Cell Specialisation - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... moving food into a specialised area, what is this called? Cilia 4. Amoeba use extensions of the flexible cell membrane to move, what do we call this? Pseudopods 5. Which unicellular organisms can photosynthesise? Euglena ...
... moving food into a specialised area, what is this called? Cilia 4. Amoeba use extensions of the flexible cell membrane to move, what do we call this? Pseudopods 5. Which unicellular organisms can photosynthesise? Euglena ...
Biotechnology - Valhalla High School
... • Cloning is the creation of an organism that is genetically identical to another organism. • Cloning in plants has been going on for thousands of years. • Many plants make clones of themselves without any human intervention. • In other cases, plants with desirable characteristics were cloned by tak ...
... • Cloning is the creation of an organism that is genetically identical to another organism. • Cloning in plants has been going on for thousands of years. • Many plants make clones of themselves without any human intervention. • In other cases, plants with desirable characteristics were cloned by tak ...
Cell Theory ppt
... 1. What TYPE of cell is this? 2. What is the name of this type of cell? 3. Can you label this cell? ...
... 1. What TYPE of cell is this? 2. What is the name of this type of cell? 3. Can you label this cell? ...
Hello!!! - Elida Local Schools
... Organelles are specialized subunits in the cell, which each have their own specific function. They are usually enclosed in their own lipid membrane. There are many types of organelles, such as ribosomes, nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. Cells are the structural and functional units of ...
... Organelles are specialized subunits in the cell, which each have their own specific function. They are usually enclosed in their own lipid membrane. There are many types of organelles, such as ribosomes, nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. Cells are the structural and functional units of ...
Homework Exercise 1 - Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. Place the
... other organs which help. The stomach and intestines form the digestive system, the heart and blood vessels form the circulatory system and they work together to circulate blood around the body. (a) What term is given to a living organism that consists of more than one cell? ...
... other organs which help. The stomach and intestines form the digestive system, the heart and blood vessels form the circulatory system and they work together to circulate blood around the body. (a) What term is given to a living organism that consists of more than one cell? ...
Stages of Meiosis
... The process by which a diploid cell (46 chromosomes in a human) replicates to produce four daughter haploids cells (half the number of chromosomes). Meiosis is the type of cell division by which germ cells (eggs and sperm) are produced. Meiosis involves a reduction in the amount of genetic material. ...
... The process by which a diploid cell (46 chromosomes in a human) replicates to produce four daughter haploids cells (half the number of chromosomes). Meiosis is the type of cell division by which germ cells (eggs and sperm) are produced. Meiosis involves a reduction in the amount of genetic material. ...
File
... What are stem cells? The unspecialized cells from which differentiated cells develop are known as stem cells. ...
... What are stem cells? The unspecialized cells from which differentiated cells develop are known as stem cells. ...
[pdf]
... program highlighted both the physical forces exerted during migration and the signaling pathways involved in the process. Celeste Nelson (Princeton University) presented results suggesting that cells migrate collectively through fibrous extracellular matrix (ECM) by exerting tensile forces at the le ...
... program highlighted both the physical forces exerted during migration and the signaling pathways involved in the process. Celeste Nelson (Princeton University) presented results suggesting that cells migrate collectively through fibrous extracellular matrix (ECM) by exerting tensile forces at the le ...
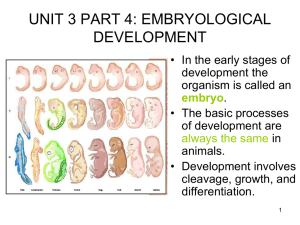
Unit 3 part 4 PPT
... divisions. mesoderm • A third layer of cells begins to grow between the inner and outer layers forming three primary germ layers. • The cells in these germ layers will differentiate to become different endoderm types of cells. ...
... divisions. mesoderm • A third layer of cells begins to grow between the inner and outer layers forming three primary germ layers. • The cells in these germ layers will differentiate to become different endoderm types of cells. ...
Chapter 21 Presentation-The Genetic Basis of Development
... encoded region is part of the protein that functions as a transcription regulator. The shape of the encoded region allows it to bind to any DNA segment, but by itself, it cannot select a specific sequence. The variable regions within the whole protein allow it to interact with other transcription ...
... encoded region is part of the protein that functions as a transcription regulator. The shape of the encoded region allows it to bind to any DNA segment, but by itself, it cannot select a specific sequence. The variable regions within the whole protein allow it to interact with other transcription ...
1. The animals which possess backbones are a. Insects b. Birds c
... 59. If the diploid number of chromosomes in an organism is 2n = 40 chromosomes, after Mitotic division, each daughter cell will contain a. 20 Chromosomes ...
... 59. If the diploid number of chromosomes in an organism is 2n = 40 chromosomes, after Mitotic division, each daughter cell will contain a. 20 Chromosomes ...
C. elegans
... • Saccharomyces cerevisiae makes an excellent model system for studying eukaryotic processes, including the cell cycle. • S. cerevisiae is genetically tractable, and is readily cultured. • Caenorhabitis elegans is an ideal model system for studying development. • C. elegans is easy to grow both sexu ...
... • Saccharomyces cerevisiae makes an excellent model system for studying eukaryotic processes, including the cell cycle. • S. cerevisiae is genetically tractable, and is readily cultured. • Caenorhabitis elegans is an ideal model system for studying development. • C. elegans is easy to grow both sexu ...
Reference for embryology
... Unfertilized egg: There are several of these scattered on the slide. They can be identified by their spherical shape and their spherical nuclei. Note the small, dark nucleolus in the nucleus. Fertilized egg (zygote): Find an egg with a very indistinct nucleus and nucleolus (or not visible). This is ...
... Unfertilized egg: There are several of these scattered on the slide. They can be identified by their spherical shape and their spherical nuclei. Note the small, dark nucleolus in the nucleus. Fertilized egg (zygote): Find an egg with a very indistinct nucleus and nucleolus (or not visible). This is ...
U of L adult stem cell research
... director of UofL's Kentucky Spinal Cord Injury Research Center but is not on Roisen's research team. "This is a major step forward." ...
... director of UofL's Kentucky Spinal Cord Injury Research Center but is not on Roisen's research team. "This is a major step forward." ...
Cell and animal reproduction
... • Metamorphosis is the changes that a frog goes through during its life cycle. • There are four main stages in the life cycle of the frog. ...
... • Metamorphosis is the changes that a frog goes through during its life cycle. • There are four main stages in the life cycle of the frog. ...
Jeopardy Review Game
... Which of the following is an advantage of adult stem cells? A. They are more likely to be rejected by a patient’s immune system. B. They do not raise the many ethical issues associated with using embryonic stem cells. C. They are few in number and hard to grow. ...
... Which of the following is an advantage of adult stem cells? A. They are more likely to be rejected by a patient’s immune system. B. They do not raise the many ethical issues associated with using embryonic stem cells. C. They are few in number and hard to grow. ...
New B1 B2 B3 Revision
... • distinguish what can be done (technical feasibility), from what should be done (values); • explain why different courses of action may be taken in different social and environmental contexts. understand how clones of animals occur: • naturally, when cells of an embryo separate (identical twins); • ...
... • distinguish what can be done (technical feasibility), from what should be done (values); • explain why different courses of action may be taken in different social and environmental contexts. understand how clones of animals occur: • naturally, when cells of an embryo separate (identical twins); • ...
GENETICS PROBLEMS - Review Questions
... embryo (in the blastula stage) was put into the enucleated egg cell and then the egg cell was stimulated to divide. 2. The nucleus that was transferred into the egg cell was from an adult cell (not an embryonic cell). Also unique was the fact that the adult sheep was no longer living. 3. recombinant ...
... embryo (in the blastula stage) was put into the enucleated egg cell and then the egg cell was stimulated to divide. 2. The nucleus that was transferred into the egg cell was from an adult cell (not an embryonic cell). Also unique was the fact that the adult sheep was no longer living. 3. recombinant ...
Biological background of cell-ECM interactions
... Lindvall, Kokaia, Stem cells in human neurodegenerative disorders: Time for clinical translation? J. Clinical Inv 120, 29-40 (2010) Progress stem cells for the treatment of neurological disorders, Nature 441 1094-1096 (2006) ...
... Lindvall, Kokaia, Stem cells in human neurodegenerative disorders: Time for clinical translation? J. Clinical Inv 120, 29-40 (2010) Progress stem cells for the treatment of neurological disorders, Nature 441 1094-1096 (2006) ...
Lecture 20 Methodology for production of transgenic animals To
... transgene. However, the success rate of producing transgenic animals individually by these methods is very low and it may be more efficient to use cloning techniques to increase their numbers. For example, gene transfer studies revealed that only 0.6% of transgenic pigs were born with a desired gene ...
... transgene. However, the success rate of producing transgenic animals individually by these methods is very low and it may be more efficient to use cloning techniques to increase their numbers. For example, gene transfer studies revealed that only 0.6% of transgenic pigs were born with a desired gene ...
correc~1
... Gardeners make use of meristem cells when growing new plants by taking cuttings, which are shoots or leaves cut from a plant. Some grow better when the ends are dipped in preplanting (rooting) powder, which contains the plant hormones called auxins. Auxins make the meristem cells develop in to new s ...
... Gardeners make use of meristem cells when growing new plants by taking cuttings, which are shoots or leaves cut from a plant. Some grow better when the ends are dipped in preplanting (rooting) powder, which contains the plant hormones called auxins. Auxins make the meristem cells develop in to new s ...
Aalborg Universitet Stem cell therapy following acute myocardial
... shown effect of stem cell transplantation (mainly bone marrow-derived stem cells) after myocardial infarction, with paracrine activity and neovascularisation playing an important role. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells have been shown to be able to differentiate in an endothelial direction and have ...
... shown effect of stem cell transplantation (mainly bone marrow-derived stem cells) after myocardial infarction, with paracrine activity and neovascularisation playing an important role. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells have been shown to be able to differentiate in an endothelial direction and have ...
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking an enucleated oocyte (egg cell) and implanting a donor nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. It is used in both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. Dolly the Sheep became famous for being the first successful case of the reproductive cloning of a mammal. ""Therapeutic cloning"" refers to the potential use of SCNT in regenerative medicine; this approach has been championed as an answer to the many issues concerning embryonic stem cells (ESC) and the destruction of viable embryos for medical use, though questions remain on how homologous the two cell types truly are.








![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008789103_1-746b7a86138a2a5bab5758b7de85a178-300x300.png)