Introduction to Wireless Ad
... Cluster nodes, and route between and within clusters Location management: finding where Routing finding how to get there Multiple levels: log(N) levels Location Mgm: Each nodes stores O(N) locations Routing overhead: O(log^3N) Dominating factor: location management and not the routing Location mgmt ...
... Cluster nodes, and route between and within clusters Location management: finding where Routing finding how to get there Multiple levels: log(N) levels Location Mgm: Each nodes stores O(N) locations Routing overhead: O(log^3N) Dominating factor: location management and not the routing Location mgmt ...
Part I: Introduction
... • After transmitting one or more packets (depending on the rules of the protocol), the node transmits a new token to the next node in one of 3 ways: 1.Single Packet Mode: Token is transmitted after receiving the last bit of transmitted packet(s) 2.Multiple Token Mode: Token is transmitted immediatel ...
... • After transmitting one or more packets (depending on the rules of the protocol), the node transmits a new token to the next node in one of 3 ways: 1.Single Packet Mode: Token is transmitted after receiving the last bit of transmitted packet(s) 2.Multiple Token Mode: Token is transmitted immediatel ...
Worm Hole Attack Detection in Wireless Sensor Network
... OTcl script, right after creating a scheduler object, that all the nodes that will be created are multicast nodes. After specifying the node type, the user can also select a specific routing protocol other than using a default one. Unicast -$ns rtproto type - type: Static, Session, DV, cost, multi-p ...
... OTcl script, right after creating a scheduler object, that all the nodes that will be created are multicast nodes. After specifying the node type, the user can also select a specific routing protocol other than using a default one. Unicast -$ns rtproto type - type: Static, Session, DV, cost, multi-p ...
Chapter 1
... RFC: Request for comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force Introduction 1-6 ...
... RFC: Request for comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force Introduction 1-6 ...
Geometric Ad-Hoc Routing: Of Theory and Practice
... • That’s why some researchers proposed partial link reversal, where nodes only reverse links that were not reversed before. • However, it was shown by Busch et al. that in the extreme case also partial link reversal is not efficient, it may in fact even worse be than regular link reversal. • Still, ...
... • That’s why some researchers proposed partial link reversal, where nodes only reverse links that were not reversed before. • However, it was shown by Busch et al. that in the extreme case also partial link reversal is not efficient, it may in fact even worse be than regular link reversal. • Still, ...
ppt
... Resource reservation and admission control Source describes its desired flow rate and sends this information to the routers and the receiver Network admits requests and reserves resources Source must send at this rate (controlled by network) Provides a sort of “dedicated” connection within ...
... Resource reservation and admission control Source describes its desired flow rate and sends this information to the routers and the receiver Network admits requests and reserves resources Source must send at this rate (controlled by network) Provides a sort of “dedicated” connection within ...
Cloud RAN - Ericsson
... and it is unlikely to mean the same thing in a RAN context as in, for example, a data server context. The reason for this is the substantial difference in real-time requirements imposed by the radio access protocol. Many of the synchronization requirements that ensure the performance of the radio ac ...
... and it is unlikely to mean the same thing in a RAN context as in, for example, a data server context. The reason for this is the substantial difference in real-time requirements imposed by the radio access protocol. Many of the synchronization requirements that ensure the performance of the radio ac ...
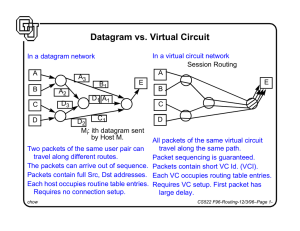
Datagram vs. Virtual Circuit
... Find the shortest paths form a given source node to all other nodes by developing paths in order of increasing path length. Let the set of nodes in a network be N. 1. start with a source node S in node set M. Let the nodes not in M be M’. 2. Let L with the set of links connecting M and M’. l Among t ...
... Find the shortest paths form a given source node to all other nodes by developing paths in order of increasing path length. Let the set of nodes in a network be N. 1. start with a source node S in node set M. Let the nodes not in M be M’. 2. Let L with the set of links connecting M and M’. l Among t ...
CIMARRON TELEPHONE COMPANY BROADBAND
... primarily a function of the distance between two points of transmission, but also can be affected by the quality of the network or networks used in transmission. Latency is typically measured in milliseconds, and generally has no significant impact on typical everyday Internet usage. As latency vari ...
... primarily a function of the distance between two points of transmission, but also can be affected by the quality of the network or networks used in transmission. Latency is typically measured in milliseconds, and generally has no significant impact on typical everyday Internet usage. As latency vari ...
ppt
... phone call • The playout delay is computed for each talk spurt based on observed average delay and observed deviation from this average delay • Estimated average delay and deviation of average delay are computed in a manner similar to estimates of RTT and deviation in TCP • The beginning of a talk s ...
... phone call • The playout delay is computed for each talk spurt based on observed average delay and observed deviation from this average delay • Estimated average delay and deviation of average delay are computed in a manner similar to estimates of RTT and deviation in TCP • The beginning of a talk s ...
sockets-bridge-learning
... • Keep track of source address of packet (S) and the arriving interface (I). – Fill in the forwarding table based on this information – Packet with destination address S must be sent to interface I! ...
... • Keep track of source address of packet (S) and the arriving interface (I). – Fill in the forwarding table based on this information – Packet with destination address S must be sent to interface I! ...
MOBILE COMPUTING - Technicalsymposium
... is cached by nodes processing the route discovery packets. The learned paths are used to route packets. To accomplish source routing, the routed packets contain the address of each device the packet will traverse. This may result in high overhead for long paths or large addresses, like IPv6. To avoi ...
... is cached by nodes processing the route discovery packets. The learned paths are used to route packets. To accomplish source routing, the routed packets contain the address of each device the packet will traverse. This may result in high overhead for long paths or large addresses, like IPv6. To avoi ...
Frame Relay and MPLS
... Like Frame Relay network diagrams represent them as a cloud packets in an MPLS network are prefixed with an MPLS header (called a label stack) The header contains one or more labels, a traffic-class field (used for quality of service [QoS]), a bottom-of-stack flag, and an 8-bit time-to-live (TTL) fi ...
... Like Frame Relay network diagrams represent them as a cloud packets in an MPLS network are prefixed with an MPLS header (called a label stack) The header contains one or more labels, a traffic-class field (used for quality of service [QoS]), a bottom-of-stack flag, and an 8-bit time-to-live (TTL) fi ...
Schedulable deterministic end-to-end pipes
... Overlay - Lessons learned What’s wrong with the overlay model ? • How to handle (redundant) functionality? • How to support routing peering hierarchy (needed for scalability) among the routers connected to an ATM network ? • ATMARP, MARS, NHRP, LEC, LES, LECS, BUS, etc… trying to bring the two to ...
... Overlay - Lessons learned What’s wrong with the overlay model ? • How to handle (redundant) functionality? • How to support routing peering hierarchy (needed for scalability) among the routers connected to an ATM network ? • ATMARP, MARS, NHRP, LEC, LES, LECS, BUS, etc… trying to bring the two to ...
cdma450 Core Network - CDMA Development Group
... – Push to Talk over Cellular (PoC) being addressed in OMA • With 3GPP2 review and comment ...
... – Push to Talk over Cellular (PoC) being addressed in OMA • With 3GPP2 review and comment ...
CPSC 441: Introduction
... The purpose of a layer is to offer services to the layer above it using an interface ...
... The purpose of a layer is to offer services to the layer above it using an interface ...
lect04
... can imagine a computer doing something, you can program a computer to do that. Unbounded opportunity... limited only by your imagination. And a couple of laws of physics. TCP/IP, HTTP How, Why, What, When? ...
... can imagine a computer doing something, you can program a computer to do that. Unbounded opportunity... limited only by your imagination. And a couple of laws of physics. TCP/IP, HTTP How, Why, What, When? ...
Generalized Multiprotocol Label Switching: An Overview of
... A node passing transit connections should be able to notify the node responsible for restoring the connections when failures occur The Notify message has been added to RSVP-TE for GMPLS to provide a mechanism for informing nonadjacent nodes of LSP-related failures Application: to notify when the con ...
... A node passing transit connections should be able to notify the node responsible for restoring the connections when failures occur The Notify message has been added to RSVP-TE for GMPLS to provide a mechanism for informing nonadjacent nodes of LSP-related failures Application: to notify when the con ...
ppt
... division of the string D by the polynomial G and appends the remainder R to it The receiver divides < D,R> by G; if the remainder is non-zero, the transmission was corrupted International standards for G polynomials of degrees 8, 12, 15 and 32 have been defined ARPANET was using a 24 bit CRC for the ...
... division of the string D by the polynomial G and appends the remainder R to it The receiver divides < D,R> by G; if the remainder is non-zero, the transmission was corrupted International standards for G polynomials of degrees 8, 12, 15 and 32 have been defined ARPANET was using a 24 bit CRC for the ...
Ch05-2 - LINK@KoreaTech
... segment, uses CSMA/CD to access segment transparent hosts are unaware of presence of switches plug-and-play, self-learning switches do not need to be configured ...
... segment, uses CSMA/CD to access segment transparent hosts are unaware of presence of switches plug-and-play, self-learning switches do not need to be configured ...
4th Edition: Chapter 1
... RFC: Request for comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force Introduction ...
... RFC: Request for comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force Introduction ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.