Chapter 16 PART ONE - Western Europe During the Early Middle
... The Manorial System During the Middle Ages, the The lord’s land was manorial system was the way called a manor in which people survived The lord provided peasants with housing, ...
... The Manorial System During the Middle Ages, the The lord’s land was manorial system was the way called a manor in which people survived The lord provided peasants with housing, ...
Middle Ages - Pearland ISD
... Tribes in the Middle Ages became divided into a series of Germanic kingdoms Germanic people lived in small communities led by chiefs & his loyal warriors ...
... Tribes in the Middle Ages became divided into a series of Germanic kingdoms Germanic people lived in small communities led by chiefs & his loyal warriors ...
Chapter Europe Emerges, 600-1200 Chapter 9
... What did he choose as the official state religion? Why? Adopted culture of Byzantine Internal political struggles and conflict with external foes led to a decline in Kievan Russia after 1100. ...
... What did he choose as the official state religion? Why? Adopted culture of Byzantine Internal political struggles and conflict with external foes led to a decline in Kievan Russia after 1100. ...
Chapter 20 Western Europe During the High Middle Ages
... Pope believed they would increase his power and stop them from fighting one another. ...
... Pope believed they would increase his power and stop them from fighting one another. ...
Practice Test - dgordondesign
... 11. In Europe during the Middle Ages, increases in trade and commerce resulted in ...
... 11. In Europe during the Middle Ages, increases in trade and commerce resulted in ...
Medieval Pwr Pt SCHS-1
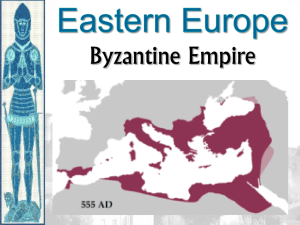
... • Invaded by Abbasid Islamic forces in late 600’s • Strong gov’t control of economy (capital enriched at expense of rural areas) • Conquered in 1453 by Ottoman Turks (Central Asians converted to Islam) ...
... • Invaded by Abbasid Islamic forces in late 600’s • Strong gov’t control of economy (capital enriched at expense of rural areas) • Conquered in 1453 by Ottoman Turks (Central Asians converted to Islam) ...
Chapter 13-14 Review Questions
... A: After Germanic invaders stormed Rome, few people except priests and other church officials were literate. A: In the Roman province of Gaul these Germanic people gained control. A: This Frank leader brought Christianity his kingdom and created an allegiance with the Catholic Church. A: This perso ...
... A: After Germanic invaders stormed Rome, few people except priests and other church officials were literate. A: In the Roman province of Gaul these Germanic people gained control. A: This Frank leader brought Christianity his kingdom and created an allegiance with the Catholic Church. A: This perso ...
Middle Ages - Georgetown ISD
... Homework: You must write a 1-2 page typewritten, first-person account of daily life for a person living in the Middle Ages. You should make up a name, develop a voice, and describe your life as a king, noble, knight, or peasant. Feel free to give yourself a family and describe ...
... Homework: You must write a 1-2 page typewritten, first-person account of daily life for a person living in the Middle Ages. You should make up a name, develop a voice, and describe your life as a king, noble, knight, or peasant. Feel free to give yourself a family and describe ...
Middle_Ages
... Homework: You must write a 1-2 page typewritten, first-person account of daily life for a person living in the Middle Ages. You should make up a name, develop a voice, and describe your life as a king, noble, knight, or peasant. Feel free to give yourself a family and describe ...
... Homework: You must write a 1-2 page typewritten, first-person account of daily life for a person living in the Middle Ages. You should make up a name, develop a voice, and describe your life as a king, noble, knight, or peasant. Feel free to give yourself a family and describe ...
File
... Homework: You must write a 1-2 page typewritten, first-person account of daily life for a person living in the Middle Ages. You should make up a name, develop a voice, and describe your life as a king, noble, knight, or peasant. Feel free to give yourself a family and describe ...
... Homework: You must write a 1-2 page typewritten, first-person account of daily life for a person living in the Middle Ages. You should make up a name, develop a voice, and describe your life as a king, noble, knight, or peasant. Feel free to give yourself a family and describe ...
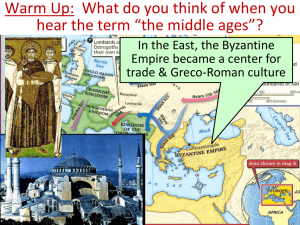
Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman
... Homework: You must write a 1-2 page typewritten, first-person account of daily life for a person living in the Middle Ages. You should make up a name, develop a voice, and describe your life as a king, noble, knight, or peasant. Feel free to give yourself a family and describe ...
... Homework: You must write a 1-2 page typewritten, first-person account of daily life for a person living in the Middle Ages. You should make up a name, develop a voice, and describe your life as a king, noble, knight, or peasant. Feel free to give yourself a family and describe ...
Ch 7 Middle Ages: The Rise of Europe 2010
... Charlemagne saw education as another way to unify his kingdom. Even though he could not read or write, he felt education was important. He brought back Latin learning. He also set up local schools. 9. However, the unity did not last. Charlemagne’s grandsons split up the empire in 843. In about 900 A ...
... Charlemagne saw education as another way to unify his kingdom. Even though he could not read or write, he felt education was important. He brought back Latin learning. He also set up local schools. 9. However, the unity did not last. Charlemagne’s grandsons split up the empire in 843. In about 900 A ...
2010_Expanding_zones_vocab_
... The Roman Catholic Church – The largest Christian branch and claims over a billion members, representing approximately half of all Christians. The Church's highest earthly authority is the Pope. During the Middle Ages, it was the most powerful institution in Western Europe because it dominated socia ...
... The Roman Catholic Church – The largest Christian branch and claims over a billion members, representing approximately half of all Christians. The Church's highest earthly authority is the Pope. During the Middle Ages, it was the most powerful institution in Western Europe because it dominated socia ...
Medieval Europe Reading Directions: Using Cornell format, on a
... 12. Who belonged to each of the three estates of medieval European society and what was the primary duty of a member of each estate? ...
... 12. Who belonged to each of the three estates of medieval European society and what was the primary duty of a member of each estate? ...
The European Middle Ages Study Guide-Chapter 13
... defend all land by himself, so he granted land (fiefs) to his loyal and titles followers (Nobles). In return, they were ...
... defend all land by himself, so he granted land (fiefs) to his loyal and titles followers (Nobles). In return, they were ...
The Middle Ages
... • Family ties and personal loyalty • People lived in small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions • Ruled by a Chief who led a band or warriors loyal only to him – not some emperor they’d never seen ...
... • Family ties and personal loyalty • People lived in small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions • Ruled by a Chief who led a band or warriors loyal only to him – not some emperor they’d never seen ...
The Middle Ages
... • Family ties and personal loyalty • People lived in small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions • Ruled by a Chief who led a band or warriors loyal only to him – not some emperor they’d never seen ...
... • Family ties and personal loyalty • People lived in small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions • Ruled by a Chief who led a band or warriors loyal only to him – not some emperor they’d never seen ...
European Geography notes!
... • Family ties and personal loyalty • People lived in small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions • Ruled by a Chief who led a band or warriors loyal only to him – not some emperor they’d never seen ...
... • Family ties and personal loyalty • People lived in small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions • Ruled by a Chief who led a band or warriors loyal only to him – not some emperor they’d never seen ...
Unit Exam 1, SF 1
... military service to those above, and those above provided land and protection to those below. ...
... military service to those above, and those above provided land and protection to those below. ...
Middle_Ages - Cobb Learning
... Knights were specially trained soldiers who protected the lords & peasants – vassals took an oath of fealty (loyalty) Some peasants were serfs & could not leave the lord’s estate ...
... Knights were specially trained soldiers who protected the lords & peasants – vassals took an oath of fealty (loyalty) Some peasants were serfs & could not leave the lord’s estate ...
In the early Middle Ages, was there social mobility?
... Middle Ages where land was the basis of wealth ...
... Middle Ages where land was the basis of wealth ...
High Middle Ages

The High Middle Ages or High Medieval Period was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries (c. 1001–1300). The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500.The key historical trend of the High Middle Ages was the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250 the robust population increase greatly benefited the European economy, reaching levels it would not see again in some areas until the 19th century. This trend was checked in the Late Middle Ages by a series of calamities, notably the Black Death but also including numerous wars and economic stagnation.From about the year 780 onwards, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance led to scientific and philosophical revival of Europe. The first universities were established in Bologna, Paris, Oxford and Modena. The Vikings had settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, whilst Norse Christian kingdoms were developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars had ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary was recognized in central Europe, forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire of the Macedonian and Komnenos dynasties gradually gave way to resurrected Serbia and Bulgaria and to a successor Crusade state from 1204 to 1261, while countering the continuous threat of the Seljuk Turks in Asia Minor.In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps began to settle new lands, some of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Roman Empire. In what is known as the ""great clearances"", vast forests and marshes of Europe were cleared and cultivated. At the same time settlements moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire to new frontiers in Europe, beyond the Elbe River, tripling the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church, reaching the peak of its political power at this time, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades against the Seljuk Turks, who occupied the Holy Land, thereby founding the Crusader States in the Levant. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades, while Christian kingdoms conquered the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, and the Normans colonized southern Italy, all part of the major population increase and resettlement pattern of the era.The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. This age saw the rise of ethnocentrism, which evolved later into modern civic nationalisms in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-states, and the rise and fall of the Muslim civilization of Al-Andalus. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle led Thomas Aquinas and other thinkers of the period to develop Scholasticism, a combination of Catholicism and ancient philosophy. For much of the time period Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city and Byzantine art reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals were built or completed during this era.The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, beginning at the start of the 14th century, marked the end of this era.