Warm-Up Question
... Medieval Christianity was so important Early medieval cathedrals were built with The Role of the Medieval Church that small churches were built on manors, Romanesque architecture but large cathedrals were built in cities ...
... Medieval Christianity was so important Early medieval cathedrals were built with The Role of the Medieval Church that small churches were built on manors, Romanesque architecture but large cathedrals were built in cities ...
WH 1 Lesson 47 Instructional Resource 1
... Catholic Church established for the investigation of heresy and punishment of the ...
... Catholic Church established for the investigation of heresy and punishment of the ...
Final Exam for World History
... to provide military troops whenever called upon by their lords. 51) _________________ When Charlemagne died, his empire split up. 52) ________________ Master craft workers could belong to a guild. ...
... to provide military troops whenever called upon by their lords. 51) _________________ When Charlemagne died, his empire split up. 52) ________________ Master craft workers could belong to a guild. ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... Part C. Read each statement. If it is true, write T. If it is false, write F. 42) _________________ German tribes had a system of laws very much like that of the Romans. 43) _________________ Although the Western Roman Empire fell to the barbarians, the Eastern Roman Empire did not. 44) ____________ ...
... Part C. Read each statement. If it is true, write T. If it is false, write F. 42) _________________ German tribes had a system of laws very much like that of the Romans. 43) _________________ Although the Western Roman Empire fell to the barbarians, the Eastern Roman Empire did not. 44) ____________ ...
Outline 1 for Students Late Middle Ages
... 25% harvests in the early 14th century were poor as torrential rains destroyed wheat, oats, and hay crops; some instances of cannibalism occurred. 5. Poor hygiene also played a significant role. Many people believed that their water was contaminated and feared taking baths. B. Results: loss of 1 ...
... 25% harvests in the early 14th century were poor as torrential rains destroyed wheat, oats, and hay crops; some instances of cannibalism occurred. 5. Poor hygiene also played a significant role. Many people believed that their water was contaminated and feared taking baths. B. Results: loss of 1 ...
File 3 middle ages ppt
... Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
... Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
Review for Chapter 13 Test with answers
... 3. Why was the interdict an effective weapon for a pope to use against a king? It cost the king the LOYALTY of his subjects, who feared for their own souls. 4. What issue did Pope Gregory VII and the German emperor Henry IV fight over? Secular appointment of Bishops 5. Why did Henry IV stand barefoo ...
... 3. Why was the interdict an effective weapon for a pope to use against a king? It cost the king the LOYALTY of his subjects, who feared for their own souls. 4. What issue did Pope Gregory VII and the German emperor Henry IV fight over? Secular appointment of Bishops 5. Why did Henry IV stand barefoo ...
Christians… - Chandler Unified School District
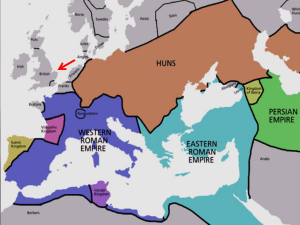
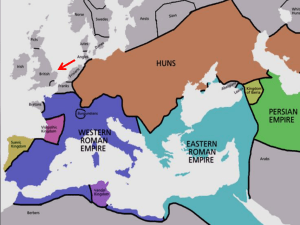
... The Middle Ages were a dangerous time in Europe The strong empires of Rome and Greece that protected trade routes and encouraged science and personal liberties were fading away. The Roman empire not only had to fight the plague but fight invaders from Europe and Asia. ...
... The Middle Ages were a dangerous time in Europe The strong empires of Rome and Greece that protected trade routes and encouraged science and personal liberties were fading away. The Roman empire not only had to fight the plague but fight invaders from Europe and Asia. ...
Post-Classical Europe - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Women’s rights limited, some professional rights, educated at convents Territorial states with common cultures expand, but decentralized Great Lords sometimes recognized as kings, but power limited by feudalism Italian city-states retain independence (Venice, Milan, Genoa, Bologna) German ...
... Women’s rights limited, some professional rights, educated at convents Territorial states with common cultures expand, but decentralized Great Lords sometimes recognized as kings, but power limited by feudalism Italian city-states retain independence (Venice, Milan, Genoa, Bologna) German ...
Chapter 14 Identifications By Lizbeth Diaz
... 14. New Monarchies – English monarchs after 1453 strove to consolidate control within the British Isles. French monarchies worked to tame the independence of their powerful noble vassals. 15. Reconquest – Spain and Portugal’s reconquest of Iberia from Muslim rule was also a religious crusade. The Ch ...
... 14. New Monarchies – English monarchs after 1453 strove to consolidate control within the British Isles. French monarchies worked to tame the independence of their powerful noble vassals. 15. Reconquest – Spain and Portugal’s reconquest of Iberia from Muslim rule was also a religious crusade. The Ch ...
The Middle Ages
... holds yet another…and continues into heaven… • It is a commonly held myth that people of the Medieval period thought the Earth was flat…FALSE! – It was round, but at the center of the universe! ...
... holds yet another…and continues into heaven… • It is a commonly held myth that people of the Medieval period thought the Earth was flat…FALSE! – It was round, but at the center of the universe! ...
What are the Middle Ages?
... What was life like back then? What are some key technologies they did not have? What comes to mind when you think about “chivalry”? What do you know about knights/castles? What do you think the church (the Catholic Church) was like back then? How were women/peasants treated? ...
... What was life like back then? What are some key technologies they did not have? What comes to mind when you think about “chivalry”? What do you know about knights/castles? What do you think the church (the Catholic Church) was like back then? How were women/peasants treated? ...
Document
... What was life like back then? What are some key technologies they did not have? What comes to mind when you think about “chivalry”? What do you know about knights/castles? What do you think the church (the Catholic Church) was like back then? How were women/peasants treated? ...
... What was life like back then? What are some key technologies they did not have? What comes to mind when you think about “chivalry”? What do you know about knights/castles? What do you think the church (the Catholic Church) was like back then? How were women/peasants treated? ...
The Early Middle Ages
... After winning a battle in 496, King Clovis established a Christian kingdom in Western Europe. It was one of many kingdoms that developed when Roman authority collapsed. ...
... After winning a battle in 496, King Clovis established a Christian kingdom in Western Europe. It was one of many kingdoms that developed when Roman authority collapsed. ...
The Middle Ages
... Medieval Europe The Middle Ages were a dark age for Europe. Near constant invasions and limited resources led to Europeans developing a new system for living. This system included all aspects of life, social, political, and economic. ...
... Medieval Europe The Middle Ages were a dark age for Europe. Near constant invasions and limited resources led to Europeans developing a new system for living. This system included all aspects of life, social, political, and economic. ...
HIS 101 Study Guide #5: Spielvogel, Chapters 810 Professor Linda
... Saint Francis of Assisi Thomas Becket Lay Investiture Dominicans Magna Carta Pope Gregory VII Cathars/Albigensians Parliament Papal Monarchy Pope Urban II Capetian Monarchy Pope Innocent III The Crusades Philip II Augustus Inquisition Saladin Holy Roman Empire Cistercians Study Que ...
... Saint Francis of Assisi Thomas Becket Lay Investiture Dominicans Magna Carta Pope Gregory VII Cathars/Albigensians Parliament Papal Monarchy Pope Urban II Capetian Monarchy Pope Innocent III The Crusades Philip II Augustus Inquisition Saladin Holy Roman Empire Cistercians Study Que ...
Middle Ages Essential Questions
... 11. How was the next king of England chosen during the events of the Norman Conquest? ...
... 11. How was the next king of England chosen during the events of the Norman Conquest? ...
9 D Social Studies Questionnaire for the exam Dear students the
... 3. Name the main buildings for the Romans and write what did they use to do inside of them? Example: Roman Aqueduct = People used the fresh water for the baths _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ________________ ...
... 3. Name the main buildings for the Romans and write what did they use to do inside of them? Example: Roman Aqueduct = People used the fresh water for the baths _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ________________ ...
The Middle Ages
... farming techniques that vastly expanded the yield of the farms of Europe. That agricultural revolution was based on the cultivation of more land and new ways of farming those lands. Forests were cleared, and land was reclaimed from swamps or lakes. Lands were taken through conquest and then settled ...
... farming techniques that vastly expanded the yield of the farms of Europe. That agricultural revolution was based on the cultivation of more land and new ways of farming those lands. Forests were cleared, and land was reclaimed from swamps or lakes. Lands were taken through conquest and then settled ...
The Middle Ages
... They learned many ideas from the Muslims: math, science, literature, art and medicine (some came from China) They were reintroduced to Greek and Roman ideas: art, philosophy and literature, that were preserved by the Muslims and Byzantine Empire ...
... They learned many ideas from the Muslims: math, science, literature, art and medicine (some came from China) They were reintroduced to Greek and Roman ideas: art, philosophy and literature, that were preserved by the Muslims and Byzantine Empire ...
1. - AP World History
... community of the middle ages? 2. Peter Abelard, 12th century a. Rational examination of doctrine showed inconsistency in church teachings 3. Debate in universities fueled by new info from the Middle East 4. Thomas Aquinas a. Summas – Reason and Faith can coexist ...
... community of the middle ages? 2. Peter Abelard, 12th century a. Rational examination of doctrine showed inconsistency in church teachings 3. Debate in universities fueled by new info from the Middle East 4. Thomas Aquinas a. Summas – Reason and Faith can coexist ...
Chapter 10
... • Third Crusade (1187–1192) – Launched after Saladin unified the Muslims and re-captured most Crusader holdings – A treaty allowed trade for merchants and unarmed Christian pilgrims to make pilgrimages to the Holy Land, while it remained under Muslim control. ...
... • Third Crusade (1187–1192) – Launched after Saladin unified the Muslims and re-captured most Crusader holdings – A treaty allowed trade for merchants and unarmed Christian pilgrims to make pilgrimages to the Holy Land, while it remained under Muslim control. ...
Medieval Europe
... • How did the Germanic kingdoms that took over the Western Roman Empire differ from the society the Romans had organized in that region? • What is feudalism, and how did medieval feudalism differ from political rule by a central authority or state, such as the one that ruled the Roman Empire? • What ...
... • How did the Germanic kingdoms that took over the Western Roman Empire differ from the society the Romans had organized in that region? • What is feudalism, and how did medieval feudalism differ from political rule by a central authority or state, such as the one that ruled the Roman Empire? • What ...
High Middle Ages

The High Middle Ages or High Medieval Period was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries (c. 1001–1300). The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500.The key historical trend of the High Middle Ages was the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250 the robust population increase greatly benefited the European economy, reaching levels it would not see again in some areas until the 19th century. This trend was checked in the Late Middle Ages by a series of calamities, notably the Black Death but also including numerous wars and economic stagnation.From about the year 780 onwards, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance led to scientific and philosophical revival of Europe. The first universities were established in Bologna, Paris, Oxford and Modena. The Vikings had settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, whilst Norse Christian kingdoms were developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars had ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary was recognized in central Europe, forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire of the Macedonian and Komnenos dynasties gradually gave way to resurrected Serbia and Bulgaria and to a successor Crusade state from 1204 to 1261, while countering the continuous threat of the Seljuk Turks in Asia Minor.In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps began to settle new lands, some of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Roman Empire. In what is known as the ""great clearances"", vast forests and marshes of Europe were cleared and cultivated. At the same time settlements moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire to new frontiers in Europe, beyond the Elbe River, tripling the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church, reaching the peak of its political power at this time, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades against the Seljuk Turks, who occupied the Holy Land, thereby founding the Crusader States in the Levant. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades, while Christian kingdoms conquered the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, and the Normans colonized southern Italy, all part of the major population increase and resettlement pattern of the era.The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. This age saw the rise of ethnocentrism, which evolved later into modern civic nationalisms in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-states, and the rise and fall of the Muslim civilization of Al-Andalus. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle led Thomas Aquinas and other thinkers of the period to develop Scholasticism, a combination of Catholicism and ancient philosophy. For much of the time period Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city and Byzantine art reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals were built or completed during this era.The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, beginning at the start of the 14th century, marked the end of this era.