results of this calculation can be understood without going into all of the details involved. It is useful, though, to be able to switch to and fro between thinking about the wavefunction of a neutron—the squared modulus of which tells us the probability ...
... the neutron and the nucleus. Fortunately the results of this calculation can be understood without going into all of the details involved. It is useful, though, to be able to switch to and fro between thinking about the wavefunction of a neutron—the squared modulus of which tells us the probability ...
On the genesis of the Earth`s magnetism
... it must be admitted that what they could do in 1819 was very limited; the Earth’s core was not discovered until 1906 by Richard Dixon Oldham. That it was fluid was not known for certain until two decades later. The first mathematician to take up Hansteen’s challenge was Karl Friedrich Gauss who, in ...
... it must be admitted that what they could do in 1819 was very limited; the Earth’s core was not discovered until 1906 by Richard Dixon Oldham. That it was fluid was not known for certain until two decades later. The first mathematician to take up Hansteen’s challenge was Karl Friedrich Gauss who, in ...
Word
... The dynamo effect of the spinning motion of the coil in a magnetic field causes an induced emf, referred to as a back emf, in the coil, acting against the motor supply. Most motors used in industrial applications are induction motors. In an induction motor, the currents in the rotor are not fed dire ...
... The dynamo effect of the spinning motion of the coil in a magnetic field causes an induced emf, referred to as a back emf, in the coil, acting against the motor supply. Most motors used in industrial applications are induction motors. In an induction motor, the currents in the rotor are not fed dire ...
Condensed matter physics

Condensed matter physics is a branch of physics that deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by using physical laws. In particular, these include the laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism and statistical mechanics.The most familiar condensed phases are solids and liquids, while more exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on atomic lattices, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in cold atomic systems. The study of condensed matter physics involves measuring various material properties via experimental probes along with using techniques of theoretical physics to develop mathematical models that help in understanding physical behavior.The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists identify themselves as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division at the American Physical Society. The field overlaps with chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology, and relates closely to atomic physics and biophysics. Theoretical condensed matter physics shares important concepts and techniques with theoretical particle and nuclear physics.A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography, metallurgy, elasticity, magnetism, etc., were treated as distinct areas, until the 1940s when they were grouped together as solid state physics. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquids was added to this list, forming the basis for the new, related specialty of condensed matter physics. According to physicist Phil Anderson, the term was coined by him and Volker Heine when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge from ""Solid state theory"" to ""Theory of Condensed Matter"" in 1967, as they felt it did not exclude their interests in the study of liquids, nuclear matter and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name ""condensed matter"", it had been present in Europe for some years, most prominently in the form of a journal published in English, French, and German by Springer-Verlag titled Physics of Condensed Matter, which was launched in 1963. The funding environment and Cold War politics of the 1960s and 1970s were also factors that lead some physicists to prefer the name ""condensed matter physics"", which emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, over ""solid state physics"", which was often associated with the industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics.References to ""condensed"" state can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 ""Kinetic theory of liquids"" book, Yakov Frenkel proposed that ""The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies"". As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of ""condensed bodies"".