Name: Date: ______ Global 9 Period: ______ Global 9: Final Exam
... on important texts created by the Greeks and Romans. v. Cultural Diffusion- the Byzantine Empire had a major influence on the neighboring civilization of Russia. Through contact with the Byzantine Empire, Russia received: 1. The Eastern Orthodox Religion (which is still practiced in Russia today) 2. ...
... on important texts created by the Greeks and Romans. v. Cultural Diffusion- the Byzantine Empire had a major influence on the neighboring civilization of Russia. Through contact with the Byzantine Empire, Russia received: 1. The Eastern Orthodox Religion (which is still practiced in Russia today) 2. ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... Church officials. Pope Gregory VII wanted the Church free from lay (non-church) control. To do this he banned lay investiture, in which the emperor rather than the pope named and installed bishops. However, Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV said that bishops held royal lands under his control, so he had t ...
... Church officials. Pope Gregory VII wanted the Church free from lay (non-church) control. To do this he banned lay investiture, in which the emperor rather than the pope named and installed bishops. However, Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV said that bishops held royal lands under his control, so he had t ...
developmentoffrancea..
... known as “the Lion-Hearted” freed Eleanor from prison popular national hero reigned 10 years, less than 1 year in England spent reign fighting, causing debt and taxes a leader of Third Crusade • went for religious reasons • John ruled England for him ...
... known as “the Lion-Hearted” freed Eleanor from prison popular national hero reigned 10 years, less than 1 year in England spent reign fighting, causing debt and taxes a leader of Third Crusade • went for religious reasons • John ruled England for him ...
Back to select
... William the Conqueror was Duke of Normandy who defeated the Saxons at the Battle of Hastings and then became King of England. ...
... William the Conqueror was Duke of Normandy who defeated the Saxons at the Battle of Hastings and then became King of England. ...
The Development of Feudalism Pages 290-297
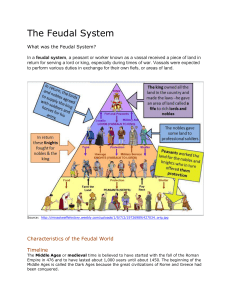
... Feudalism: A New Social Order ESSENTIAL QUESTION What was feudalism and how did it work? After Charlemagne’s death in 814, his son, Louis I, became emperor. When Louis died, his three sons fought each other for control of the kingdom. They all signed a treaty in 843 that divided the empire into thre ...
... Feudalism: A New Social Order ESSENTIAL QUESTION What was feudalism and how did it work? After Charlemagne’s death in 814, his son, Louis I, became emperor. When Louis died, his three sons fought each other for control of the kingdom. They all signed a treaty in 843 that divided the empire into thre ...
The Feudal System
... living in a state of almost continual warfare, and few people wrote accounts of the time. Because we know so little about this period of history, people call the period the Dark Ages. For the most part, the Germans and Celts lived in tribes under local rulers. But in the eighth century, one Germanic ...
... living in a state of almost continual warfare, and few people wrote accounts of the time. Because we know so little about this period of history, people call the period the Dark Ages. For the most part, the Germans and Celts lived in tribes under local rulers. But in the eighth century, one Germanic ...
The Feudal System - John Bowne High School
... living in a state of almost continual warfare, and few people wrote accounts of the time. Because we know so little about this period of history, people call the period the Dark Ages. For the most part, the Germans and Celts lived in tribes under local rulers. But in the eighth century, one Germanic ...
... living in a state of almost continual warfare, and few people wrote accounts of the time. Because we know so little about this period of history, people call the period the Dark Ages. For the most part, the Germans and Celts lived in tribes under local rulers. But in the eighth century, one Germanic ...
The Feudal System
... Source: http://missokeeffehistory.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/7/2/19726989/427034_orig.jpg ...
... Source: http://missokeeffehistory.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/7/2/19726989/427034_orig.jpg ...
Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne
... • Charles was large and strong, and of lofty stature, though not disproportionately tall (his height is well known to have been seven times the length of his foot); the upper part of his head was round, his eyes very large and animated, nose a little long, hair fair, and face laughing and merry. Thu ...
... • Charles was large and strong, and of lofty stature, though not disproportionately tall (his height is well known to have been seven times the length of his foot); the upper part of his head was round, his eyes very large and animated, nose a little long, hair fair, and face laughing and merry. Thu ...
From the Ashes of Empire
... Emperor was considered to have been chosen by God. Differences from Western church and implications? ...
... Emperor was considered to have been chosen by God. Differences from Western church and implications? ...
Chapter 18-1
... and Western Christian Churches. In 1054, relations between the Greek speaking Eastern of the Byzantine empire and the Latin speaking Western traditions within the Christian Church reached a terminal crisis. This crisis led to the separation between the Eastern and Western churches and is referred to ...
... and Western Christian Churches. In 1054, relations between the Greek speaking Eastern of the Byzantine empire and the Latin speaking Western traditions within the Christian Church reached a terminal crisis. This crisis led to the separation between the Eastern and Western churches and is referred to ...
Final Review Semester 1
... of one person from communion and the church =loss of salvation, no hope for heaven unless forgiven by Pope 2. Interdiction – A locational and/or ...
... of one person from communion and the church =loss of salvation, no hope for heaven unless forgiven by Pope 2. Interdiction – A locational and/or ...
Life in Europe after the Romans
... women killed • Jews rounded up, placed in a temple then the building was set on fire ...
... women killed • Jews rounded up, placed in a temple then the building was set on fire ...
Western Christendom after the fall of Rome WHAP/Napp “In the
... “In the early centuries of the postclassical era, history must have seemed more significant than geography, for the Roman Empire, long a fixture of the western Mediterranean region, had collapsed. The traditional date marking the fall of Rome is 476, when the German general Odoacer overthrew the las ...
... “In the early centuries of the postclassical era, history must have seemed more significant than geography, for the Roman Empire, long a fixture of the western Mediterranean region, had collapsed. The traditional date marking the fall of Rome is 476, when the German general Odoacer overthrew the las ...
Topic #7 Medieval Christian Europe_ Lessons 1-4
... After the Fall • Roman Empire included most of the Western European world • Unification of the region came through Roman control, allowed ...
... After the Fall • Roman Empire included most of the Western European world • Unification of the region came through Roman control, allowed ...
Chapter 22 Study Guide
... 6. Which religious leader from the Catholic Church helped to organize the First Crusade? a. The bishop b. King Richard c. Saladin d. The Pope 7. Feudalism came about because of a. No strong central government b. Ideal system for wealth and prosperity c. Trading contacts with Middle East were good d. ...
... 6. Which religious leader from the Catholic Church helped to organize the First Crusade? a. The bishop b. King Richard c. Saladin d. The Pope 7. Feudalism came about because of a. No strong central government b. Ideal system for wealth and prosperity c. Trading contacts with Middle East were good d. ...
European Middle Ages - iBlog Teacher Websites
... • Concordant of Worms-Compromise in which the Church alone could name bishops but the Emperor could veto the selection ...
... • Concordant of Worms-Compromise in which the Church alone could name bishops but the Emperor could veto the selection ...
Western Civilization I HIS-101
... Both Henry and Gregory treated each other with deference Gregory had hoped to create a strong working relationship with Henry as long as the latter remained submissive to his ...
... Both Henry and Gregory treated each other with deference Gregory had hoped to create a strong working relationship with Henry as long as the latter remained submissive to his ...
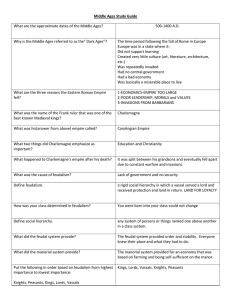
Middle Ages Study Guide Key
... Vassals/Knights allowed peasants (serfs) to work their land. Majority of the population. Serfs/Peasants provided food and other services to Vassals/Knights when demanded. Kings start to produce kingdoms A. Eventually powerful kings combined the military power and created nation-states. B. Nation-Sta ...
... Vassals/Knights allowed peasants (serfs) to work their land. Majority of the population. Serfs/Peasants provided food and other services to Vassals/Knights when demanded. Kings start to produce kingdoms A. Eventually powerful kings combined the military power and created nation-states. B. Nation-Sta ...
Assignment - Paradise.net.nz
... Charlemagne inherited from his father Pepin and grandfather Charles Martel the mantle of a new dynasty in Europe. The Merovingian state had fallen into decay and what real power was left was being wielded not by the kings but by their palace administrators. In AD 752 this state of affairs was legiti ...
... Charlemagne inherited from his father Pepin and grandfather Charles Martel the mantle of a new dynasty in Europe. The Merovingian state had fallen into decay and what real power was left was being wielded not by the kings but by their palace administrators. In AD 752 this state of affairs was legiti ...
renaissance and reformation in western europe
... independence of the papacy was finally restores at the Council of Constance (1414-1417). For the next century under the “Renaissance Popes” Rome became one of the leading city-states in Italy, and a significant participant in the Renaissance. Social and Economic Foundations of the Renaissance. Unlik ...
... independence of the papacy was finally restores at the Council of Constance (1414-1417). For the next century under the “Renaissance Popes” Rome became one of the leading city-states in Italy, and a significant participant in the Renaissance. Social and Economic Foundations of the Renaissance. Unlik ...
1. Emperor/Empress 2. Han Dynasty/Yuan Dynasty 3. City
... civilizations/empires (Han Dynasty [Chinese Empire], Ancient Greece [Athenian Empire], Alexander the Great [Hellenistic Empire], and Ancient Rome)? Explain the importance as to why modern societies should study and understand the common factors that led to the decline/downfall of the civilizations/e ...
... civilizations/empires (Han Dynasty [Chinese Empire], Ancient Greece [Athenian Empire], Alexander the Great [Hellenistic Empire], and Ancient Rome)? Explain the importance as to why modern societies should study and understand the common factors that led to the decline/downfall of the civilizations/e ...
File
... 1. "In conformity, therefore, to the clear doctrine of the Scripture, we assert, that by an eternal and immutable counsel, God has once for all determined, both whom he would admit to salvation, and whom he would condemn to destruction." The idea expressed in the above passage is most closely associ ...
... 1. "In conformity, therefore, to the clear doctrine of the Scripture, we assert, that by an eternal and immutable counsel, God has once for all determined, both whom he would admit to salvation, and whom he would condemn to destruction." The idea expressed in the above passage is most closely associ ...
Chapter 25: The Church
... expanded the power of Germany. 13. In the early 1200s, Germany, under the leadership of Frederick II, began conquering territories in Italy. The Church, fearful of his growing power excommunicated him, thus making ____________________ an independent country free from control of the Church. 14. Spain ...
... expanded the power of Germany. 13. In the early 1200s, Germany, under the leadership of Frederick II, began conquering territories in Italy. The Church, fearful of his growing power excommunicated him, thus making ____________________ an independent country free from control of the Church. 14. Spain ...
Late Middle Ages

The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history generally comprising the 14th and 15th centuries (c. 1301–1500). The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern era (and, in much of Europe, the Renaissance).Around 1300, centuries of prosperity and growth in Europe came to a halt. A series of famines and plagues, such as the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the Black Death, reduced the population to around half of what it was before the calamities. Along with depopulation came social unrest and endemic warfare. France and England experienced serious peasant uprisings: the Jacquerie, the Peasants' Revolt, as well as over a century of intermittent conflict in the Hundred Years' War. To add to the many problems of the period, the unity of the Catholic Church was shattered by the Western Schism. Collectively these events are sometimes called the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages.Despite these crises, the 14th century was also a time of great progress within the arts and sciences. Following a renewed interest in ancient Greek and Roman texts that took root in the High Middle Ages, the Italian Renaissance began. The absorption of Latin texts had started before the Renaissance of the 12th century through contact with Arabs during the Crusades, but the availability of important Greek texts accelerated with the capture of Constantinople by the Ottoman Turks, when many Byzantine scholars had to seek refuge in the West, particularly Italy.Combined with this influx of classical ideas was the invention of printing which facilitated dissemination of the printed word and democratized learning. These two things would later lead to the Protestant Reformation. Toward the end of the period, an era of discovery began (Age of Discovery). The growth of the Ottoman Empire, culminating in the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, eroded the last remnants of the Byzantine Empire and cut off trading possibilities with the east. Europeans were forced to discover new trading routes, as was the case with Columbus’s travel to the Americas in 1492, and Vasco da Gama’s circumnavigation of India and Africa in 1498. Their discoveries strengthened the economy and power of European nations.The changes brought about by these developments have caused many scholars to see it as leading to the end of the Middle Ages, and the beginning of modern history and early modern Europe. However, the division will always be a somewhat artificial one for scholars, since ancient learning was never entirely absent from European society. As such there was developmental continuity between the ancient age (via classical antiquity) and the modern age. Some historians, particularly in Italy, prefer not to speak of late Middle Ages at all, but rather see the high period of the Middle Ages transitioning to the Renaissance and the modern era.