The OSI Model
... Internetworking Protocol (IP) Transmission mechanism by the TCP/IP An unreliable and connectionless datagram protocol – best-effort delivery service; IP provides no error checking or tracking ...
... Internetworking Protocol (IP) Transmission mechanism by the TCP/IP An unreliable and connectionless datagram protocol – best-effort delivery service; IP provides no error checking or tracking ...
Question Bank - Technical Symposium.
... 3. Describe the error detecting and correcting techniques employed in data communication. 4. Discuss about collision free protocols. 5. Discuss the function and structure of e-mail protocol. 6. Write short notes on a. Packet Switching b. Message Switching c. Circuit Switching 7. Explain the transpor ...
... 3. Describe the error detecting and correcting techniques employed in data communication. 4. Discuss about collision free protocols. 5. Discuss the function and structure of e-mail protocol. 6. Write short notes on a. Packet Switching b. Message Switching c. Circuit Switching 7. Explain the transpor ...
MPLS
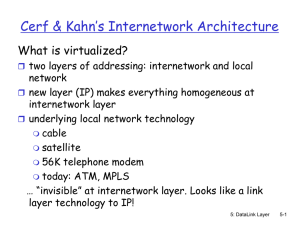
... Cerf & Kahn’s Internetwork Architecture What is virtualized? two layers of addressing: internetwork and local ...
... Cerf & Kahn’s Internetwork Architecture What is virtualized? two layers of addressing: internetwork and local ...
Networking Standards and Models
... TCP/IP stands for Transport Control Protocol / Internet Protocol suite. TCP/IP was created in 1983 to replace NCP. TCP/IP can successfully switch packets from all shapes and sizes and varieties of networks. Therfore TCP/IP has become the backbone of the Internet and its composite LANs and WA ...
... TCP/IP stands for Transport Control Protocol / Internet Protocol suite. TCP/IP was created in 1983 to replace NCP. TCP/IP can successfully switch packets from all shapes and sizes and varieties of networks. Therfore TCP/IP has become the backbone of the Internet and its composite LANs and WA ...
SIMILARITIES TCP/IP and OSI
... to communicate), middle layer (the decision about HOW the idea will be communicated), bottom layer(the creation of sound to communicate). The same concept of layers can be used to explain how networks distribute information from source to destination. Packets move from source to destination through ...
... to communicate), middle layer (the decision about HOW the idea will be communicated), bottom layer(the creation of sound to communicate). The same concept of layers can be used to explain how networks distribute information from source to destination. Packets move from source to destination through ...
Virtual Private Network
... uses a public network (usually the Internet) to connect remote sites or users together. Instead of using a dedicated connection such as leased line, a VPN uses “virtual” connections routed though the internet. ...
... uses a public network (usually the Internet) to connect remote sites or users together. Instead of using a dedicated connection such as leased line, a VPN uses “virtual” connections routed though the internet. ...
Wireless Networks Protocols
... • Protocol: is a set of rules and conventions used by the layer to communicate with similar peer layer in another (remote) system. • Peer: The similar layer on a different machine. – The peer processes communicate with each other using a protocol. ...
... • Protocol: is a set of rules and conventions used by the layer to communicate with similar peer layer in another (remote) system. • Peer: The similar layer on a different machine. – The peer processes communicate with each other using a protocol. ...
IP Forwarding and ICMP
... Unreliable: IP does not make an attempt to recover lost packets Connectionless: Each packet (“datagram”) is handled independently. IP is not aware that packets between hosts may be sent in a logical sequence Best effort: IP does not make guarantees on the service (no throughput guarantee, no d ...
... Unreliable: IP does not make an attempt to recover lost packets Connectionless: Each packet (“datagram”) is handled independently. IP is not aware that packets between hosts may be sent in a logical sequence Best effort: IP does not make guarantees on the service (no throughput guarantee, no d ...
What is a Network?
... A Network is a number of electronic devices which are connected so that data is able to be transferred between them. ...
... A Network is a number of electronic devices which are connected so that data is able to be transferred between them. ...
Hour 5
... Name resolution is an example of an Application layer service that functions integrally with lower protocol layers and actively participates in the interactions of the protocol stack. ...
... Name resolution is an example of an Application layer service that functions integrally with lower protocol layers and actively participates in the interactions of the protocol stack. ...
Lecture 14
... Architectural Approaches • Connection oriented: Assume that each network is connection oriented ...
... Architectural Approaches • Connection oriented: Assume that each network is connection oriented ...
Overview/Questions Network Addresses Network Addresses
... DNS cache entries have a time to live (TTL) metric which prevents stale information from being used. ...
... DNS cache entries have a time to live (TTL) metric which prevents stale information from being used. ...
APP-G
... Assignment may be temporary: Address “leased” to a client for a limited time. SENS supports DHCP client, server and relay agent operation ...
... Assignment may be temporary: Address “leased” to a client for a limited time. SENS supports DHCP client, server and relay agent operation ...
Module 2
... • The ARPANET was originally utilized to interconnect a small number of government agencies and universities • ARPANET has evolved into what we now know as the Internet ...
... • The ARPANET was originally utilized to interconnect a small number of government agencies and universities • ARPANET has evolved into what we now know as the Internet ...
CCNA2 3.0-09 Basic Router Troubleshooting
... •RTA then forwards the packet out an interface (Ethernet0) based on the routing table entry. If RTA receives a packet destined for 10.3.21.5, it sends that packet out Serial 0/0. ...
... •RTA then forwards the packet out an interface (Ethernet0) based on the routing table entry. If RTA receives a packet destined for 10.3.21.5, it sends that packet out Serial 0/0. ...
Computer Security
... Moves the ‘last mile’ from analog to digital Data rates of 64 Kbps Circuit-switched instead of packet-switched Uses bearer channels to move data and a single separate channel (D) to setup Used by most companies as backup BRI – 2 64-kbps B channels and 1 D PRI – 23 64-kbps B channels and 1 D ...
... Moves the ‘last mile’ from analog to digital Data rates of 64 Kbps Circuit-switched instead of packet-switched Uses bearer channels to move data and a single separate channel (D) to setup Used by most companies as backup BRI – 2 64-kbps B channels and 1 D PRI – 23 64-kbps B channels and 1 D ...
History of the Internet - DCU School of Computing
... arrive at their correct destination – Packets are sent over many different routes at the same time • Hardware restriction – data broken into packets of 1,500 bytes each. • Packet given header with order of packet & checksum (based on the amount of data in packet) • Each packet is put into separate I ...
... arrive at their correct destination – Packets are sent over many different routes at the same time • Hardware restriction – data broken into packets of 1,500 bytes each. • Packet given header with order of packet & checksum (based on the amount of data in packet) • Each packet is put into separate I ...
Lecture 2 - Networking Devices
... However, while MAC addresses are physical addresses that are actually hardcoded into the NIC card and occur at the data link layer IP addresses are implemented in software and occur at the network layer of the OSI model. ...
... However, while MAC addresses are physical addresses that are actually hardcoded into the NIC card and occur at the data link layer IP addresses are implemented in software and occur at the network layer of the OSI model. ...
Lecture 2 - Networking Devices
... However, while MAC addresses are physical addresses that are actually hard-coded into the NIC card and occur at the data link layer IP addresses are implemented in software and occur at the network layer of the OSI model. ...
... However, while MAC addresses are physical addresses that are actually hard-coded into the NIC card and occur at the data link layer IP addresses are implemented in software and occur at the network layer of the OSI model. ...
Hello, I`m Brian Farrell, and welcome to PACE
... Then there's Layer 5, the session layer. This is the layer that is responsible for establishing the initial parameters between two systems. It sets up and tears down the communication channel. Layer 6, or the presentation layer, is responsible for taking data and converting it from a machine-depende ...
... Then there's Layer 5, the session layer. This is the layer that is responsible for establishing the initial parameters between two systems. It sets up and tears down the communication channel. Layer 6, or the presentation layer, is responsible for taking data and converting it from a machine-depende ...
Lec_1: Syllabus
... Differentiate between requirements and challenges of client-server applications and Peer-to-peer applications Describe the operations and services of traditional network applications like WWW, HTTP & FTP and services provided by E-mail, DNS & DHCP applications ...
... Differentiate between requirements and challenges of client-server applications and Peer-to-peer applications Describe the operations and services of traditional network applications like WWW, HTTP & FTP and services provided by E-mail, DNS & DHCP applications ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.