Rare variation of flexor digitorum longus muscle of
... of flexor digitorum longus (going between flexor hallucis longus and tibialis posterior into the sole). However, some of the fibers were originating from the fascia covering the flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior. Regarding its insertion, it merged with the tendon of flexor digitorum lon ...
... of flexor digitorum longus (going between flexor hallucis longus and tibialis posterior into the sole). However, some of the fibers were originating from the fascia covering the flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior. Regarding its insertion, it merged with the tendon of flexor digitorum lon ...
Spring 00
... a) interosseous membrane b) intermuscular membrane c) aponeurosis d) tendon e) ligament 27) The primary muscle that moves a joint is called the _______. a) agonist b) synergist c) promover d) antimover e) none of the above 28) The pectoralis major muscle is an example of a ____ muscle. a) strap b) m ...
... a) interosseous membrane b) intermuscular membrane c) aponeurosis d) tendon e) ligament 27) The primary muscle that moves a joint is called the _______. a) agonist b) synergist c) promover d) antimover e) none of the above 28) The pectoralis major muscle is an example of a ____ muscle. a) strap b) m ...
TONGUE
... • inferior longitudinal muscle: lines the sides of the tongue, and is joined to the styloglossus muscle • verticalis muscle: joins the superior and inferior longitudinal muscles • transversus muscle: divides the tongue at the middle ...
... • inferior longitudinal muscle: lines the sides of the tongue, and is joined to the styloglossus muscle • verticalis muscle: joins the superior and inferior longitudinal muscles • transversus muscle: divides the tongue at the middle ...
Muscles of the Knee
... Hamstring muscles have roles in Knee Flexion. – C1 and C2 is an example of “bilateral knee flexion” – E1 and E2 are examples of “unilateral knee flexion” – F1 and F2 are examples of “bilateral knee flexion” (focusing on the eccentric contractions of the hamstring muscles) ...
... Hamstring muscles have roles in Knee Flexion. – C1 and C2 is an example of “bilateral knee flexion” – E1 and E2 are examples of “unilateral knee flexion” – F1 and F2 are examples of “bilateral knee flexion” (focusing on the eccentric contractions of the hamstring muscles) ...
Flexor Digitorum Longus Muscle — an Unusual
... usage of the fifth toe in humans is minimal. According to Darwin’s disuse theory, therefore, FDB tendon to the fifth toe may be undergoing phylogenetic variation. This is supported by Reeser et al. (5) in their electromyographic study of human foot which showed that FDB is not preferentially recruit ...
... usage of the fifth toe in humans is minimal. According to Darwin’s disuse theory, therefore, FDB tendon to the fifth toe may be undergoing phylogenetic variation. This is supported by Reeser et al. (5) in their electromyographic study of human foot which showed that FDB is not preferentially recruit ...
Benha University Histology Exam for 2nd year Faculty of Veterinary
... swim bladder of some species a distinctive silver color. The outer layers of connective tissue are joined to the inner layers of the structure by a loose, elastic, connective tissue layer. The inner epithelium of the swim bladder is commonly cuboidal and may be ciliated, partially ciliated, or compl ...
... swim bladder of some species a distinctive silver color. The outer layers of connective tissue are joined to the inner layers of the structure by a loose, elastic, connective tissue layer. The inner epithelium of the swim bladder is commonly cuboidal and may be ciliated, partially ciliated, or compl ...
It is All About the Foot - Pedorthic Footcare Association
... Thus far, we have covered the bones and articulations of the foot, along with bipedal motion in this series. These are the foundations of what makeups the foot, but this is not enough. We need to ask now, what makes it come all together? It is time to connect all the previous parts we have discussed ...
... Thus far, we have covered the bones and articulations of the foot, along with bipedal motion in this series. These are the foundations of what makeups the foot, but this is not enough. We need to ask now, what makes it come all together? It is time to connect all the previous parts we have discussed ...
Full Text of
... control subjects was approximately 1.0. The mean ratio of muscle volume of the MR, LR, and IR of the paretic eye to the normal eye was approximately 1.0 for both congenital and acquired SO palsy patients. Using a 2 standard deviation of the SO in control subjects as a criterion, we classified the mu ...
... control subjects was approximately 1.0. The mean ratio of muscle volume of the MR, LR, and IR of the paretic eye to the normal eye was approximately 1.0 for both congenital and acquired SO palsy patients. Using a 2 standard deviation of the SO in control subjects as a criterion, we classified the mu ...
The Stretch-Shortening Cycle and Plyometric Training
... this study was specific to the explosive fast-twitch fibers (type 2b)—the ones you would use in an Olympic lift or short sprint. Distance running and other endurance activities would focus on slow-twitch fibers and decrease the cross-sectional area of the explosive type 2b fasttwitch fibers compared ...
... this study was specific to the explosive fast-twitch fibers (type 2b)—the ones you would use in an Olympic lift or short sprint. Distance running and other endurance activities would focus on slow-twitch fibers and decrease the cross-sectional area of the explosive type 2b fasttwitch fibers compared ...
Axillary Aug Video Clip Legends
... Using the retractor to establish exposure, the surgeon can roam the pocket and zoom in and out by holding the endoscope in the non-dominant hand separate from the retractor. Clip 02: Division of pectoralis major muscle origins along the inframammary fold. With the retractor positioned at the junctio ...
... Using the retractor to establish exposure, the surgeon can roam the pocket and zoom in and out by holding the endoscope in the non-dominant hand separate from the retractor. Clip 02: Division of pectoralis major muscle origins along the inframammary fold. With the retractor positioned at the junctio ...
muscle - People Server at UNCW
... first three muscles are arranged from superficial to deep: external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, and transversus abdominis. Together, these layers wrap around the abdomen. In each layer the muscle fascicles extend in a different direction. This structural arrangement affords consid ...
... first three muscles are arranged from superficial to deep: external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, and transversus abdominis. Together, these layers wrap around the abdomen. In each layer the muscle fascicles extend in a different direction. This structural arrangement affords consid ...
sample - Create Training
... any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publishers. Permissions for Netter Art figures may be sought directly from Elsevier’s Health Science Licensing Department in P ...
... any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publishers. Permissions for Netter Art figures may be sought directly from Elsevier’s Health Science Licensing Department in P ...
Stretch
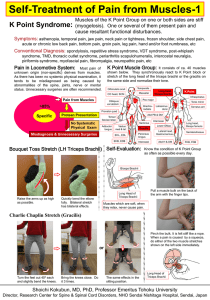
... shown below. They synchronously react to K Point block or stretch of the long head of the triceps brachii or the gracilis on the same side and normalize their tone. ...
... shown below. They synchronously react to K Point block or stretch of the long head of the triceps brachii or the gracilis on the same side and normalize their tone. ...
File - Dentalelle Tutoring
... the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Above the mastoid process is the Supramastoid Crest to which the posterior portion of the temporal muscle is attached. Dentalelle Tutoring ...
... the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Above the mastoid process is the Supramastoid Crest to which the posterior portion of the temporal muscle is attached. Dentalelle Tutoring ...
muscle - People Server at UNCW
... muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall – The anterolateral abdominal wall is composed of skin, fascia, and four pairs of muscles: The first three muscles are arranged from superficial to deep: external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, and transversus abdominis. Together, these lay ...
... muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall – The anterolateral abdominal wall is composed of skin, fascia, and four pairs of muscles: The first three muscles are arranged from superficial to deep: external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, and transversus abdominis. Together, these lay ...
General Anatomy - Biblioteca RegieLive
... from the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramen. When they come out, they divide into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) rami. Above the clavicle, the brachial plexus forms three trunks: Superior trunk: C5-C6 Middle trunk: C7 Inferior trunk: C8-T1 ...
... from the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramen. When they come out, they divide into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) rami. Above the clavicle, the brachial plexus forms three trunks: Superior trunk: C5-C6 Middle trunk: C7 Inferior trunk: C8-T1 ...
Treating Sciatica - Intent Multimedia
... causes of that pain to work with sciatica clients. If the biomechanical dysfunction of the body is not corrected, sciatica will keep occurring—the imbalance in the body is irritating the sciatic injury. For example, if a client has a leg length discrepancy on one side, and her biceps femoris and glu ...
... causes of that pain to work with sciatica clients. If the biomechanical dysfunction of the body is not corrected, sciatica will keep occurring—the imbalance in the body is irritating the sciatic injury. For example, if a client has a leg length discrepancy on one side, and her biceps femoris and glu ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.