Chapter 10 Cycles and Patterns in Space D64 Lesson Preview
... star is a ball of hot gases that gives off light and other forms of energy. Stars come in different sizes. The smallest stars are only about 20 km (about 12 mi) across. White dwarf stars are about the size of Earth. Supergiant stars can be more than 500 million km (about 300 million mi) wide. That i ...
... star is a ball of hot gases that gives off light and other forms of energy. Stars come in different sizes. The smallest stars are only about 20 km (about 12 mi) across. White dwarf stars are about the size of Earth. Supergiant stars can be more than 500 million km (about 300 million mi) wide. That i ...
Chapter 10
... trillions of icy bodies believed to lie far beyond Pluto’s orbit to a distance of about 150,000 AU ...
... trillions of icy bodies believed to lie far beyond Pluto’s orbit to a distance of about 150,000 AU ...
Apr/May 2003 - Madison Astronomical Society
... roughly about every 26 months, all these oppositions are not equal. Mars’ orbit is significantly more elliptical than Earth’s, so only those oppositions that occur close to Mars’ perihelion will be extremely favorable for observation from Earth. These so-called perihelic oppositions occur roughly ev ...
... roughly about every 26 months, all these oppositions are not equal. Mars’ orbit is significantly more elliptical than Earth’s, so only those oppositions that occur close to Mars’ perihelion will be extremely favorable for observation from Earth. These so-called perihelic oppositions occur roughly ev ...
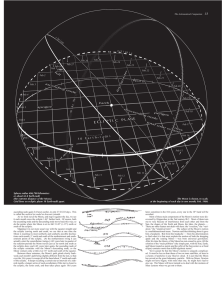
Lecture 8 - Kepler and Brahe
... that this is a voluntary choice based on his attitude. He refused to add epicycles. But now, of course, he had no model of the motions of the planets. Kepler realized that to get the most out of Tycho’s data, he first needed to determine the Earth’s orbit, since all planetary observations are made f ...
... that this is a voluntary choice based on his attitude. He refused to add epicycles. But now, of course, he had no model of the motions of the planets. Kepler realized that to get the most out of Tycho’s data, he first needed to determine the Earth’s orbit, since all planetary observations are made f ...
Outline of Lecture on Copernican Revolution: 1. Source of word
... Surely experts noted this. It is very hard to believe that this fact is an accident. It results naturally if the earth in fact orbits the sun, but in Ptolemy’s model it emerges as a completely unmotivated result. In fact, in Ptolemy’s model the periods in which also Jupiter and Saturn go around thei ...
... Surely experts noted this. It is very hard to believe that this fact is an accident. It results naturally if the earth in fact orbits the sun, but in Ptolemy’s model it emerges as a completely unmotivated result. In fact, in Ptolemy’s model the periods in which also Jupiter and Saturn go around thei ...
Lecture 1a: Class overview and Early Observations 8/27
... beyond human-built experiments and studying them increases understanding of sciences • Early studies of planetary motion lead to understanding of gravity and forces (physics and in this course). Modern studies of planets concern geology and weather (not in this course). Studies of stars, the format ...
... beyond human-built experiments and studying them increases understanding of sciences • Early studies of planetary motion lead to understanding of gravity and forces (physics and in this course). Modern studies of planets concern geology and weather (not in this course). Studies of stars, the format ...
equato equator - Universal Workshop
... to find what it is that must explain the motion of both the dropping apple and the soaring Moon—was born universal gravitation. After his time the theory of the Moon has not ceased to grow, till the solution of the “main problem” (the simple part, with the Sun, Earth, and Moon treated as points and ...
... to find what it is that must explain the motion of both the dropping apple and the soaring Moon—was born universal gravitation. After his time the theory of the Moon has not ceased to grow, till the solution of the “main problem” (the simple part, with the Sun, Earth, and Moon treated as points and ...
Preview Sample 2
... make sense because all galaxies are defined as collections of many (a billion or more) star systems, so a single star system cannot be larger than a galaxy. The universe is billions of light-years in age. This statement does not make sense because it uses the term light-years as a time, rather than ...
... make sense because all galaxies are defined as collections of many (a billion or more) star systems, so a single star system cannot be larger than a galaxy. The universe is billions of light-years in age. This statement does not make sense because it uses the term light-years as a time, rather than ...
slides - Relativity Group
... • A 10-km asteroid would produce the explosion equivalent of several billion nuclear bombs • Initial destruction by high temperatures, blast, and acid rain would be followed by months of darkness and intense cold as the Sun’s light is blotted out by clouds of dust • Further evidence of the impact is ...
... • A 10-km asteroid would produce the explosion equivalent of several billion nuclear bombs • Initial destruction by high temperatures, blast, and acid rain would be followed by months of darkness and intense cold as the Sun’s light is blotted out by clouds of dust • Further evidence of the impact is ...
Solar Eclipses
... Moon that pulls the Moon ahead in its orbit - Moon moves farther away Conservation of Angular Momentum ...
... Moon that pulls the Moon ahead in its orbit - Moon moves farther away Conservation of Angular Momentum ...
Pluto Reading
... Pluto is a dwarf planet (or plutoid) that usually orbits past the orbit of Neptune. It was classified as a dwarf planet in 2006; before that it was considered to be a planet, the smallest planet in our solar system. There are many other dwarf planets in our Solar System. Pluto is smaller than a lot ...
... Pluto is a dwarf planet (or plutoid) that usually orbits past the orbit of Neptune. It was classified as a dwarf planet in 2006; before that it was considered to be a planet, the smallest planet in our solar system. There are many other dwarf planets in our Solar System. Pluto is smaller than a lot ...
The cosmic distance ladder
... However, he noticed that when Jupiter was aligned with the Earth, the orbit advanced slightly; when Jupiter was opposed, the orbit lagged. ...
... However, he noticed that when Jupiter was aligned with the Earth, the orbit advanced slightly; when Jupiter was opposed, the orbit lagged. ...
The cosmic distance ladder
... However, he noticed that when Jupiter was aligned with the Earth, the orbit advanced slightly; when Jupiter was opposed, the orbit lagged. ...
... However, he noticed that when Jupiter was aligned with the Earth, the orbit advanced slightly; when Jupiter was opposed, the orbit lagged. ...
2. Chapter 11
... To be considered a planet, a body must orbit one or more stars, be large enough that its own gravity holds it in a spherical shape, and be the only body occupying the orbital path. Large distances keep our solar neighbourhood’s family of eight planets well separated from each other (Figure 11.9). In ...
... To be considered a planet, a body must orbit one or more stars, be large enough that its own gravity holds it in a spherical shape, and be the only body occupying the orbital path. Large distances keep our solar neighbourhood’s family of eight planets well separated from each other (Figure 11.9). In ...
Astronomy Puzzle-1
... 1. Danish astronomer who is well known for the astronomical observations. In the history, a discovered supernova is named after his name 2. Developed the theories of gravitation and mechanics, and invented differential calculus 3. Developed a simple heliocentric model of the solar system that explai ...
... 1. Danish astronomer who is well known for the astronomical observations. In the history, a discovered supernova is named after his name 2. Developed the theories of gravitation and mechanics, and invented differential calculus 3. Developed a simple heliocentric model of the solar system that explai ...
Lecture 7: Extrasolar Planets 01/08/2013 update: 725 exoplanets
... where MJ is the mass of Jupiter, should have almost the same radii (i.e. a flat mass-radius relation). -> Giant extrasolar planets transiting solar-type stars produce transits with a depth of around 1%. Close-in planets are strongly irradiated, so their radii can be (detectably) larger. But this hea ...
... where MJ is the mass of Jupiter, should have almost the same radii (i.e. a flat mass-radius relation). -> Giant extrasolar planets transiting solar-type stars produce transits with a depth of around 1%. Close-in planets are strongly irradiated, so their radii can be (detectably) larger. But this hea ...
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
sci jupiter power point
... • The rings are divided into three main parts. • Main Ring • Halo Ring- orbits closer to Jupiter • Gossamer Ring- very wide, extends far from Jupiter ...
... • The rings are divided into three main parts. • Main Ring • Halo Ring- orbits closer to Jupiter • Gossamer Ring- very wide, extends far from Jupiter ...
On Hyperdimensional Physics… and More….
... In terms of actual physics, Riemann was suggesting something clearly revolutionary: a major break with Newton's "force creates action-at-a-distance" theories of the time, which had been proposed to explain the "magical" properties of magnetic and electrical attraction and repulsion, gravitationally- ...
... In terms of actual physics, Riemann was suggesting something clearly revolutionary: a major break with Newton's "force creates action-at-a-distance" theories of the time, which had been proposed to explain the "magical" properties of magnetic and electrical attraction and repulsion, gravitationally- ...
CHAPTER XI
... directly. But our planet is spinning, racing, with the utmost speed, and in our astronomical observations we are forced to follow its movements, and to incline our telescopes in the direction[Pg 300] of its advance. This phenomenon, known under the name of aberration of light, is the result of the c ...
... directly. But our planet is spinning, racing, with the utmost speed, and in our astronomical observations we are forced to follow its movements, and to incline our telescopes in the direction[Pg 300] of its advance. This phenomenon, known under the name of aberration of light, is the result of the c ...
The Detection and Characterization of Extrasolar Planets
... Abstract: We have now confirmed the existence of > 1800 planets orbiting stars other than the Sun; known as extrasolar planets or exoplanets. The different methods for detecting such planets are sensitive to different regions of parameter space, and so, we are discovering a wide diversity of exoplan ...
... Abstract: We have now confirmed the existence of > 1800 planets orbiting stars other than the Sun; known as extrasolar planets or exoplanets. The different methods for detecting such planets are sensitive to different regions of parameter space, and so, we are discovering a wide diversity of exoplan ...
EEn.1.1 Explain the Earth`s role as a body in space. EEn
... center of the primary (the larger body). For example, the moon does not orbit the exact center of the Earth, but a point on a line between the Earth and the Moon approximately 1,710 km below the surface of the Earth, where their respective masses balance. This is the point about which the Earth a ...
... center of the primary (the larger body). For example, the moon does not orbit the exact center of the Earth, but a point on a line between the Earth and the Moon approximately 1,710 km below the surface of the Earth, where their respective masses balance. This is the point about which the Earth a ...
Prospects for detection of protoplanets
... is at a distance of not more than about 100 pc. For larger distances, the contrast between the planetary region and the adjacent disk in all of the considered planet/star/disk configurations will be too low to be detectable. ...
... is at a distance of not more than about 100 pc. For larger distances, the contrast between the planetary region and the adjacent disk in all of the considered planet/star/disk configurations will be too low to be detectable. ...
Lecture 23: Jupiter Solar System Jupiter`s Orbit
... Atmosphere of Jupiter •Jupiter’s atmosphere shows very complex patterns of motion •There are bands, clouds, and storms •The bands display shear flow •The Great Red Spot is a storm a few times the size of Earth that has lasted for hundreds of years •The complex motions are explained by the combinatio ...
... Atmosphere of Jupiter •Jupiter’s atmosphere shows very complex patterns of motion •There are bands, clouds, and storms •The bands display shear flow •The Great Red Spot is a storm a few times the size of Earth that has lasted for hundreds of years •The complex motions are explained by the combinatio ...
Satellite system (astronomy)

A satellite system is a set of gravitationally bound objects in orbit around a planetary mass object or minor planet. Generally speaking, it is a set of natural satellites (moons), although such systems may also consist of bodies such as circumplanetary disks, ring systems, moonlets, minor-planet moons and artificial satellites any of which may themselves have satellite systems of their own. Some satellite systems have complex interactions with both their parent and other moons, including magnetic, tidal, atmospheric and orbital interactions such as orbital resonances and libration. Individually major satellite objects are designated in Roman numerals. Satellite systems are referred to either by the possessive adjectives of their primary (e.g. ""Jovian system""), or less commonly by the name of their primary (e.g. ""Jupiter system""). Where only one satellite is known, or it is a binary orbiting a common centre of gravity, it may be referred to using the hyphenated names of the primary and major satellite (e.g. the ""Earth-Moon system"").Many Solar System objects are known to possess satellite systems, though their origin is still unclear. Notable examples include the largest satellite system, the Jovian system, with 67 known moons (including the large Galilean moons) and the Saturnian System with 62 known moons (and the most visible ring system in the Solar System). Both satellite systems are large and diverse. In fact all of the giant planets of the Solar System possess large satellite systems as well as planetary rings, and it is inferred that this is a general pattern. Several objects farther from the Sun also have satellite systems consisting of multiple moons, including the complex Plutonian system where multiple objects orbit a common center of mass, as well as many asteroids and plutinos. Apart from the Earth-Moon system and Mars' system of two tiny natural satellites, the other terrestrial planets are generally not considered satellite systems, although some have been orbited by artificial satellites originating from Earth.Little is known of satellite systems beyond the Solar System, although it is inferred that natural satellites are common. J1407b is an example of an extrasolar satellite system. It is also theorised that Rogue planets ejected from their planetary system could retain a system of satellites.