The High Middle Ages(1050–1450)
... and political condisons to have important jobs. tions in Europe led The Church set up schools to to a revival of train the clergy, but eventually learning during the laymen, or people who were High Middle Ages. not in the clergy, could attend. Some of these schools became the first universities. Wom ...
... and political condisons to have important jobs. tions in Europe led The Church set up schools to to a revival of train the clergy, but eventually learning during the laymen, or people who were High Middle Ages. not in the clergy, could attend. Some of these schools became the first universities. Wom ...
Charlemagne “Charles the Great” Holy Roman Empire
... • Reading and writing almost disappeared from Europe because many of the invading groups could do neither. ...
... • Reading and writing almost disappeared from Europe because many of the invading groups could do neither. ...
Charlemagne Unites Germanic Kingdoms.key
... became a secular, or worldly, power involved in politics. ...
... became a secular, or worldly, power involved in politics. ...
WHAP Student Copy Western Christendom after the fall of Rome
... …Trade Guilds, composed of individuals practicing the same craft, constituted one the most important forms of social organization in medieval cities. The guilds set standards for production through a formalized training system. A young man would be apprenticed to a master craftsman, and learn the ba ...
... …Trade Guilds, composed of individuals practicing the same craft, constituted one the most important forms of social organization in medieval cities. The guilds set standards for production through a formalized training system. A young man would be apprenticed to a master craftsman, and learn the ba ...
Chapter 15 A New Civilization Emerges in Western Europe
... Banking arose in Italy as well as southern Germany, the Low Countries, France, and Britain. As the market expertise of Western merchants increased, Italians began to connect Europe with other parts of Eurasia through Mediterranean trade routes. Commercial alliances resulted in the formation of urban ...
... Banking arose in Italy as well as southern Germany, the Low Countries, France, and Britain. As the market expertise of Western merchants increased, Italians began to connect Europe with other parts of Eurasia through Mediterranean trade routes. Commercial alliances resulted in the formation of urban ...
File - Mr. Bowers Classroom
... The Crusades 3rd Crusade (1187-1192) started in reaction to the total defeat of the 2nd Crusade and the power of Saladin, who united the Muslims and had control of Jerusalem Largest crusader army – led by kings – Frederick I (German Kingdoms), Philip II (France), and Richard the Lion-Hearted ...
... The Crusades 3rd Crusade (1187-1192) started in reaction to the total defeat of the 2nd Crusade and the power of Saladin, who united the Muslims and had control of Jerusalem Largest crusader army – led by kings – Frederick I (German Kingdoms), Philip II (France), and Richard the Lion-Hearted ...
Chapter 1 Multiple Choice All of the following were effects of the
... 1. All of the following were effects of the Hundred Years War EXCEPT a. a significant decrease in the population b. a series of peasant rebellions c. a more politically unified France d. an economically weaker England e. the rise of a Spanish Empire in the New World 2. The period from about 400-900 ...
... 1. All of the following were effects of the Hundred Years War EXCEPT a. a significant decrease in the population b. a series of peasant rebellions c. a more politically unified France d. an economically weaker England e. the rise of a Spanish Empire in the New World 2. The period from about 400-900 ...
Carolingian
... Remained fragmented throughout the medieval period and would not be united as a sovereign nation-state until ...
... Remained fragmented throughout the medieval period and would not be united as a sovereign nation-state until ...
Islam
... _Muslim house of worship __________________________________________________________ 7. Who was Leif Erikson? What did he discover? (Look in your Vikings activity worksheet) __Leif Erikson was a Viking explorer who discovered the “New World”_______________________ 8. Read about Charles Martel on page ...
... _Muslim house of worship __________________________________________________________ 7. Who was Leif Erikson? What did he discover? (Look in your Vikings activity worksheet) __Leif Erikson was a Viking explorer who discovered the “New World”_______________________ 8. Read about Charles Martel on page ...
Section 3.3 Sacraments and Salvation in the Middle Ages
... support the Church. How did the church gain its political power? Latin, the language of the Church, was the only common language in Europe. Church officials were often the only people who could read. They kept records for monarchs and became trusted scribes and advisers. What happened between Pope G ...
... support the Church. How did the church gain its political power? Latin, the language of the Church, was the only common language in Europe. Church officials were often the only people who could read. They kept records for monarchs and became trusted scribes and advisers. What happened between Pope G ...
Germanic Kingdoms Unite under Charlemagne
... obliterated by the US Air Force towards the end of WWII ...
... obliterated by the US Air Force towards the end of WWII ...
1 Medieval Europe 300 - 1500 Medieval Europe • 1. Kingdoms and
... • Emperor Heraclius, who took over after the death of Justinian, had finally defeated the Persians The Empire Declines • Muslims had been threatening the empire as far back as the reign of Heraclius • Over time, Islam, pressure from migrating tribes, and internal conflict brought an end to the Byzan ...
... • Emperor Heraclius, who took over after the death of Justinian, had finally defeated the Persians The Empire Declines • Muslims had been threatening the empire as far back as the reign of Heraclius • Over time, Islam, pressure from migrating tribes, and internal conflict brought an end to the Byzan ...
Law, Empire, Government, and Society in the Middle Ages
... Roman Empire fell, the eastern half became known as the Byzantine Empire. One the greatest leader of this empire was Justinian, who ruled from 527 to 565 A.D. Among his significant accomplishments was the Justinian Code. This preserved Roman laws and Roman traditions. This code dealt with marriage, ...
... Roman Empire fell, the eastern half became known as the Byzantine Empire. One the greatest leader of this empire was Justinian, who ruled from 527 to 565 A.D. Among his significant accomplishments was the Justinian Code. This preserved Roman laws and Roman traditions. This code dealt with marriage, ...
Chapter 22 Study Guide
... a. The bishop b. King Richard c. Saladin d. The Pope 7. Feudalism came about because of a. No strong central government b. Ideal system for wealth and prosperity c. Trading contacts with Middle East were good d. Serfs were paid twice what peasants were 8. The Crusades had the accidental benefit of a ...
... a. The bishop b. King Richard c. Saladin d. The Pope 7. Feudalism came about because of a. No strong central government b. Ideal system for wealth and prosperity c. Trading contacts with Middle East were good d. Serfs were paid twice what peasants were 8. The Crusades had the accidental benefit of a ...
AP European History Summer Assignment
... while Germanic tribes invaded the Empire from the North and East. The fall of Rome actually occurred gradually over a period of many years, but is usually set at 476 A.D. During the centuries of Roman rule, all of the civilized European world was united under a single government. (The Romans called ...
... while Germanic tribes invaded the Empire from the North and East. The fall of Rome actually occurred gradually over a period of many years, but is usually set at 476 A.D. During the centuries of Roman rule, all of the civilized European world was united under a single government. (The Romans called ...
The Middle Ages in Europe - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... – King gives land to nobles for loyalty and service – Nobles give protection and food to peasants – Peasants work for the nobles as workers and soldiers Why would nobles and peasants agree to this system of government? ...
... – King gives land to nobles for loyalty and service – Nobles give protection and food to peasants – Peasants work for the nobles as workers and soldiers Why would nobles and peasants agree to this system of government? ...
The Foundations of Christian Society in Western Europe
... Franks emerged as the dominant military and political power in western Europe. Beginning in the fifth century with Clovis and continuing into the ninth century with Charlemagne, the Franks used religious ties with the Roman Catholic Church to secure and maintain authority. Charlemagne used his ...
... Franks emerged as the dominant military and political power in western Europe. Beginning in the fifth century with Clovis and continuing into the ninth century with Charlemagne, the Franks used religious ties with the Roman Catholic Church to secure and maintain authority. Charlemagne used his ...
Western Europe during Middle Ages
... Directions. Printout and review the Chapter outline & Study Guide prior to reading the Chapter. “People & Terms” are to be highlighted on the Chapter Outline. Words not appearing in the outline must be added to the outline. Incorporate the information for the Study questions into the notes you add t ...
... Directions. Printout and review the Chapter outline & Study Guide prior to reading the Chapter. “People & Terms” are to be highlighted on the Chapter Outline. Words not appearing in the outline must be added to the outline. Incorporate the information for the Study questions into the notes you add t ...
in format - Modern World History @ SDA
... Directions. Printout and review the Chapter outline & Study Guide prior to reading the Chapter. “People & Terms” are to be highlighted on the Chapter Outline. Words not appearing in the outline must be added to the outline. Incorporate the information for the Study questions into the notes you add t ...
... Directions. Printout and review the Chapter outline & Study Guide prior to reading the Chapter. “People & Terms” are to be highlighted on the Chapter Outline. Words not appearing in the outline must be added to the outline. Incorporate the information for the Study questions into the notes you add t ...
CHAPTER 10 The West in Crisis: The Later Middle Ages, 1300 – 1450
... They swept across Asia and even into Russia and Hungary. They maintained peace and order, thereby permitting a revival of trans-Eurasian trade. ...
... They swept across Asia and even into Russia and Hungary. They maintained peace and order, thereby permitting a revival of trans-Eurasian trade. ...
After Charlemagne - Saugerties Central School
... The Germanic Kingdoms The Franks •Between 400 and 700, Germanic tribes carved Western Europe into small kingdoms •The strongest kingdom to emerge was that of the Franks In 486, their king, Clovis, conquered the former Roman province of Gaul He converted to Christianity This gained him the suppor ...
... The Germanic Kingdoms The Franks •Between 400 and 700, Germanic tribes carved Western Europe into small kingdoms •The strongest kingdom to emerge was that of the Franks In 486, their king, Clovis, conquered the former Roman province of Gaul He converted to Christianity This gained him the suppor ...
Middle Ages powerpoint
... • Henry IV of Germany and Pope Gregory VII fought over lay investiture. • Concordat of Worms – an agreement in 1122 that said the church could appoint a bishop but the emperor could veto. ...
... • Henry IV of Germany and Pope Gregory VII fought over lay investiture. • Concordat of Worms – an agreement in 1122 that said the church could appoint a bishop but the emperor could veto. ...
Development of Feudalism
... Missionaries spread Christianity to the Germanic and Celtic tribes that bordered the old Roman Empire Many Europeans along the coast converted to Christianity due to fear of Muslim invasions ...
... Missionaries spread Christianity to the Germanic and Celtic tribes that bordered the old Roman Empire Many Europeans along the coast converted to Christianity due to fear of Muslim invasions ...
High Middle Ages

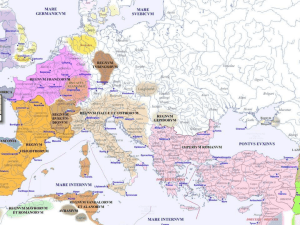
The High Middle Ages or High Medieval Period was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries (c. 1001–1300). The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500.The key historical trend of the High Middle Ages was the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250 the robust population increase greatly benefited the European economy, reaching levels it would not see again in some areas until the 19th century. This trend was checked in the Late Middle Ages by a series of calamities, notably the Black Death but also including numerous wars and economic stagnation.From about the year 780 onwards, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance led to scientific and philosophical revival of Europe. The first universities were established in Bologna, Paris, Oxford and Modena. The Vikings had settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, whilst Norse Christian kingdoms were developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars had ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary was recognized in central Europe, forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire of the Macedonian and Komnenos dynasties gradually gave way to resurrected Serbia and Bulgaria and to a successor Crusade state from 1204 to 1261, while countering the continuous threat of the Seljuk Turks in Asia Minor.In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps began to settle new lands, some of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Roman Empire. In what is known as the ""great clearances"", vast forests and marshes of Europe were cleared and cultivated. At the same time settlements moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire to new frontiers in Europe, beyond the Elbe River, tripling the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church, reaching the peak of its political power at this time, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades against the Seljuk Turks, who occupied the Holy Land, thereby founding the Crusader States in the Levant. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades, while Christian kingdoms conquered the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, and the Normans colonized southern Italy, all part of the major population increase and resettlement pattern of the era.The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. This age saw the rise of ethnocentrism, which evolved later into modern civic nationalisms in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-states, and the rise and fall of the Muslim civilization of Al-Andalus. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle led Thomas Aquinas and other thinkers of the period to develop Scholasticism, a combination of Catholicism and ancient philosophy. For much of the time period Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city and Byzantine art reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals were built or completed during this era.The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, beginning at the start of the 14th century, marked the end of this era.