Corporate network capacity planning - is there a need?
... What are the challenges? • Understanding the network infrastructure • Current state of the network • The cost of poor performance and unavailability • What needs to be measured and why? ...
... What are the challenges? • Understanding the network infrastructure • Current state of the network • The cost of poor performance and unavailability • What needs to be measured and why? ...
Document
... Compilation made by Tim Moors, UNSW Australia Original slides by David Wetherall, University of Washington ...
... Compilation made by Tim Moors, UNSW Australia Original slides by David Wetherall, University of Washington ...
the importance of securing workstations
... focused on viruses, worms, and spyware, since such malware can affect productivity. Unfortunately, too many organizations fail to consider the other threats to PC systems and the consequences of a successful security breach by a person, rather than by a random automated attack. Some of the most lucr ...
... focused on viruses, worms, and spyware, since such malware can affect productivity. Unfortunately, too many organizations fail to consider the other threats to PC systems and the consequences of a successful security breach by a person, rather than by a random automated attack. Some of the most lucr ...
Wireless LANs and Introduction to IP
... • A detail: Fragmentation to be done in 8 byte units of data -- Offset field counts only in units of 8 bytes. • Assignment: Read code on Reassembly-- Implementation -Important -- what are maps ? why are holes created ? how can they be filled ? ...
... • A detail: Fragmentation to be done in 8 byte units of data -- Offset field counts only in units of 8 bytes. • Assignment: Read code on Reassembly-- Implementation -Important -- what are maps ? why are holes created ? how can they be filled ? ...
Presentation11-Internet-Protocol_www
... When a router receives a multicast packet but it has no hosts that listening to that address, it send a prune message to the originating router in which the ...
... When a router receives a multicast packet but it has no hosts that listening to that address, it send a prune message to the originating router in which the ...
Computer Networking Concepts 2
... l every one of these services required a different technology to carry its particular communication signal l each service had its own set of rules and standards to ensure successful communication of its signal across a specific medium l Converged networks l consolidate these disparate networks onto ...
... l every one of these services required a different technology to carry its particular communication signal l each service had its own set of rules and standards to ensure successful communication of its signal across a specific medium l Converged networks l consolidate these disparate networks onto ...
Fondamenti di Internet: “Aspetti pratici delle reti di telecomunicazioni ”
... 2. In this case, a virtual (tap) interface will be created on the host machine and will be connected to the specific VM interface Example (in lab.conf) pc1[0]=tap,10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2 In this case the eth0 interface on pc1 will be connected to a tap on the host machine with address 10.0.0.1 while eth0 ...
... 2. In this case, a virtual (tap) interface will be created on the host machine and will be connected to the specific VM interface Example (in lab.conf) pc1[0]=tap,10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2 In this case the eth0 interface on pc1 will be connected to a tap on the host machine with address 10.0.0.1 while eth0 ...
SAVAH: Source address validation with Host Identity Protocol
... – A plain HIP/IPSec communication with filtering based on the list of allowed Host Identity Tags (HITs) – A source address authentication with HIP and SAVAH extension – A source address authentication with HIP and SAVAH in tunnelling mode •Replacement of CGA based authentication in a local area ...
... – A plain HIP/IPSec communication with filtering based on the list of allowed Host Identity Tags (HITs) – A source address authentication with HIP and SAVAH extension – A source address authentication with HIP and SAVAH in tunnelling mode •Replacement of CGA based authentication in a local area ...
Network Adapters (continued)
... • A hub is a repeater with more than one output port • A simple hub may contain multiple ports connecting a group of computers in a peer-to-peer fashion, accepting and repeating signals from ...
... • A hub is a repeater with more than one output port • A simple hub may contain multiple ports connecting a group of computers in a peer-to-peer fashion, accepting and repeating signals from ...
Chapter 1 Communication Networks and Services
... To implement new services such as caller ID, voice mail, . . . To enable mobility and roaming in cellular networks ...
... To implement new services such as caller ID, voice mail, . . . To enable mobility and roaming in cellular networks ...
What is a communication network?
... To implement new services such as caller ID, voice mail, . . . To enable mobility and roaming in cellular networks ...
... To implement new services such as caller ID, voice mail, . . . To enable mobility and roaming in cellular networks ...
Wireless Network Security
... Find MAC addresses, end-points, topology Monitors wired and wireless devices Unified monitoring provides complete picture Anomalies can be correlated ...
... Find MAC addresses, end-points, topology Monitors wired and wireless devices Unified monitoring provides complete picture Anomalies can be correlated ...
Chapter 17 - Networking Essentials
... The OSI Reference Model (continued) • Set of layers in OSI model is called a stack • Layers called by actual name or placement in stack • Layers also divided into three groups – Bottom: handles physical communications – Middle: coordinates communication between nodes – Top: involves data presentati ...
... The OSI Reference Model (continued) • Set of layers in OSI model is called a stack • Layers called by actual name or placement in stack • Layers also divided into three groups – Bottom: handles physical communications – Middle: coordinates communication between nodes – Top: involves data presentati ...
CS219: Advanced Topics in Internet Research
... • Two-tier addressing (location independent addressing <> location dependent addressing) • A smart forwarding agent which encapsulates packets from unware host to forward them to MH • Location directory for managing location updates) ...
... • Two-tier addressing (location independent addressing <> location dependent addressing) • A smart forwarding agent which encapsulates packets from unware host to forward them to MH • Location directory for managing location updates) ...
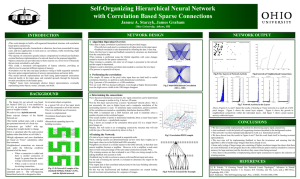
Self-Organizing Hierarchical Neural Network
... •This work attempts to build a self-organized hierarchical structure with correlation based sparse connectivity. •Self-organizing networks, hierarchical or otherwise, have been researched for many years, and have applications in such areas as: surveillance, traffic monitoring, flight control, rescue ...
... •This work attempts to build a self-organized hierarchical structure with correlation based sparse connectivity. •Self-organizing networks, hierarchical or otherwise, have been researched for many years, and have applications in such areas as: surveillance, traffic monitoring, flight control, rescue ...
Interconnection networks 2, clusters
... • Cut-through routing or wormhole routing: switch examines the header, decides where to send the message, and then starts forwarding it immediately – In wormhole routing, when head of message is blocked, message stays strung out over the network, potentially blocking other messages (needs only buffe ...
... • Cut-through routing or wormhole routing: switch examines the header, decides where to send the message, and then starts forwarding it immediately – In wormhole routing, when head of message is blocked, message stays strung out over the network, potentially blocking other messages (needs only buffe ...
QoS Guarantee in Wirless Network
... – The state of links is a function of mobility (e.g., link lifetime, fading, multipath effects, direction of a link, etc.) – The neighborhood of a node changes with mobility, which impacts reliable exchanges, channel division (space, time, code, frequency) among neighbors, and forms of cooperation b ...
... – The state of links is a function of mobility (e.g., link lifetime, fading, multipath effects, direction of a link, etc.) – The neighborhood of a node changes with mobility, which impacts reliable exchanges, channel division (space, time, code, frequency) among neighbors, and forms of cooperation b ...
Networking
... computer systems are organized. The concept of the computer center as a room with a large computer to which users bring their work for processing is now totally obsolete. The old model of single computer serving all of the organizations computational needs has been replaced by one in which a large n ...
... computer systems are organized. The concept of the computer center as a room with a large computer to which users bring their work for processing is now totally obsolete. The old model of single computer serving all of the organizations computational needs has been replaced by one in which a large n ...
Overlay/Underlay Interaction
... • Restrictive path-selection model – Destination-based packet forwarding – Single best BGP path per prefix – BGP routing constrained by policies – Ignoring congestion and delay – Ignoring application requirements ...
... • Restrictive path-selection model – Destination-based packet forwarding – Single best BGP path per prefix – BGP routing constrained by policies – Ignoring congestion and delay – Ignoring application requirements ...