Objectives - Paramedic.EMSzone.com
... exhaled breath yet positive control of the airway does not exist. The risk of tube dislodgement is great, and the risk of aspiration remains. The most common cause of a false-negative result is a significant disruption in pulmonary blood flow. It takes a severe interruption in pulmonary blood flow t ...
... exhaled breath yet positive control of the airway does not exist. The risk of tube dislodgement is great, and the risk of aspiration remains. The most common cause of a false-negative result is a significant disruption in pulmonary blood flow. It takes a severe interruption in pulmonary blood flow t ...
Document
... Issues around communication, continuity of care, or care planning cited as root cause in >80% of reported sentinel ...
... Issues around communication, continuity of care, or care planning cited as root cause in >80% of reported sentinel ...
The Air We Breath - Faculty Sites
... inserted between the ribs into the chest and is connected to a bottle or canister that contains sterile water. Suction is attached to the system to encourage drainage. A stitch (suture) and adhesive tape is used to keep the tube in place. The chest tube usually remains in place until the X-rays sh ...
... inserted between the ribs into the chest and is connected to a bottle or canister that contains sterile water. Suction is attached to the system to encourage drainage. A stitch (suture) and adhesive tape is used to keep the tube in place. The chest tube usually remains in place until the X-rays sh ...
respiratory bronchioles
... When the rib cage returns to its original position and the diaphragm relaxes, the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases. Pressure Thoracic cavity volume decreases within the lungs increases, and air moves out. Poutside < Pinside ...
... When the rib cage returns to its original position and the diaphragm relaxes, the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases. Pressure Thoracic cavity volume decreases within the lungs increases, and air moves out. Poutside < Pinside ...
PAP Therapy Training TEST Module II
... 24. The lab has a standing order for the patient to receive ___________ if necessary. Supplemental oxygen ...
... 24. The lab has a standing order for the patient to receive ___________ if necessary. Supplemental oxygen ...
Este - Delmar
... Midaxillary line The midaxillary line is the imaginary vertical line drawn from the apex of the axillae and lying midway between the anterior and posterior lines. ...
... Midaxillary line The midaxillary line is the imaginary vertical line drawn from the apex of the axillae and lying midway between the anterior and posterior lines. ...
Adenoidectomy with Grommets Application Form
... Exceptional Status (what makes the individual sufficiently different from the ‘usual’ in policy terms). Central to consideration of individual requests for funding is the concept of the case being exceptional. In order for funding to be agreed there must be unusual or unique clinical factors about t ...
... Exceptional Status (what makes the individual sufficiently different from the ‘usual’ in policy terms). Central to consideration of individual requests for funding is the concept of the case being exceptional. In order for funding to be agreed there must be unusual or unique clinical factors about t ...
Chapter 23.
... – For example, in alveoli • walls must be very thin (< 1 µm) • surface area must be very great (about 35 times the surface area of the body) ...
... – For example, in alveoli • walls must be very thin (< 1 µm) • surface area must be very great (about 35 times the surface area of the body) ...
Chapter 22 Respiratory
... – Elasticity of lungs causes them to assume smallest possible size – Surface tension of alveolar fluid draws alveoli to their smallest possible size ...
... – Elasticity of lungs causes them to assume smallest possible size – Surface tension of alveolar fluid draws alveoli to their smallest possible size ...
Application of the Passy-Muir® Swallowing and Speaking Valves for
... • Our pulmonologist will not let us use the Valve with our patients during weaning from mechanical ventilation, stating that: “the valve will increase the work of breathing” • A clinician asks: Q: How do I convince him otherwise? – Work of breathing is multifactoral. – Patients may actually benefit ...
... • Our pulmonologist will not let us use the Valve with our patients during weaning from mechanical ventilation, stating that: “the valve will increase the work of breathing” • A clinician asks: Q: How do I convince him otherwise? – Work of breathing is multifactoral. – Patients may actually benefit ...
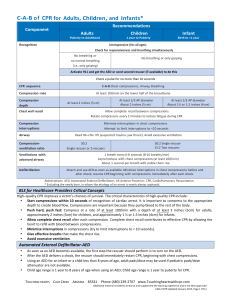
C-‐A-‐B of CPR for Adults, Children, and Infants
... • Bag-‐mask device/technique is not recommended for a single rescuer to provide breaths during CPR. • The rescue breath for an adult, child, or infant is effective when the chest rises visibly. • During b ...
... • Bag-‐mask device/technique is not recommended for a single rescuer to provide breaths during CPR. • The rescue breath for an adult, child, or infant is effective when the chest rises visibly. • During b ...
Chapter 42: Neonatology
... Provide ventilation via BVM for 30 seconds and reassess If not resolved begin CPR (a rate of > 100) ...
... Provide ventilation via BVM for 30 seconds and reassess If not resolved begin CPR (a rate of > 100) ...
File - Prepared Rescuer, LLC
... Sudden drop in ETCO2 immediately signals obstructed or dislodged tube Detection of a displaced or obstructed ETT using pulse oximetry or changes in HR / BP can be delayed 2-3 minutes* *Guidelines for Cardiovascular Resuscitation &Emergency Cardiovascular Care, Circulation August, 2000 ...
... Sudden drop in ETCO2 immediately signals obstructed or dislodged tube Detection of a displaced or obstructed ETT using pulse oximetry or changes in HR / BP can be delayed 2-3 minutes* *Guidelines for Cardiovascular Resuscitation &Emergency Cardiovascular Care, Circulation August, 2000 ...
Respiratory Mechanics
... collapses; in this animal preparation both pleural cavities can be widely opened to atmospheric pressure and both lungs are seen to be completely collapsed. The concepts of lung recoil and transpulmonary pressure are demonstrated by showing that the lungs can be re-expanded by either sucking air out ...
... collapses; in this animal preparation both pleural cavities can be widely opened to atmospheric pressure and both lungs are seen to be completely collapsed. The concepts of lung recoil and transpulmonary pressure are demonstrated by showing that the lungs can be re-expanded by either sucking air out ...
H24 - Lying behaviour
... smoke or an anemometer and recording the ammonia level. Draught is defined as air speeds above 0.2 m / s if the difference between the temperature of the inlet air and the temperature of the facility is higher than 4° C. ...
... smoke or an anemometer and recording the ammonia level. Draught is defined as air speeds above 0.2 m / s if the difference between the temperature of the inlet air and the temperature of the facility is higher than 4° C. ...
Adenoidectomy with Grommets Application Form
... Exceptional Status (what makes the individual sufficiently different from the ‘usual’ in policy terms). Central to consideration of individual requests for funding is the concept of the case being exceptional. In order for funding to be agreed there must be unusual or unique clinical factors about t ...
... Exceptional Status (what makes the individual sufficiently different from the ‘usual’ in policy terms). Central to consideration of individual requests for funding is the concept of the case being exceptional. In order for funding to be agreed there must be unusual or unique clinical factors about t ...
Feet below
... • At the onset of inspiration the pleural pressure changes at faster rate than lung volume-”hysteresis” • Air filled lung vs. saline filled lung – Easier to inflate a saline filled lung than an air filled lung because surface tension forces have been eliminated in the saline filled lung ...
... • At the onset of inspiration the pleural pressure changes at faster rate than lung volume-”hysteresis” • Air filled lung vs. saline filled lung – Easier to inflate a saline filled lung than an air filled lung because surface tension forces have been eliminated in the saline filled lung ...
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS)
... volume at a low inspiratory flow followed by an inspiratory pause of approximately 2-3 seconds and expiration with a high expiratory flow where inspiratory: expiratory ratio of approximately 1/2 was followed by an uninterrupted expiration during which the bag was held compressed then a ‘quick releas ...
... volume at a low inspiratory flow followed by an inspiratory pause of approximately 2-3 seconds and expiration with a high expiratory flow where inspiratory: expiratory ratio of approximately 1/2 was followed by an uninterrupted expiration during which the bag was held compressed then a ‘quick releas ...
File
... o Normal (adults): 12 to 20 times per minute o Eupnea: normal respiration Rhythm: pattern of spacing/time between breaths Depth: volume of air inhaled & exhaled Factors Influencing Respiration Physical condition Disease Medication Exercise Pain Emotions Breathing Conditions Ta ...
... o Normal (adults): 12 to 20 times per minute o Eupnea: normal respiration Rhythm: pattern of spacing/time between breaths Depth: volume of air inhaled & exhaled Factors Influencing Respiration Physical condition Disease Medication Exercise Pain Emotions Breathing Conditions Ta ...
April 2016 - Department of Medicine
... a validated instrument3 that can be used to assess respiratory distress in patients who cannot self-report their symptoms, including patients who are approaching death. Validity of the RDOS instrument was initially established by comparing patient self-report of dyspnea to clinician observations in ...
... a validated instrument3 that can be used to assess respiratory distress in patients who cannot self-report their symptoms, including patients who are approaching death. Validity of the RDOS instrument was initially established by comparing patient self-report of dyspnea to clinician observations in ...
Module 19
... Oxygen humidifying devices: Oxygen is a dry gas as it is delivered from its supply source, and moisture must be added prior to its administration to a patient. When dry gases are given to patients, the respiratory mucous membranes become dehydrated. Humidifiers work by passing the gas through water ...
... Oxygen humidifying devices: Oxygen is a dry gas as it is delivered from its supply source, and moisture must be added prior to its administration to a patient. When dry gases are given to patients, the respiratory mucous membranes become dehydrated. Humidifiers work by passing the gas through water ...
Bronchodilator premedication does not decrease respiratory
... anticholinergic drug may not be able to exert its effect on a damaged receptor. • 4. The study drug may not have been delivered adequately to its target. ...
... anticholinergic drug may not be able to exert its effect on a damaged receptor. • 4. The study drug may not have been delivered adequately to its target. ...
Respiratory Ventilation
... Simply: It is the maximum amount of expiration that the person can do until an obligatory (uncontrolled) stoppage of the expiration. ...
... Simply: It is the maximum amount of expiration that the person can do until an obligatory (uncontrolled) stoppage of the expiration. ...
The t a s t
... Transition from apnoea to spontaneous breathing When a mechanically ventilated patient with no spontaneous effort is disconnected from the ventilator, a variable period of time to the first detectable ventilatory efforts ensues. In the absence of hypoxia, the duration of this period depends on the d ...
... Transition from apnoea to spontaneous breathing When a mechanically ventilated patient with no spontaneous effort is disconnected from the ventilator, a variable period of time to the first detectable ventilatory efforts ensues. In the absence of hypoxia, the duration of this period depends on the d ...
Bag valve mask

A bag valve mask, abbreviated to BVM and sometimes known by the proprietary name Ambu bag or generically as a manual resuscitator or “self-inflating bag”, is a hand-held device commonly used to provide positive pressure ventilation to patients who are not breathing or not breathing adequately. The device is a required part of resuscitation kits for trained professionals in out-of-hospital settings (such as ambulance crews) and is also frequently used in hospitals as part of standard equipment found on a crash cart, in emergency rooms or other critical care settings. Underscoring the frequency and prominence of BVM use in the United States, the American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiac Care recommend that ""all healthcare providers should be familiar with the use of the bag-mask device."" Manual resuscitators are also used within the hospital for temporary ventilation of patients dependent on mechanical ventilators when the mechanical ventilator needs to be examined for possible malfunction, or when ventilator-dependent patients are transported within the hospital. Two principal types of manual resuscitator exist; one version is self-filling with air, although additional oxygen (O2) can be added but is not necessary for the device to function. The other principal type of manual resuscitator (flow-inflation) is heavily used in non-emergency applications in the operating room to ventilate patients during anesthesia induction and recovery.Use of manual resuscitators to ventilate a patient is frequently called ""bagging"" the patient and is regularly necessary in medical emergencies when the patient's breathing is insufficient (respiratory failure) or has ceased completely (respiratory arrest). Use of the manual resuscitator force-feeds air or oxygen into the lungs in order to inflate them under pressure, thus constituting a means to manually provide positive-pressure ventilation. It is used by professional rescuers in preference to mouth-to-mouth ventilation, either directly or through an adjunct such as a pocket mask). The full-form of AMBU is Artificial Manual Breathing Unit.