Germanic Kingdoms in the West
... time, Germanic tribes and nations descended on the provinces of the Roman Empire and claimed the lands of Gaul and Iberia. The Germanic peoples were formerly spread across the forests south of the Baltic Sea and the plains and river valleys of Eastern Europe. During the later years of the Roman Empi ...
... time, Germanic tribes and nations descended on the provinces of the Roman Empire and claimed the lands of Gaul and Iberia. The Germanic peoples were formerly spread across the forests south of the Baltic Sea and the plains and river valleys of Eastern Europe. During the later years of the Roman Empi ...
The Development of Feudalism in Western Civilization
... army yet seen in England -- called the Great Army - set off a long and bitter war against the AngloSaxons for control of England. ...
... army yet seen in England -- called the Great Army - set off a long and bitter war against the AngloSaxons for control of England. ...
Exploring The Renaissance
... these ruins, the leaders of the Renaissance rediscovered some wonderful ideas that had been all but lost for nearly 1000 years. The Historical Background of the Renaissance Because the Renaissance was founded on the rediscovery of a long-lost way of life, it is important to spend some time comparing ...
... these ruins, the leaders of the Renaissance rediscovered some wonderful ideas that had been all but lost for nearly 1000 years. The Historical Background of the Renaissance Because the Renaissance was founded on the rediscovery of a long-lost way of life, it is important to spend some time comparing ...
III. THE BARRIERS TO ECONOMIC GROWTH: THE STRUCTURE
... • but never spread effectively south of Loire river: • Because Roman Law, Roman institutions, and urban civilization remained much stronger there as barrier to feudalism & manorialism • But also because Mediterranean agriculture was far less suited to raising horses than was northern agriculture ...
... • but never spread effectively south of Loire river: • Because Roman Law, Roman institutions, and urban civilization remained much stronger there as barrier to feudalism & manorialism • But also because Mediterranean agriculture was far less suited to raising horses than was northern agriculture ...
The Holy Roman Empire and the Church
... freeing his subjects from their allegiance to the emperor. The pope then headed north to crown a new emperor. Faced with revolts, Henry was forced to make peace. In January 1077, he presented himself to the pope as a repentant sinner. Gregory knew that Henry was just trying to save his throne. Still ...
... freeing his subjects from their allegiance to the emperor. The pope then headed north to crown a new emperor. Faced with revolts, Henry was forced to make peace. In January 1077, he presented himself to the pope as a repentant sinner. Gregory knew that Henry was just trying to save his throne. Still ...
iii. the barriers to economic growth: the structure
... Rhine river (Germany) • (2) Carolingian feudalism spread eastwards, into Germany, Central Europe, Scandinavia • (3) Spread Westward: into England, with the Norman Conquest of 1066 ...
... Rhine river (Germany) • (2) Carolingian feudalism spread eastwards, into Germany, Central Europe, Scandinavia • (3) Spread Westward: into England, with the Norman Conquest of 1066 ...
Concept of a Crusade
... give them something to drink; for by doing this you will heap burning coals on their heads.’ Do not be overcome by evil, but overcome evil with good.”15 However, elsewhere in The New Testament, Jesus acknowledges the legitimate use of force, when telling the apostles, "let him who has no sword sell ...
... give them something to drink; for by doing this you will heap burning coals on their heads.’ Do not be overcome by evil, but overcome evil with good.”15 However, elsewhere in The New Testament, Jesus acknowledges the legitimate use of force, when telling the apostles, "let him who has no sword sell ...
Baldwin Nanni di Bancos Four Martyrs
... classicism took up the same Florentine pride in Roman origins but now on behalf of the city’s lowly artisans. If this showed the wider resonance of Renaissance humanism beyond the city’s educated elites, it also allowed uneducated stone workers to join a lofty humanist discourse, largely monopolized ...
... classicism took up the same Florentine pride in Roman origins but now on behalf of the city’s lowly artisans. If this showed the wider resonance of Renaissance humanism beyond the city’s educated elites, it also allowed uneducated stone workers to join a lofty humanist discourse, largely monopolized ...
The Holy Roman Empire and the Church
... archbishop of Canterbury without the pope’s approval, Innocent excommunicated the king and placed his kingdom under interdict. Innocent ordered the same punishment for France when Philip II tried unlawfully to annul, or invalidate, his marriage. In 1209, Innocent, aided by Philip II, launched a brut ...
... archbishop of Canterbury without the pope’s approval, Innocent excommunicated the king and placed his kingdom under interdict. Innocent ordered the same punishment for France when Philip II tried unlawfully to annul, or invalidate, his marriage. In 1209, Innocent, aided by Philip II, launched a brut ...
Medieval Europe - Change Our Story
... attack religion itself. The respect given to a king is religious in nature. ...
... attack religion itself. The respect given to a king is religious in nature. ...
Medieval Theatre
... issues more deeply, there was a need for non religious drama and so the religious plays declined in the 15th Century. This change was driven by two things: The split in the Church and the introduction of Protestantism The introduction of The Renaissance and its different general philosophy ...
... issues more deeply, there was a need for non religious drama and so the religious plays declined in the 15th Century. This change was driven by two things: The split in the Church and the introduction of Protestantism The introduction of The Renaissance and its different general philosophy ...
Chapter 10: Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000-1500
... East, where a gush of blood from the nose was the plain sign of inevitable death; but it began both in men and women with certain swellings in the groin or under the armpit. They grew to the size of a small apple or an egg, more or less, and were vulgarly called tumours. In a short space of time the ...
... East, where a gush of blood from the nose was the plain sign of inevitable death; but it began both in men and women with certain swellings in the groin or under the armpit. They grew to the size of a small apple or an egg, more or less, and were vulgarly called tumours. In a short space of time the ...
The Rise of Feudalism in Europe
... 1. The Vikings invaded from Scandinavia- They were quick and savage. They attacked Ireland, England and France. They looted and captured people to sell into slavery. Most Europeans lived in terror of them ...
... 1. The Vikings invaded from Scandinavia- They were quick and savage. They attacked Ireland, England and France. They looted and captured people to sell into slavery. Most Europeans lived in terror of them ...
EUROPE AND SERBIAN FEUDALISM
... Sigismund’s relocation, in 1411, in Germany, Hungarian business had to be somehow administrated. Perhaps Lazarevic was commissioned as a kind of regent for Hungary. This is visible from sources related to Stephan Lazarevic’s life, like Constantin of Kostenec, who spoke about the fact that Hungarian ...
... Sigismund’s relocation, in 1411, in Germany, Hungarian business had to be somehow administrated. Perhaps Lazarevic was commissioned as a kind of regent for Hungary. This is visible from sources related to Stephan Lazarevic’s life, like Constantin of Kostenec, who spoke about the fact that Hungarian ...
The Middle Ages PPT
... The Crusades • The Crusades (1095-1270), a series of wars waged by European Christians against Muslims, were waged during the period. • The prize of The Crusades was Jerusalem and the Holy Land. ...
... The Crusades • The Crusades (1095-1270), a series of wars waged by European Christians against Muslims, were waged during the period. • The prize of The Crusades was Jerusalem and the Holy Land. ...
The evoloving world system (6 Mar 06)
... Most of the enormously diverse populations of these empires had little or no cultural or historical relationship to the ruling classes – and in many cases no religious link either – yet the twin pillars of authority (religious and secular), backed up by military force, kept them going for centuries. ...
... Most of the enormously diverse populations of these empires had little or no cultural or historical relationship to the ruling classes – and in many cases no religious link either – yet the twin pillars of authority (religious and secular), backed up by military force, kept them going for centuries. ...
Using Foreign Languages in the Middle Ages
... patronized AngloNorman literature to a much greater extent that within France, seizing the middle ground between English, spoken by all, and Latin, which women were thought unable to learn. In literature, law, courts, and government, French became firmly established only after 1200, when it became i ...
... patronized AngloNorman literature to a much greater extent that within France, seizing the middle ground between English, spoken by all, and Latin, which women were thought unable to learn. In literature, law, courts, and government, French became firmly established only after 1200, when it became i ...
Assisting Struggling Readers in Intermediate
... Step 4: Complete your answer. 1. Why is this era of European history called the Middle Ages? This era of European history is called the Middle Ages because it was the period of time between the fall of the Roman Empire and the beginning of the modern world. 2. Describe the role of Church in medieval ...
... Step 4: Complete your answer. 1. Why is this era of European history called the Middle Ages? This era of European history is called the Middle Ages because it was the period of time between the fall of the Roman Empire and the beginning of the modern world. 2. Describe the role of Church in medieval ...
LEGAL HISTORY II TEACHING GUIDE Nr. 2 “The origin of European
... Middle Ages, monarchs such as Henry II of England in the 12th century, or Alfonso X, the Wise, in Castile in the second half of the 13th century, succeeded in consolidating their power by expanding the king’s jurisdiction over local judges. As Anderson (2006, 152) has indicated, one of the “constitu ...
... Middle Ages, monarchs such as Henry II of England in the 12th century, or Alfonso X, the Wise, in Castile in the second half of the 13th century, succeeded in consolidating their power by expanding the king’s jurisdiction over local judges. As Anderson (2006, 152) has indicated, one of the “constitu ...
Questions for week 1
... the English almost entirely out of France? 3. What were the causes of the Black Death, and why did it spread so quickly throughout Western Europe? Where was it most virulent? How did it affect European society? How important do you think disease is in changing the course of history? 4. How did the c ...
... the English almost entirely out of France? 3. What were the causes of the Black Death, and why did it spread so quickly throughout Western Europe? Where was it most virulent? How did it affect European society? How important do you think disease is in changing the course of history? 4. How did the c ...
You can tell that these men are warriors. On their wonderfully swift
... into disrepair. In fact, entire cities fell into ruins. Moreover, the barbarians destroyed Roman culture: artwork, books and buildings were destroyed. Much of this knowledge and learning was ____________ to history forever. Yet, despite the devastating loss of the Roman Empire, the ________________ ...
... into disrepair. In fact, entire cities fell into ruins. Moreover, the barbarians destroyed Roman culture: artwork, books and buildings were destroyed. Much of this knowledge and learning was ____________ to history forever. Yet, despite the devastating loss of the Roman Empire, the ________________ ...
Setting History Straight - History of the Twelve Tribes of Israel
... That is not the only celestial event recorded in early history. The Bible records a Meteor Event during the time of Hezekiah. 2Ch 32:1 After these things, and the establishment thereof, Sennacherib king of Assyria came, and entered into Judah, and encamped against the fenced cities, and thought to w ...
... That is not the only celestial event recorded in early history. The Bible records a Meteor Event during the time of Hezekiah. 2Ch 32:1 After these things, and the establishment thereof, Sennacherib king of Assyria came, and entered into Judah, and encamped against the fenced cities, and thought to w ...
The Late Middle Ages: Social a,nd ·Political Breakdown (1300
... win King John the Good's release. In return, Edward simply renounced his claim to the French throne. Such a partition was unrealistic, and sober observers on both sides knew it could not last. France struck back in the late 1360s and, by the time of Edward's death in 1377, had beaten the English bac ...
... win King John the Good's release. In return, Edward simply renounced his claim to the French throne. Such a partition was unrealistic, and sober observers on both sides knew it could not last. France struck back in the late 1360s and, by the time of Edward's death in 1377, had beaten the English bac ...
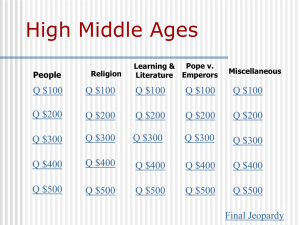
High Middle Ages

The High Middle Ages or High Medieval Period was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries (c. 1001–1300). The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500.The key historical trend of the High Middle Ages was the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250 the robust population increase greatly benefited the European economy, reaching levels it would not see again in some areas until the 19th century. This trend was checked in the Late Middle Ages by a series of calamities, notably the Black Death but also including numerous wars and economic stagnation.From about the year 780 onwards, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance led to scientific and philosophical revival of Europe. The first universities were established in Bologna, Paris, Oxford and Modena. The Vikings had settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, whilst Norse Christian kingdoms were developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars had ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary was recognized in central Europe, forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire of the Macedonian and Komnenos dynasties gradually gave way to resurrected Serbia and Bulgaria and to a successor Crusade state from 1204 to 1261, while countering the continuous threat of the Seljuk Turks in Asia Minor.In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps began to settle new lands, some of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Roman Empire. In what is known as the ""great clearances"", vast forests and marshes of Europe were cleared and cultivated. At the same time settlements moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire to new frontiers in Europe, beyond the Elbe River, tripling the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church, reaching the peak of its political power at this time, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades against the Seljuk Turks, who occupied the Holy Land, thereby founding the Crusader States in the Levant. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades, while Christian kingdoms conquered the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, and the Normans colonized southern Italy, all part of the major population increase and resettlement pattern of the era.The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. This age saw the rise of ethnocentrism, which evolved later into modern civic nationalisms in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-states, and the rise and fall of the Muslim civilization of Al-Andalus. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle led Thomas Aquinas and other thinkers of the period to develop Scholasticism, a combination of Catholicism and ancient philosophy. For much of the time period Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city and Byzantine art reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals were built or completed during this era.The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, beginning at the start of the 14th century, marked the end of this era.