Lecture 1: Introduction to complex algebra
... monotonic decreasing sequence of real numbers must either tend to −∞ or to a finite real number. The set of all rational numbers form an ordered field, but is not complete. This means that the limit of a sequence of rational numbers need not be a rational number. Cauchy and Dedekind showed that the ...
... monotonic decreasing sequence of real numbers must either tend to −∞ or to a finite real number. The set of all rational numbers form an ordered field, but is not complete. This means that the limit of a sequence of rational numbers need not be a rational number. Cauchy and Dedekind showed that the ...
1 - Nutley schools
... 1.5 Day 1 Solving Equations using Factoring Do Now: Factor. 1) x2 – 7x + 10 2) 3x2 – 27x ...
... 1.5 Day 1 Solving Equations using Factoring Do Now: Factor. 1) x2 – 7x + 10 2) 3x2 – 27x ...
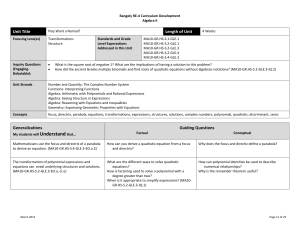
High School Algebra II
... Given an equation or system of equations, reason about the number or nature of the solutions. Content scope: A‐REI.11, involving any of the function types measured in the standards. PARCC Calculator (HS.C.5.11) ...
... Given an equation or system of equations, reason about the number or nature of the solutions. Content scope: A‐REI.11, involving any of the function types measured in the standards. PARCC Calculator (HS.C.5.11) ...
Lesson14 - Purdue Math
... *There is a good visual picture of completing the square on page 141 of the textbook. Ex 3: What number should be added to each binomial so that it becomes a perfect square trinomial? a ) x 2 14 x b) r 2 22r c) n 2 3n ...
... *There is a good visual picture of completing the square on page 141 of the textbook. Ex 3: What number should be added to each binomial so that it becomes a perfect square trinomial? a ) x 2 14 x b) r 2 22r c) n 2 3n ...