Algebra 1B Map
... graph first degree, single variable equations and inequalities, including absolute value, based in real-world and mathematical problems and graph the solutions on a number line. DOK 2 ...
... graph first degree, single variable equations and inequalities, including absolute value, based in real-world and mathematical problems and graph the solutions on a number line. DOK 2 ...
Lecture 2: Mathematical preliminaries (part 2)
... function k·k satisfying the following properties: 1. Positive definiteness: k A k ≥ 0 for all A ∈ L (X , Y ), with k A k = 0 if and only if A = 0. 2. Positive scalability: k αA k = | α | k A k for all A ∈ L (X , Y ) and α ∈ C. 3. The triangle inequality: k A + B k ≤ k A k + k B k for all A, B ∈ L (X ...
... function k·k satisfying the following properties: 1. Positive definiteness: k A k ≥ 0 for all A ∈ L (X , Y ), with k A k = 0 if and only if A = 0. 2. Positive scalability: k αA k = | α | k A k for all A ∈ L (X , Y ) and α ∈ C. 3. The triangle inequality: k A + B k ≤ k A k + k B k for all A, B ∈ L (X ...
All about polynomials booklet
... Adding polynomials: add the coefficients of like terms and keep the variables and exponents the same Parenthesis are not necessary in this step, the simply separate terms to be added ...
... Adding polynomials: add the coefficients of like terms and keep the variables and exponents the same Parenthesis are not necessary in this step, the simply separate terms to be added ...
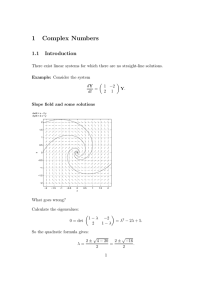
1 Complex Numbers
... z2 on a graph. Calculate the polar forms of z1 z2 and z1 /z2 and show these complex numbers on the same graph. Show the arguments and absolute values (moduli) of these complex numbers on your graph. ...
... z2 on a graph. Calculate the polar forms of z1 z2 and z1 /z2 and show these complex numbers on the same graph. Show the arguments and absolute values (moduli) of these complex numbers on your graph. ...
Unit 9 – Roots, Radicals, and Root Functions
... Complex numbers are of the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers. The number a is called the real part and b is called the imaginary part. If a is 0 they are called pure imaginary numbers. Add and subtract complex numbers We use the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to add ...
... Complex numbers are of the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers. The number a is called the real part and b is called the imaginary part. If a is 0 they are called pure imaginary numbers. Add and subtract complex numbers We use the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to add ...