PC Ch4
... The number of positive real zeroes of f either equals the number of variations in the sign of the coefficients of f(x) or equals that number minus an even integer. The number of negative real zeros of f either equals the number of variations in the sign of the coefficients of f(-x) or equals that nu ...
... The number of positive real zeroes of f either equals the number of variations in the sign of the coefficients of f(x) or equals that number minus an even integer. The number of negative real zeros of f either equals the number of variations in the sign of the coefficients of f(-x) or equals that nu ...
Spectra of Products and Numerical Ranges1 4-4 C WA
... 3. LINEAR OPERATORS ON A BANACH SPACE For our first application we need a few facts about Banach spaces. First, if X is a Banach space then the Hahn-Banach theorem guarantees that for each x E X there is an x* E X* of norm 1 such that (x, x*) = Ij x 11.The space X (or more properly, the unit ball of ...
... 3. LINEAR OPERATORS ON A BANACH SPACE For our first application we need a few facts about Banach spaces. First, if X is a Banach space then the Hahn-Banach theorem guarantees that for each x E X there is an x* E X* of norm 1 such that (x, x*) = Ij x 11.The space X (or more properly, the unit ball of ...
Complex Numbers
... But scientists and engineers have found applications where is it useful to have numbers that are negative when squared. ...
... But scientists and engineers have found applications where is it useful to have numbers that are negative when squared. ...
Algebra Cheat Sheet
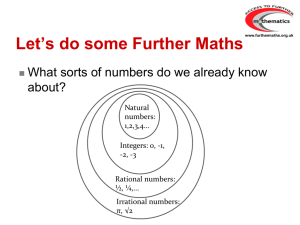
... irrational number: A number that is not rational (cannot be written as a fraction x/y, with x a natural number and y an integer); for example, √3 or π. rational number: An integer or fraction such as 7/8 or 9/4 or 5/1. Any number that can be written as a fraction x/y with x a natural number and y an ...
... irrational number: A number that is not rational (cannot be written as a fraction x/y, with x a natural number and y an integer); for example, √3 or π. rational number: An integer or fraction such as 7/8 or 9/4 or 5/1. Any number that can be written as a fraction x/y with x a natural number and y an ...
University of Toledo Algebra Ph.D. Qualifying Exam April 21, 2007
... (6) Prove that the group of all automorphisms of the field R of real numbers is trivial. (7) Determine the Galois group of f (x) = x4 − 2 ∈ Q[x]. Illustrate explicitly the lattice of subgroups and the corresponding lattice of subfields under the fundamental theorem of Galois Theory. (8) We say a fie ...
... (6) Prove that the group of all automorphisms of the field R of real numbers is trivial. (7) Determine the Galois group of f (x) = x4 − 2 ∈ Q[x]. Illustrate explicitly the lattice of subgroups and the corresponding lattice of subfields under the fundamental theorem of Galois Theory. (8) We say a fie ...




![Chapter 4, Arithmetic in F[x] Polynomial arithmetic and the division](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000416179_1-cd8ab6f583cc31262823299b7fe0d22a-300x300.png)