Electromagnetic generation of sound in metals located in a magnetic
... Ho, as a consequence of the action of which certain groups of electrons excited by the electromagnetic wave in the skin layer congregate in narrow layers at definite distances from the surface-distances that depend on Ho. For this reason, the force exciting the sound is modulated spatially with a pe ...
... Ho, as a consequence of the action of which certain groups of electrons excited by the electromagnetic wave in the skin layer congregate in narrow layers at definite distances from the surface-distances that depend on Ho. For this reason, the force exciting the sound is modulated spatially with a pe ...
Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Pure and Substituted Yttrium
... magnetoelectrics involves both ferroelectric and magnetic properties of matter, it has attracted researchers from both backgrounds: magnetism and ferroelectricity. The multiferroics can be defined as the class of materials which exhibits two or more “ferroic” order parameters (i.e. ferroelectricity, ...
... magnetoelectrics involves both ferroelectric and magnetic properties of matter, it has attracted researchers from both backgrounds: magnetism and ferroelectricity. The multiferroics can be defined as the class of materials which exhibits two or more “ferroic” order parameters (i.e. ferroelectricity, ...
Исследование вещественного состава и органического
... resonance (EPR) devoted the presented work. In the period 1985-1990 in the laboratory of physics of minerals Kazan University headed by Professor VM Vinokurov methods have been developed of correlation of coeval deposits (especially "dumb" in paleontological terms) based on the study of paramagnetic ...
... resonance (EPR) devoted the presented work. In the period 1985-1990 in the laboratory of physics of minerals Kazan University headed by Professor VM Vinokurov methods have been developed of correlation of coeval deposits (especially "dumb" in paleontological terms) based on the study of paramagnetic ...
phys1444-lec19
... Suspending a wire with current. A horizontal wire carries a current I1=80A DC. A second parallel wire 20cm below it must carry how much current I2 so that it doesn’t fall due to the gravity? The lower has a mass of 0.12g per meter of length. Which direction is the gravitational force? Downward This ...
... Suspending a wire with current. A horizontal wire carries a current I1=80A DC. A second parallel wire 20cm below it must carry how much current I2 so that it doesn’t fall due to the gravity? The lower has a mass of 0.12g per meter of length. Which direction is the gravitational force? Downward This ...
B y
... A charged particle moves through a region of space that has both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field. In order for the particle to move through this region at a constant velocity, A. the electric and magnetic fields must point in the same direction. B. the electric and magnetic fie ...
... A charged particle moves through a region of space that has both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field. In order for the particle to move through this region at a constant velocity, A. the electric and magnetic fields must point in the same direction. B. the electric and magnetic fie ...
RF heating due to conductive wires during MRI depends on the
... wire properties (diameter, insulation thickness) and the properties of the tissue it was placed in (electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, perfusion) were explored. This theoretical understanding and experimental validation established safety thresholds on the SAR (specific absorption rate) ...
... wire properties (diameter, insulation thickness) and the properties of the tissue it was placed in (electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, perfusion) were explored. This theoretical understanding and experimental validation established safety thresholds on the SAR (specific absorption rate) ...
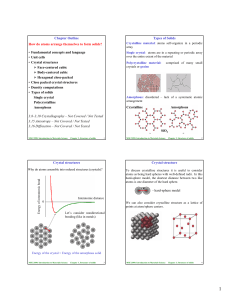
How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? • Fundamental
... Since the entire crystal can be generated by the repetition of the unit cell, the density of a crystalline material, ρ = the density of the unit cell = (atoms in the unit cell, n ) × (mass of an atom, M) / (the volume of the cell, Vc) Atoms in the unit cell, n = 2 (BCC); 4 (FCC); 6 (HCP) Mass of an ...
... Since the entire crystal can be generated by the repetition of the unit cell, the density of a crystalline material, ρ = the density of the unit cell = (atoms in the unit cell, n ) × (mass of an atom, M) / (the volume of the cell, Vc) Atoms in the unit cell, n = 2 (BCC); 4 (FCC); 6 (HCP) Mass of an ...
How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? • Fundamental
... Since the entire crystal can be generated by the repetition of the unit cell, the density of a crystalline material, ρ = the density of the unit cell = (atoms in the unit cell, n ) × (mass of an atom, M) / (the volume of the cell, Vc) Atoms in the unit cell, n = 2 (BCC); 4 (FCC); 6 (HCP) Mass of an ...
... Since the entire crystal can be generated by the repetition of the unit cell, the density of a crystalline material, ρ = the density of the unit cell = (atoms in the unit cell, n ) × (mass of an atom, M) / (the volume of the cell, Vc) Atoms in the unit cell, n = 2 (BCC); 4 (FCC); 6 (HCP) Mass of an ...
Roles of non-equilibrium conduction electrons on magnetization
... and then by using the same s-d model to calculate the spin torque on the magnetization dynamics as a result of the induced non-equilibrium conduction electron spin. Among other things, we have found four distinct spin torques on the magnetization. Three of them are closely related to previously deri ...
... and then by using the same s-d model to calculate the spin torque on the magnetization dynamics as a result of the induced non-equilibrium conduction electron spin. Among other things, we have found four distinct spin torques on the magnetization. Three of them are closely related to previously deri ...
AP Physics Practice Test: Magnetic Fields
... 5. A conductor lying in the xy plane is exposed to a magnetic field in the +z direction, and connected to a source of potential as shown above. Which statement correctly describes the electric field within the conductor? a. There is only an E field in the +x direction b. There is only an E field in ...
... 5. A conductor lying in the xy plane is exposed to a magnetic field in the +z direction, and connected to a source of potential as shown above. Which statement correctly describes the electric field within the conductor? a. There is only an E field in the +x direction b. There is only an E field in ...
Investigation of the Electron Energy Distribution Function in Hollow
... radically from both those studied in [1–4] and those studied in [5–8]. Specifically, we are interested in steady hollow-cathode glow discharges in nitrogen and oxygen. In such discharges, which are widely used in various technological applications, the applied voltage drops preferentially across a n ...
... radically from both those studied in [1–4] and those studied in [5–8]. Specifically, we are interested in steady hollow-cathode glow discharges in nitrogen and oxygen. In such discharges, which are widely used in various technological applications, the applied voltage drops preferentially across a n ...
Syllabus 9749
... Forces at a distance are explained by fields that can transfer energy and can be described in terms of the arrangement and properties of the interacting objects. These forces can be used to describe the relationship between electrical and magnetic fields. 1.7. Equilibrium is a unique state where the ...
... Forces at a distance are explained by fields that can transfer energy and can be described in terms of the arrangement and properties of the interacting objects. These forces can be used to describe the relationship between electrical and magnetic fields. 1.7. Equilibrium is a unique state where the ...
Graphene: carbon in two dimensions
... Fig. 5 Scanning electron micrograph of a graphene device. The graphene crystal is contacted by Au electrodes and patterned into Hall bar geometry by e-beam lithography with subsequent reactive plasma etching. The width of the channel is 1 µm. (Courtesy of K. Novoselov and A. Geim.) ...
... Fig. 5 Scanning electron micrograph of a graphene device. The graphene crystal is contacted by Au electrodes and patterned into Hall bar geometry by e-beam lithography with subsequent reactive plasma etching. The width of the channel is 1 µm. (Courtesy of K. Novoselov and A. Geim.) ...
Template file in Microsoft Word 97 for Windows
... where X is the exchange functional and C the correlation functional, which is of course zero for HF wavefunctions. In order to calculate X and C it is necessary to assume some functional form to the two potentials and then calculate the contribution to the electronic energy as an integral over t ...
... where X is the exchange functional and C the correlation functional, which is of course zero for HF wavefunctions. In order to calculate X and C it is necessary to assume some functional form to the two potentials and then calculate the contribution to the electronic energy as an integral over t ...
Unit 26
... To you alone . . . who seek knowledge, not from books only, but also from things themselves, do I address these magnetic principles and this new sort of philosophy. If any disagree with my opinion, let them at least take note of the experiments. . . and employ them to better use if they are able. Gi ...
... To you alone . . . who seek knowledge, not from books only, but also from things themselves, do I address these magnetic principles and this new sort of philosophy. If any disagree with my opinion, let them at least take note of the experiments. . . and employ them to better use if they are able. Gi ...
2011 HSC Examination - Physics - Board of Studies Teaching and
... The diagram shows a stationary spacecraft next to a building, as seen by an observer across the street. ...
... The diagram shows a stationary spacecraft next to a building, as seen by an observer across the street. ...
- TestbankU
... A) there is much more distance [at least 10 times more] between neighboring atoms in a liquid than between neighboring atoms in a solid. B) the liquid's atoms move throughout the liquid, while the solid's atoms remain near their original locations. C) in a liquid, the individual atoms are larger. D) ...
... A) there is much more distance [at least 10 times more] between neighboring atoms in a liquid than between neighboring atoms in a solid. B) the liquid's atoms move throughout the liquid, while the solid's atoms remain near their original locations. C) in a liquid, the individual atoms are larger. D) ...
Fine Structure of the Hydrogen Atom. Part I
... There are some German papers"" between 1932 and 1935 dealing with attempts to detect such a transition. At that time, only spark gap oscillators of exceedingly low power output were available for such wave-lengths. One had to work with a continuous spectrum of radiation, using the interference metho ...
... There are some German papers"" between 1932 and 1935 dealing with attempts to detect such a transition. At that time, only spark gap oscillators of exceedingly low power output were available for such wave-lengths. One had to work with a continuous spectrum of radiation, using the interference metho ...
Condensed matter physics

Condensed matter physics is a branch of physics that deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by using physical laws. In particular, these include the laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism and statistical mechanics.The most familiar condensed phases are solids and liquids, while more exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on atomic lattices, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in cold atomic systems. The study of condensed matter physics involves measuring various material properties via experimental probes along with using techniques of theoretical physics to develop mathematical models that help in understanding physical behavior.The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists identify themselves as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division at the American Physical Society. The field overlaps with chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology, and relates closely to atomic physics and biophysics. Theoretical condensed matter physics shares important concepts and techniques with theoretical particle and nuclear physics.A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography, metallurgy, elasticity, magnetism, etc., were treated as distinct areas, until the 1940s when they were grouped together as solid state physics. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquids was added to this list, forming the basis for the new, related specialty of condensed matter physics. According to physicist Phil Anderson, the term was coined by him and Volker Heine when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge from ""Solid state theory"" to ""Theory of Condensed Matter"" in 1967, as they felt it did not exclude their interests in the study of liquids, nuclear matter and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name ""condensed matter"", it had been present in Europe for some years, most prominently in the form of a journal published in English, French, and German by Springer-Verlag titled Physics of Condensed Matter, which was launched in 1963. The funding environment and Cold War politics of the 1960s and 1970s were also factors that lead some physicists to prefer the name ""condensed matter physics"", which emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, over ""solid state physics"", which was often associated with the industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics.References to ""condensed"" state can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 ""Kinetic theory of liquids"" book, Yakov Frenkel proposed that ""The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies"". As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of ""condensed bodies"".