1.5 Modern and smart materials
... Ability to change colour in response to UV or an applied voltage Replaces the need for separate reading and sunglasses ...
... Ability to change colour in response to UV or an applied voltage Replaces the need for separate reading and sunglasses ...
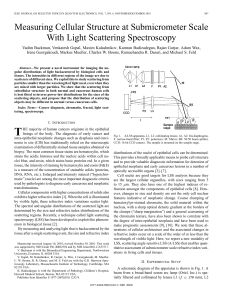
Measuring cellular structure at submicrometer scale with light
... diluting the stock suspension with de-ionized and distilled water to obtain the required optical density. Fig. 3 summarizes the experimental results obtained for polystyrene particles. To demonstrate the symmetry of the A/LSS scattering patterns, the parallel-polarized component of the backscattered ...
... diluting the stock suspension with de-ionized and distilled water to obtain the required optical density. Fig. 3 summarizes the experimental results obtained for polystyrene particles. To demonstrate the symmetry of the A/LSS scattering patterns, the parallel-polarized component of the backscattered ...
PPT - Purdue University Cytometry Laboratories
... Steradian (sphere radius r has surface area of 4 r2; one steradian is defined as that solid angle which intercepts an area equal to r2 on the surface. Mole - contains Avogadro's number of molecules (6.02 x 1023) and contains a mass in grams = molecular weight. Photons - light particles - waves - Ph ...
... Steradian (sphere radius r has surface area of 4 r2; one steradian is defined as that solid angle which intercepts an area equal to r2 on the surface. Mole - contains Avogadro's number of molecules (6.02 x 1023) and contains a mass in grams = molecular weight. Photons - light particles - waves - Ph ...
Lecture Notes
... drop. This is known as refraction. According to the Snell's Law sini/sinr=RI of the latter isotropic medium. This can also be expressed as RImedium=velocity of light in vacuum/velocity of light in the isotropic medium, RImedium=c/vnedium ie., RI of a medium is inversely proportional to the speed of ...
... drop. This is known as refraction. According to the Snell's Law sini/sinr=RI of the latter isotropic medium. This can also be expressed as RImedium=velocity of light in vacuum/velocity of light in the isotropic medium, RImedium=c/vnedium ie., RI of a medium is inversely proportional to the speed of ...
On Level FOCUS curriculum
... Light travels in a straight line until it hits an object. It may pass through the object or bounce off the object. ...
... Light travels in a straight line until it hits an object. It may pass through the object or bounce off the object. ...
Group 5 - Index of
... Medical lasers are used because of their ability to produce thermal, physical, mechanical and welding effects when exposed to tissues. Some of the applications of lasers include stone removal (laser lithotripsy), activation of specific drugs or molecules and denaturizing of tissues and cells in body ...
... Medical lasers are used because of their ability to produce thermal, physical, mechanical and welding effects when exposed to tissues. Some of the applications of lasers include stone removal (laser lithotripsy), activation of specific drugs or molecules and denaturizing of tissues and cells in body ...
Colorimeters
... absorb light for a variety of reasons. Pigments absorb light at different wavelengths. A cloudy solution will simply scatter/block the passage of light (sometimes a colorimeter is used to monitor the growth of a bacterial or yeast culture). The % transmission or the % absorbance is recorded (you c ...
... absorb light for a variety of reasons. Pigments absorb light at different wavelengths. A cloudy solution will simply scatter/block the passage of light (sometimes a colorimeter is used to monitor the growth of a bacterial or yeast culture). The % transmission or the % absorbance is recorded (you c ...
One-way invisible cloak using parity-time symmetric transformation optics Xuefeng Zhu, Liang Feng,
... distributions of permittivity and permeability from a virtual space to a physical space, myriad exotic effects such as invisibility cloaking become possible [3,8,11]. The previous studies were mainly focused on the perfect cloaks to make the concealed object omnidirectionally invisible to the outsid ...
... distributions of permittivity and permeability from a virtual space to a physical space, myriad exotic effects such as invisibility cloaking become possible [3,8,11]. The previous studies were mainly focused on the perfect cloaks to make the concealed object omnidirectionally invisible to the outsid ...
The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4th ed Donald R
... Single crystal is a crystalline material that is made of only one crystal (there are no grain boundaries). Grains are the crystals in a polycrystalline material. Polycrystalline material is a material comprised of many crystals (as opposed to a single-crystal material that has only one crystal ...
... Single crystal is a crystalline material that is made of only one crystal (there are no grain boundaries). Grains are the crystals in a polycrystalline material. Polycrystalline material is a material comprised of many crystals (as opposed to a single-crystal material that has only one crystal ...
4 Lab 1: Scattering and Reflection of Polarized Light
... In opaque materials, on the other hand, there is no refraction or transmission. To understand this, they are classified into two categories: insulators (also called dielectrics) and conductors. Insulating opaque materials are usually appear colored when seen in white light. This is because these mat ...
... In opaque materials, on the other hand, there is no refraction or transmission. To understand this, they are classified into two categories: insulators (also called dielectrics) and conductors. Insulating opaque materials are usually appear colored when seen in white light. This is because these mat ...
I2 Medical imaging
... • X-rays pass through human (or dog) flesh very easy, but do not pass through bone as easily. ...
... • X-rays pass through human (or dog) flesh very easy, but do not pass through bone as easily. ...
Skylights
... below. This factor is determined by the geometry of the light well and the reflectance of the surfaces of the light well. To calculate a WF, you need to first determine the well cavity ratio (WCR) and the reflectances of the well surfaces. ...
... below. This factor is determined by the geometry of the light well and the reflectance of the surfaces of the light well. To calculate a WF, you need to first determine the well cavity ratio (WCR) and the reflectances of the well surfaces. ...
Self-Organization of Atomic Samples in Resonators and Collective Light Forces.
... cooperativity parameter), T is the temperature of the sample, and Nef f is the effective number of atoms coupled to the cavity mode (effective number of atoms at the cavity center producing the same response as the spatially extended atomic sample). If we treat the problem from a two-level superradi ...
... cooperativity parameter), T is the temperature of the sample, and Nef f is the effective number of atoms coupled to the cavity mode (effective number of atoms at the cavity center producing the same response as the spatially extended atomic sample). If we treat the problem from a two-level superradi ...
Module 6: Attenuation in Optical Fibers
... typically result in an extension of absorption into the transparency region (band tail states). Such defect structures often form as the result of thermal processing atmosphere (e.g. redox conditions) or through the stress-induced structural modification (residual strain) produced during fiber drawi ...
... typically result in an extension of absorption into the transparency region (band tail states). Such defect structures often form as the result of thermal processing atmosphere (e.g. redox conditions) or through the stress-induced structural modification (residual strain) produced during fiber drawi ...
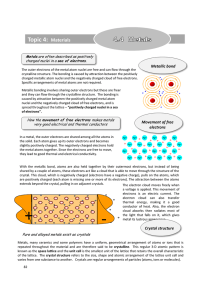
Topic 4: Materials - Education Umbrella
... shared by a couple of atoms, these electrons act like a cloud that is able to move through the structure of the crystal. This cloud, which is negatively charged (electrons have a negative charge), pulls on the atoms, which are positively charged (each atom is missing one or more of its electrons). T ...
... shared by a couple of atoms, these electrons act like a cloud that is able to move through the structure of the crystal. This cloud, which is negatively charged (electrons have a negative charge), pulls on the atoms, which are positively charged (each atom is missing one or more of its electrons). T ...
Looking through walls and around corners with
... ‘scattering-lens’ with a focal length R at the corrected wavelength . The entire system (scatteringmedium - SLM - lens) is then a telescopic imaging system with a magnification of M=f/R, i.e. a widefield ‘scattering microscope’ (Figs.1c). The field of view (FOV) of this ‘scattering microscope’ is li ...
... ‘scattering-lens’ with a focal length R at the corrected wavelength . The entire system (scatteringmedium - SLM - lens) is then a telescopic imaging system with a magnification of M=f/R, i.e. a widefield ‘scattering microscope’ (Figs.1c). The field of view (FOV) of this ‘scattering microscope’ is li ...
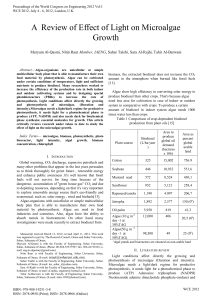
A Review of Effect of Light on Microalgae Growth
... and enhance public awareness .It's well known that fossil fuels will not survive for long time because of the dangerous accumulation of "green house gas" CO2 and due to depleting resources, depending on that it's very important to explore renewable energy source that's eco-friendly and economical, s ...
... and enhance public awareness .It's well known that fossil fuels will not survive for long time because of the dangerous accumulation of "green house gas" CO2 and due to depleting resources, depending on that it's very important to explore renewable energy source that's eco-friendly and economical, s ...
SLR-17-03e
... For light sources with integrated electronics this "Electronic light source control gear" should be components between the supply and the light emitting elements. The definition was derived from IEC and CIE, where a light source is the light emitting element. Provisions for "electronic light source ...
... For light sources with integrated electronics this "Electronic light source control gear" should be components between the supply and the light emitting elements. The definition was derived from IEC and CIE, where a light source is the light emitting element. Provisions for "electronic light source ...
Input
... optical frequency near that of the light to be modulated, energy levels. Thus pumping of the medium 11 by while the separation between the ?rst and second energy energy of frequency 1112 results in an increase of the elec levels corresponds to a frequency which is advantageously tron population of t ...
... optical frequency near that of the light to be modulated, energy levels. Thus pumping of the medium 11 by while the separation between the ?rst and second energy energy of frequency 1112 results in an increase of the elec levels corresponds to a frequency which is advantageously tron population of t ...
Optical power - WordPress.com
... 1)Gas lasers: Helium and Neon enclosed in a glass tube laser, CO2 lasers --Output is continuous mono chromatic (one colour) 2)Liquid lasers: organic dye enclosed in a glass tube for an active medium --A powerful pulse of light excites the organic dye 3)Solid lasers: solid, cylindrical crys ...
... 1)Gas lasers: Helium and Neon enclosed in a glass tube laser, CO2 lasers --Output is continuous mono chromatic (one colour) 2)Liquid lasers: organic dye enclosed in a glass tube for an active medium --A powerful pulse of light excites the organic dye 3)Solid lasers: solid, cylindrical crys ...
lecture 2 Fiber properties
... Caused by impurities into the fiber material Trace metal such as Iron, Nickel, Chromium Electronic transition of these metal ions from one energy level to another causes absorption Also occurs where hydroxyl ions (OH-) are introduced into the fiber and peak at 1383 nm, 1250 nm and 950nm These a ...
... Caused by impurities into the fiber material Trace metal such as Iron, Nickel, Chromium Electronic transition of these metal ions from one energy level to another causes absorption Also occurs where hydroxyl ions (OH-) are introduced into the fiber and peak at 1383 nm, 1250 nm and 950nm These a ...
Single-Mode Photonic Band Gap Guidance of Light in Air
... structure was then fused and pulled into fiber. Of the resulting fibers, those formed by omission of just a single cane did not guide modes in the air (at least not at visible wavelengths). From this point on we restrict our discussion to fibers with a seven-unit-cell air core (Fig. 2). We carried o ...
... structure was then fused and pulled into fiber. Of the resulting fibers, those formed by omission of just a single cane did not guide modes in the air (at least not at visible wavelengths). From this point on we restrict our discussion to fibers with a seven-unit-cell air core (Fig. 2). We carried o ...
Fundamental Limit to Linear One-Dimensional Slow Light Structures
... For an ideal dispersive material, Tucker et al. [7] give a delay-bandwidth product limit of ( L / λc )(navg − nmin ) . Since navg ≥ 1 in a loss-less material, our limit always somewhat exceeds that of Tucker et al. [7] for this case by a factor ~ navg . For a set of coupled resonators (including the ...
... For an ideal dispersive material, Tucker et al. [7] give a delay-bandwidth product limit of ( L / λc )(navg − nmin ) . Since navg ≥ 1 in a loss-less material, our limit always somewhat exceeds that of Tucker et al. [7] for this case by a factor ~ navg . For a set of coupled resonators (including the ...
Applications(2)
... • The prism described above is generally coated with a thin metal film placed in contact with the base of the prism (usually the reflection site), e.g. gold. The use of a metal sensing surface in SPR is critical as this technique capitalizes upon the fact that metals contain electrons, which behave ...
... • The prism described above is generally coated with a thin metal film placed in contact with the base of the prism (usually the reflection site), e.g. gold. The use of a metal sensing surface in SPR is critical as this technique capitalizes upon the fact that metals contain electrons, which behave ...
Transparency and translucency

In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without being scattered. On a macroscopic scale (one where the dimensions investigated are much, much larger than the wavelength of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's Law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) is a super-set of transparency: it allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily (again, on the macroscopic scale) follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces where there is a change in index of refraction, or internally. In other words, a translucent medium allows the transport of light while a transparent medium not only allows the transport of light but allows for image formation. The opposite property of translucency is opacity. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color.When light encounters a material, it can interact with it in several different ways. These interactions depend on the wavelength of the light and the nature of the material. Photons interact with an object by some combination of reflection, absorption and transmission.Some materials, such as plate glass and clean water, transmit much of the light that falls on them and reflect little of it; such materials are called optically transparent. Many liquids and aqueous solutions are highly transparent. Absence of structural defects (voids, cracks, etc.) and molecular structure of most liquids are mostly responsible for excellent optical transmission.Materials which do not transmit light are called opaque. Many such substances have a chemical composition which includes what are referred to as absorption centers. Many substances are selective in their absorption of white light frequencies. They absorb certain portions of the visible spectrum while reflecting others. The frequencies of the spectrum which are not absorbed are either reflected back or transmitted for our physical observation. This is what gives rise to color. The attenuation of light of all frequencies and wavelengths is due to the combined mechanisms of absorption and scattering.Transparency can provide almost perfect camouflage for animals able to achieve it. This is easier in dimly-lit or turbid seawater than in good illumination. Many marine animals such as jellyfish are highly transparent.